Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1732 - Prevalence of Gastroparesis in Patients With Chronic Pancreatitis and Predictive Factors: A Novel Prediction Model Using Supervised Machine Learning
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Daryl Ramai, MD, MPH, Msc
University of Utah Health
Salt Lake City, UT
Presenting Author(s)
Daryl Ramai, MD, MPH, Msc1, Chun-Wei Pan, MD2, Emily Fellows, MD3, Yichen Wang, MD4, Yuting Huang, MD5, Ishani Shah, MD1, Cem Simsek, MD6, Marco Spadaccini, MD, PhD7, Marcello Maida, MD8, Saurabh Chandan, MD9, Antonio Facciorusso, MD, PhD10, David Troendle, MD11, Jorge D. Machicado, MD12
1University of Utah Health, Salt Lake City, UT; 2Cook County Health, Chicago, IL; 3University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT; 4Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA; 5Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL; 6Hacettepe University, Ankara, Ankara, Turkey; 7Humanitas Research Hospital, Rozzano, Emilia-Romagna, Italy; 8University of Enna "Kore", Enna, Lombardia, Italy; 9CHI Health Creighton University Medical Center, Omaha, NE; 10University of Foggia, Foggia, Puglia, Italy; 11University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 12University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor, MI
Introduction: Chronic pancreatitis (CP) has been suggested to be a risk factor for the development of gastroparesis. However, little is known about the specific characteristics associated with the development of gastroparesis in CP. Our study aimed to identify the prevalence of gastroparesis among patients with CP and to determine predictive factors using machine learning.
Methods: We identified adult hospitalized patients with an ICD code of CP from the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database (2016-2021). Student's t-test were used to compare proportions and means. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO)-penalized regression was used to select the most promising predictors of developing gastroparesis. Multivariate regression models were employed to adjust for confounders, and LASSO penalized regression helped identify significant predictors of gastroparesis. The model was validated using k-fold cross-validation and calibration testing and presented using a nomogram.
Results: Of 74,660 admissions for CP, 3.45% patients had comorbid gastroparesis. Compared to patients without gastroparesis, those with gastroparesis were more likely to be younger, female, Black, and Medicare insured (p< 0.005). In the final prediction model, 7 out of 34 characteristics predicted gastroparesis in patients with CP: type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus, Black race, female sex, opioid and cannabis use disorder, and autoimmune sclerosis. In cross-validation and internal validation, the model predicted gastroparesis with an area under the curve of 0.7445. The model also showed no significant miscalibration or overfitting.
Discussion: Our study is the first to identify the prevalence of gastroparesis in patients with chronic pancreatitis as well as predictive factors using machine learning. Our novel prediction model helps identify patients with CP who are at high risk for developing gastroparesis. These risk factors are crucial to consider when treating patients with chronic pancreatitis who experience vague and persistent gastrointestinal symptoms, as they may also have concurrent gastroparesis. In managing chronic pancreatitis, it is essential to control diabetes and use marijuana and opioids judiciously, to prevent and improve gastroparesis. Further research is needed to understand the efficacy of medical and endoscopic treatment modalities (e.g. G-POEM) in patients with gastroparesis associated with CP.
Disclosures:
Daryl Ramai, MD, MPH, Msc1, Chun-Wei Pan, MD2, Emily Fellows, MD3, Yichen Wang, MD4, Yuting Huang, MD5, Ishani Shah, MD1, Cem Simsek, MD6, Marco Spadaccini, MD, PhD7, Marcello Maida, MD8, Saurabh Chandan, MD9, Antonio Facciorusso, MD, PhD10, David Troendle, MD11, Jorge D. Machicado, MD12. P1732 - Prevalence of Gastroparesis in Patients With Chronic Pancreatitis and Predictive Factors: A Novel Prediction Model Using Supervised Machine Learning, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Utah Health, Salt Lake City, UT; 2Cook County Health, Chicago, IL; 3University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT; 4Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA; 5Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL; 6Hacettepe University, Ankara, Ankara, Turkey; 7Humanitas Research Hospital, Rozzano, Emilia-Romagna, Italy; 8University of Enna "Kore", Enna, Lombardia, Italy; 9CHI Health Creighton University Medical Center, Omaha, NE; 10University of Foggia, Foggia, Puglia, Italy; 11University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 12University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor, MI
Introduction: Chronic pancreatitis (CP) has been suggested to be a risk factor for the development of gastroparesis. However, little is known about the specific characteristics associated with the development of gastroparesis in CP. Our study aimed to identify the prevalence of gastroparesis among patients with CP and to determine predictive factors using machine learning.
