Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1767 - Obesity Is Associated With Worsened Endoscopic Outcomes in Patients With Pancreatic Collections and Should Be Integrated Into the QNI Classification
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- AK
Anthony Kerbage, MD
Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Anthony Kerbage, MD1, Serge Baroud, MD2, Karim Al Annan, MD3, Rudy Mrad, MD4, Jad AbiMansour, MD4, Sam Han, MD5, Eric J. Vargas, MD, MS4, Andrew Storm, MD4, Vinay Chandrasekhara, MD4, Ryan Law, DO4, Aliana Bofill-Garcia, MD4, John Martin, MD4, Bret Petersen, MD4, Fateh Bazerbachi, MD6, Shounak Majumder, MD4, Santhi Vege, MD4, Barham Abu Dayyeh, MD4
1Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 2Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN; 3Mayo Clinic, Hartford, CT; 4Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 5The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 6CentraCare St Cloud Hospital, St. Cloud, MN
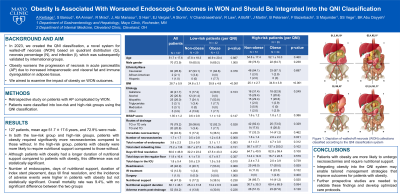
Introduction: In 2023, we created the QNI classification, a novel system for walled-off necrosis based on abdominal quadrant distribution (Q), necrosis percentage (N), and infection (I) (figure 1), which was subsequently validated by international groups. Obesity may worsen the progression of necrosis in necrotizing pancreatitis due to increased intrapancreatic and visceral fat and immune dysregulation in adipose tissue. However, the QNI classification does not currently account for obesity. We examined the impact of obesity on the outcomes of pancreatic collections.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of patients with acute pancreatitis complicated by pancreatic collections, classified into low-risk and high-risk groups using the QNI classification. Patients were further stratified based on BMI (< 30 kg/m² vs. ≥30 kg/m²). Demographics, clinical characteristics, and outcomes were compared across these groups.
Results: Among 127 patients, the average age was 51.7 years, and 72.9% were male. There were no significant differences in age, gender, or ethnicity between low- and high-risk patients based on obesity status. In both the low-risk group and high-risk groups, patients with obesity required significantly more necrosectomies compared to patients without obesity (1.2 ± 0.8 vs. 0.5 ± 0.8, p=0.008 and 2.8 ± 2.2 vs. 1.8 ± 1.4, p=0.031, respectively). In the high-risk group, patients with obesity were more likely to require nutritional support compared to patients without obesity (66.7% vs. 41.2%, p=0.020). Although patients with obesity had a longer duration of nutritional support compared to patients without obesity (69.4 ± 65.9 vs. 30.7 ± 35.3 days, p=0.054), this difference was not statistically significant. The number of endoscopies, days of nutritional support, duration of index stent placement, days till final resolution, and the incidence of adverse events were higher in patients with obesity but not statistically significant. Overall mortality rate was 9.4%, with no significant difference between patients with vs. without obesity.
