Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1833 - Non-Surgical Ablation of a Large Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm Using Tandem Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency and Chemoablation
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- VP
Vanisha Patel, MD
The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
Columbus, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Vanisha Patel, MD, Erica Park, MD, Somashekar G Krishna, MD
The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH
Introduction: Surgery is the mainstay for managing intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN) with worrisome or high-risk features. However, endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation (EUS-RFA) and chemoablation are emerging as non-surgical treatment options for patients who are poor surgical candidates. We report the first case of a patient with a large branch duct (BD)-IPMN undergoing tandem ablative treatment with EUS-RFA followed by chemoablation.
Case Description/Methods: A 71-year-old patient presented with an incidentally noted cyst on computed tomography (CT). EUS revealed a 4.3 cm x 3.0 cm cyst in the head of the pancreas. EUS-needle confocal laser endomicroscopy (nCLE) showed prominent papillae consistent with IPMN. Cyst fluid analysis identified mutations in KRAS (variant allele fraction (VAF) = 53.1%, p.G12V) and GNAS (VAF = 11.1%, p.R201C). The patient had high surgical risk due to refusal of blood transfusions as a Jehovah's Witness. Due to a growth in cyst size to 5.0 cm x 4 cm over 12 months during MRI surveillance, non-surgical management with EUS-RFA was performed.
EUS-RFA Technique: A 22g needle was used to aspirate 25 mL of slightly viscous cyst fluid. A 10 mm EUS-RFA probe was set at 30 watts for 4 applications with mean duration of 39 seconds per application. With each application, as much of the IPMN as possible was covered or ablated.
Magnetic resonance imaging at the 3-month follow-up showed the cyst size had decreased to 2.0 x 1.6 cm. At 7-month follow-up, EUS revealed a persistent 2 cm BD-IPMN. Given a partial response to EUS-RFA, EUS-chemoablation was then performed. Cyst fluid was aspirated and analysis revealed a decrease in VAF for both KRAS (0.8%) and GNAS (0.7%). Afterwards, 5 mL of submicronized large surface area microparticle (LSAM) paclitaxel was instilled in the cyst. Patient developed mild acute pancreatitis post-procedurally diagnosed with self-limited epigastric pain, CT imaging findings, and lipase level of 235 U/L (ULN 85); the patient did not require hospitalization. Follow-up imaging at one year showed complete resolution of the BD-IPMN.
Discussion: Literature shows that EUS chemoablation yields a moderate response, with resolution of cystic lesions in 55-79% of patients. We are currently conducting clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of EUS-RFA in the non-surgical management of large BD-IPMNs. Here, we present a case of tandem modality for non-surgical treatment achieving complete resolution of a large BD-IPMN.
Disclosures:
Vanisha Patel, MD, Erica Park, MD, Somashekar G Krishna, MD. P1833 - Non-Surgical Ablation of a Large Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm Using Tandem Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency and Chemoablation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Vanisha Patel, MD, Erica Park, MD, Somashekar G Krishna, MD
The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, OH
Introduction: Surgery is the mainstay for managing intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN) with worrisome or high-risk features. However, endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation (EUS-RFA) and chemoablation are emerging as non-surgical treatment options for patients who are poor surgical candidates. We report the first case of a patient with a large branch duct (BD)-IPMN undergoing tandem ablative treatment with EUS-RFA followed by chemoablation.
Case Description/Methods: A 71-year-old patient presented with an incidentally noted cyst on computed tomography (CT). EUS revealed a 4.3 cm x 3.0 cm cyst in the head of the pancreas. EUS-needle confocal laser endomicroscopy (nCLE) showed prominent papillae consistent with IPMN. Cyst fluid analysis identified mutations in KRAS (variant allele fraction (VAF) = 53.1%, p.G12V) and GNAS (VAF = 11.1%, p.R201C). The patient had high surgical risk due to refusal of blood transfusions as a Jehovah's Witness. Due to a growth in cyst size to 5.0 cm x 4 cm over 12 months during MRI surveillance, non-surgical management with EUS-RFA was performed.
EUS-RFA Technique: A 22g needle was used to aspirate 25 mL of slightly viscous cyst fluid. A 10 mm EUS-RFA probe was set at 30 watts for 4 applications with mean duration of 39 seconds per application. With each application, as much of the IPMN as possible was covered or ablated.