Methods: We identified adult hospitalized patients with an ICD code of CP from the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) database (2016-2021). Student's t-test were used to compare proportions and means. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO)-penalized regression was used to select the most promising predictors of developing gastroparesis. Multivariate regression models were employed to adjust for confounders, and LASSO penalized regression helped identify significant predictors of gastroparesis. The model was validated using k-fold cross-validation and calibration testing and presented using a nomogram.
Results: Of 74,660 admissions for CP, 3.45% patients had comorbid gastroparesis. Compared to patients without gastroparesis, those with gastroparesis were more likely to be younger, female, Black, and Medicare insured (p< 0.005). In the final prediction model, 7 out of 34 characteristics predicted gastroparesis in patients with CP: type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus, Black race, female sex, opioid and cannabis use disorder, and autoimmune sclerosis. In cross-validation and internal validation, the model predicted gastroparesis with an area under the curve of 0.7445. The model also showed no significant miscalibration or overfitting.
Discussion: Our study is the first to identify the prevalence of gastroparesis in patients with chronic pancreatitis as well as predictive factors using machine learning. Our novel prediction model helps identify patients with CP who are at high risk for developing gastroparesis. These risk factors are crucial to consider when treating patients with chronic pancreatitis who experience vague and persistent gastrointestinal symptoms, as they may also have concurrent gastroparesis. In managing chronic pancreatitis, it is essential to control diabetes and use marijuana and opioids judiciously, to prevent and improve gastroparesis. Further research is needed to understand the efficacy of medical and endoscopic treatment modalities (e.g. G-POEM) in patients with gastroparesis associated with CP.

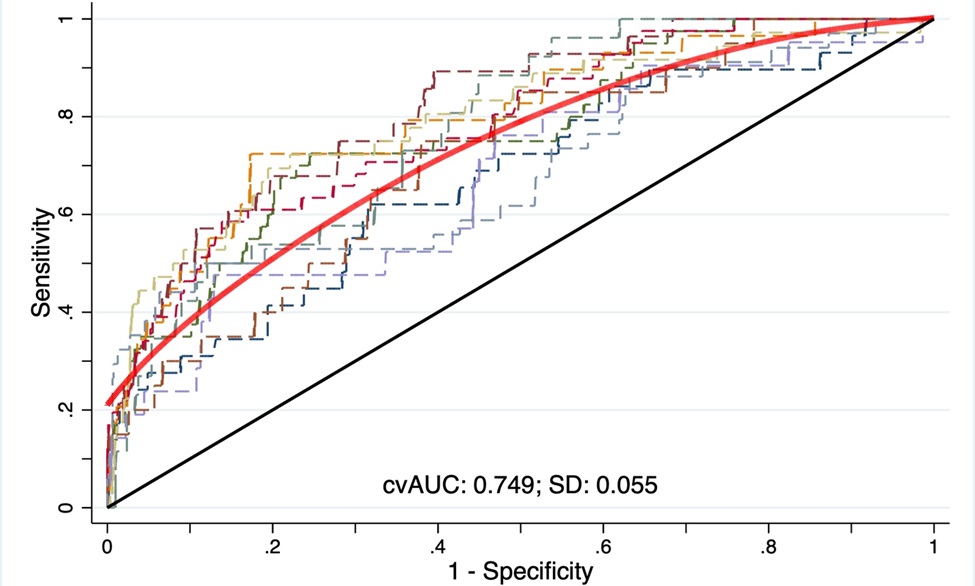
Figure: Receiver-operating curve (ROC) with mean cross-validated areas under the curve (CvAUC) after 10-fold-cross validation. AUC= 0.749 (bias-corrected bootstrap confidence interval, 0.6889 to 0.7717)
Disclosures:
Daryl Ramai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chun-Wei Pan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Emily Fellows indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yichen Wang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yuting Huang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ishani Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cem Simsek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marco Spadaccini indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marcello Maida indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saurabh Chandan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Antonio Facciorusso indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Troendle indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jorge Machicado indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daryl Ramai, MD, MPH, Msc1, Chun-Wei Pan, MD2, Emily Fellows, MD3, Yichen Wang, MD4, Yuting Huang, MD5, Ishani Shah, MD1, Cem Simsek, MD6, Marco Spadaccini, MD, PhD7, Marcello Maida, MD8, Saurabh Chandan, MD9, Antonio Facciorusso, MD, PhD10, David Troendle, MD11, Jorge D. Machicado, MD12. P1732 - Prevalence of Gastroparesis in Patients With Chronic Pancreatitis and Predictive Factors: A Novel Prediction Model Using Supervised Machine Learning, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
