Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1758 - Derivation, Interobserver Agreement and Impact of Pre-Surgical EUS-Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (CLE) Vascular Characteristics for Risk Stratification of IPMNs
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Ahmed RM Abdelbaki, MBBCh
The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
Columbus, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Ahmed RM. Abdelbaki, MBBCh1, Matthew Leupold, MD1, Stacey Culp, PhD2, Thiruvengadam Muniraj, MD3, Damien Tan, 4, Jorge D. Machicado, MD5, Anjuli Luthra, MD6, Erica Park, MD1, Wei Chen, 1, Ashwini Esnakula, MBBS1, Phil Hart, MD1, Somashekar G Krishna, MD1
1The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 2Ohio State University, Columbus, OH; 3Yale New Haven Health, New Haven, CT; 4Singapore General Hospital, Central Region, Singapore; 5University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor, MI; 6Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, FL
Introduction: EUS-nCLE enables real-time in vivo visualization of papillae for risk-stratification of IPMNs. Progressive vascular changes in branch duct (BD)-IPMNs have not been previously evalauted. Capillary level characteristics are lost in post-resection surigcal histopathology due to tissue processing. We sought to derive and evaluate pre-surgical in vivo EUS-nCLE papillary and vascular characteristics for the prediction of high-grade dysplasia/invasive carcinoma (HGD-IC; advanced neoplasia) in IPMNs.
Methods: Subjects from two prospective studies evaluating EUS-nCLE for pancreatic cyst diagnosis were included if they had both papillary and vascular features on nCLE imaging and a definitive histopathological diagnosis. Four blinded external observers reviewed nCLE videos to classify dysplasia (HGD-IC vs. low-grade). Subsequently, two internal observers assessed vascular patterns (simple vs. complex branching), density (low vs. high), morphology (tortuous vs.not), and overall classification (simple vs. complex) to detect HGD-IC. The four observers were then trained on these vascular patterns and reassessed the IPMNs using only nCLE vascular imaging.
Results: Among 49 BD-IPMNs (HGD-IC in 17), the mean IPMN size was 3.31±0.83 cm, mean age of subjects was 68.1 ± 9.3 years (51.0% male).
In the observer group (n=4), the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for nCLE papillary imaging and detection of HGD-IC were as follows:
• Observer 1: 77%, 69%, 71%
• Observer 2: 53%, 75%, 67%
• Observer 3: 35%, 78%, 63%
• Observer 4: 65%, 59%, 61%
After adding vascular features to the papillary level analysis, the diagnostic yield for detecting HGD-IC improved for each observer. Compared to detection based solely on papillary level characteristics, the improvement in the rate of detection was as follows:
• Observer 1: from 77% to 88% (p = 0.50)
• Observer 2: from 53% to 76% (p = 0.16)
• Observer 3: from 35% to 76% (p = 0.02)
• Observer 4: from 65% to 88% (p = 0.11)
The mean improvement in the detection of HGD-IC was from 56% to 82%.
Discussion: In this first-ever evaluation of pre-surgical vascular characteristics, nCLE imagin demonstrates that the presence of complex vascularity, when combined with papillary features, may enhance the detection of HGD-IC in IPMNs. However, additional exploration, refinement, and training on vasculature is still needed to further improve its performance across observers. Larger validation studies are also warranted to confirm these findings.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Ahmed RM. Abdelbaki, MBBCh1, Matthew Leupold, MD1, Stacey Culp, PhD2, Thiruvengadam Muniraj, MD3, Damien Tan, 4, Jorge D. Machicado, MD5, Anjuli Luthra, MD6, Erica Park, MD1, Wei Chen, 1, Ashwini Esnakula, MBBS1, Phil Hart, MD1, Somashekar G Krishna, MD1. P1758 - Derivation, Interobserver Agreement and Impact of Pre-Surgical EUS-Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (CLE) Vascular Characteristics for Risk Stratification of IPMNs, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 2Ohio State University, Columbus, OH; 3Yale New Haven Health, New Haven, CT; 4Singapore General Hospital, Central Region, Singapore; 5University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor, MI; 6Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, FL
Introduction: EUS-nCLE enables real-time in vivo visualization of papillae for risk-stratification of IPMNs. Progressive vascular changes in branch duct (BD)-IPMNs have not been previously evalauted. Capillary level characteristics are lost in post-resection surigcal histopathology due to tissue processing. We sought to derive and evaluate pre-surgical in vivo EUS-nCLE papillary and vascular characteristics for the prediction of high-grade dysplasia/invasive carcinoma (HGD-IC; advanced neoplasia) in IPMNs.
Methods: Subjects from two prospective studies evaluating EUS-nCLE for pancreatic cyst diagnosis were included if they had both papillary and vascular features on nCLE imaging and a definitive histopathological diagnosis. Four blinded external observers reviewed nCLE videos to classify dysplasia (HGD-IC vs. low-grade). Subsequently, two internal observers assessed vascular patterns (simple vs. complex branching), density (low vs. high), morphology (tortuous vs.not), and overall classification (simple vs. complex) to detect HGD-IC. The four observers were then trained on these vascular patterns and reassessed the IPMNs using only nCLE vascular imaging.