Magnetic resonance imaging at the 3-month follow-up showed the cyst size had decreased to 2.0 x 1.6 cm. At 7-month follow-up, EUS revealed a persistent 2 cm BD-IPMN. Given a partial response to EUS-RFA, EUS-chemoablation was then performed. Cyst fluid was aspirated and analysis revealed a decrease in VAF for both KRAS (0.8%) and GNAS (0.7%). Afterwards, 5 mL of submicronized large surface area microparticle (LSAM) paclitaxel was instilled in the cyst. Patient developed mild acute pancreatitis post-procedurally diagnosed with self-limited epigastric pain, CT imaging findings, and lipase level of 235 U/L (ULN 85); the patient did not require hospitalization. Follow-up imaging at one year showed complete resolution of the BD-IPMN.
Discussion: Literature shows that EUS chemoablation yields a moderate response, with resolution of cystic lesions in 55-79% of patients. We are currently conducting clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of EUS-RFA in the non-surgical management of large BD-IPMNs. Here, we present a case of tandem modality for non-surgical treatment achieving complete resolution of a large BD-IPMN.

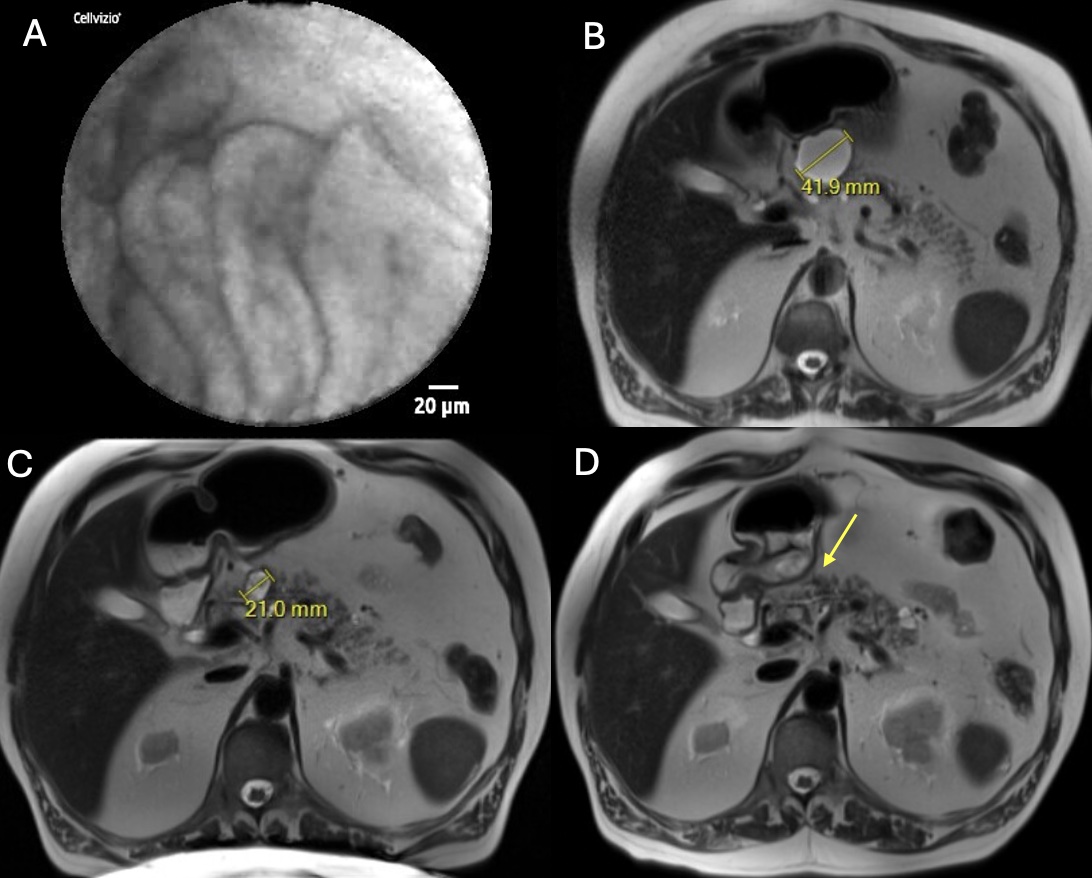
Figure: (A) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) needle confocal laser endomicroscopy image showing papillary fronds diagnostic for branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (BD-IPMN). Comparative magnetic resonance imaging of the BD-IPMN over time. (B) BD-IPMN prior to intervention. (C) BD-IPMN decrease in size 3 months after EUS-radiofrequency ablation. (D) Resolution of the BD-IPMN 6 months after EUS-chemoablation.
Disclosures:
Vanisha Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Erica Park indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Somashekar G Krishna: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Mauna Kea Technologies, and TaeWoong Medical USA – Grant/Research Support. TaeWoong Medical USA – Grant/Research Support.
Vanisha Patel, MD, Erica Park, MD, Somashekar G Krishna, MD. P1833 - Non-Surgical Ablation of a Large Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm Using Tandem Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency and Chemoablation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