Discussion: Patients with obesity, particularly those classified as high-risk per the QNI classification, are more likely to undergo necrosectomies and require nutritional support. Integrating obesity into the QNI system is essential for developing tailored management strategies that improve clinical outcomes for patients with obesity. Further prospective studies are needed to validate these findings and develop optimized care protocols.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Anthony Kerbage, MD1, Serge Baroud, MD2, Karim Al Annan, MD3, Rudy Mrad, MD4, Jad AbiMansour, MD4, Sam Han, MD5, Eric J. Vargas, MD, MS4, Andrew Storm, MD4, Vinay Chandrasekhara, MD4, Ryan Law, DO4, Aliana Bofill-Garcia, MD4, John Martin, MD4, Bret Petersen, MD4, Fateh Bazerbachi, MD6, Shounak Majumder, MD4, Santhi Vege, MD4, Barham Abu Dayyeh, MD4. P1767 - Obesity Is Associated With Worsened Endoscopic Outcomes in Patients With Pancreatic Collections and Should Be Integrated Into the QNI Classification, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 2Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN; 3Mayo Clinic, Hartford, CT; 4Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 5The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH; 6CentraCare St Cloud Hospital, St. Cloud, MN
Introduction: In 2023, we created the QNI classification, a novel system for walled-off necrosis based on abdominal quadrant distribution (Q), necrosis percentage (N), and infection (I) (figure 1), which was subsequently validated by international groups. Obesity may worsen the progression of necrosis in necrotizing pancreatitis due to increased intrapancreatic and visceral fat and immune dysregulation in adipose tissue. However, the QNI classification does not currently account for obesity. We examined the impact of obesity on the outcomes of pancreatic collections.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of patients with acute pancreatitis complicated by pancreatic collections, classified into low-risk and high-risk groups using the QNI classification. Patients were further stratified based on BMI (< 30 kg/m² vs. ≥30 kg/m²). Demographics, clinical characteristics, and outcomes were compared across these groups.
Results: Among 127 patients, the average age was 51.7 years, and 72.9% were male. There were no significant differences in age, gender, or ethnicity between low- and high-risk patients based on obesity status. In both the low-risk group and high-risk groups, patients with obesity required significantly more necrosectomies compared to patients without obesity (1.2 ± 0.8 vs. 0.5 ± 0.8, p=0.008 and 2.8 ± 2.2 vs. 1.8 ± 1.4, p=0.031, respectively). In the high-risk group, patients with obesity were more likely to require nutritional support compared to patients without obesity (66.7% vs. 41.2%, p=0.020). Although patients with obesity had a longer duration of nutritional support compared to patients without obesity (69.4 ± 65.9 vs. 30.7 ± 35.3 days, p=0.054), this difference was not statistically significant. The number of endoscopies, days of nutritional support, duration of index stent placement, days till final resolution, and the incidence of adverse events were higher in patients with obesity but not statistically significant. Overall mortality rate was 9.4%, with no significant difference between patients with vs. without obesity.
Discussion: Patients with obesity, particularly those classified as high-risk per the QNI classification, are more likely to undergo necrosectomies and require nutritional support. Integrating obesity into the QNI system is essential for developing tailored management strategies that improve clinical outcomes for patients with obesity. Further prospective studies are needed to validate these findings and develop optimized care protocols.

Figure: Figure 1. Depiction of walled-off necrosis (WON) collections classified according to the QNI classification system
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Anthony Kerbage indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Serge Baroud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karim Al Annan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rudy Mrad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jad AbiMansour indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sam Han indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eric Vargas: Philips – Grant/Research Support.
Andrew Storm: Apollo Endosurgery – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Boston Scientific – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Enterasense – Grant/Research Support. Intuitive Surgical – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant. SofTac – Grant/Research Support.
Vinay Chandrasekhara indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ryan Law: boston scientific – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Olympus – Consultant, Grant/Research Support.
Aliana Bofill-Garcia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Martin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bret Petersen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fateh Bazerbachi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shounak Majumder indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Santhi Vege indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Barham Abu Dayyeh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anthony Kerbage, MD1, Serge Baroud, MD2, Karim Al Annan, MD3, Rudy Mrad, MD4, Jad AbiMansour, MD4, Sam Han, MD5, Eric J. Vargas, MD, MS4, Andrew Storm, MD4, Vinay Chandrasekhara, MD4, Ryan Law, DO4, Aliana Bofill-Garcia, MD4, John Martin, MD4, Bret Petersen, MD4, Fateh Bazerbachi, MD6, Shounak Majumder, MD4, Santhi Vege, MD4, Barham Abu Dayyeh, MD4. P1767 - Obesity Is Associated With Worsened Endoscopic Outcomes in Patients With Pancreatic Collections and Should Be Integrated Into the QNI Classification, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