Results: Among 49 BD-IPMNs (HGD-IC in 17), the mean IPMN size was 3.31±0.83 cm, mean age of subjects was 68.1 ± 9.3 years (51.0% male).
In the observer group (n=4), the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for nCLE papillary imaging and detection of HGD-IC were as follows:
• Observer 1: 77%, 69%, 71%
• Observer 2: 53%, 75%, 67%
• Observer 3: 35%, 78%, 63%
• Observer 4: 65%, 59%, 61%
After adding vascular features to the papillary level analysis, the diagnostic yield for detecting HGD-IC improved for each observer. Compared to detection based solely on papillary level characteristics, the improvement in the rate of detection was as follows:
• Observer 1: from 77% to 88% (p = 0.50)
• Observer 2: from 53% to 76% (p = 0.16)
• Observer 3: from 35% to 76% (p = 0.02)
• Observer 4: from 65% to 88% (p = 0.11)
The mean improvement in the detection of HGD-IC was from 56% to 82%.
Discussion: In this first-ever evaluation of pre-surgical vascular characteristics, nCLE imagin demonstrates that the presence of complex vascularity, when combined with papillary features, may enhance the detection of HGD-IC in IPMNs. However, additional exploration, refinement, and training on vasculature is still needed to further improve its performance across observers. Larger validation studies are also warranted to confirm these findings.

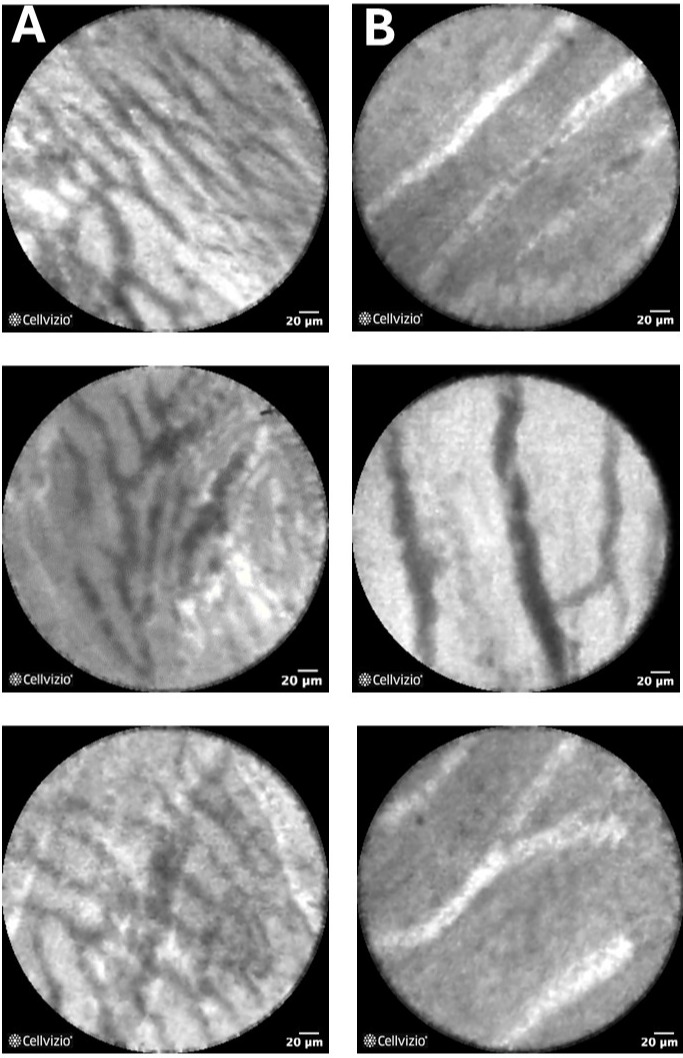
Figure: A) IPMN with complex vascular features: hyper-vascularity, excessive branching, and a tortuous morphology. B) IPMN with simple vascular features: hypo-vascularity, minimal to no branching (rope ladder), and a parallel linear morphology.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Ahmed Abdelbaki indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Leupold indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stacey Culp indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thiruvengadam Muniraj indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Damien Tan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jorge Machicado indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anjuli Luthra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Erica Park indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wei Chen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashwini Esnakula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Phil Hart indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Somashekar G Krishna: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Mauna Kea Technologies, and TaeWoong Medical USA – Grant/Research Support. TaeWoong Medical USA – Grant/Research Support.
Ahmed RM. Abdelbaki, MBBCh1, Matthew Leupold, MD1, Stacey Culp, PhD2, Thiruvengadam Muniraj, MD3, Damien Tan, 4, Jorge D. Machicado, MD5, Anjuli Luthra, MD6, Erica Park, MD1, Wei Chen, 1, Ashwini Esnakula, MBBS1, Phil Hart, MD1, Somashekar G Krishna, MD1. P1758 - Derivation, Interobserver Agreement and Impact of Pre-Surgical EUS-Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy (CLE) Vascular Characteristics for Risk Stratification of IPMNs, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

