Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P2209 - Pharmacokinetics and Local Tolerability of EP-104GI, an Extended-Release Formulation of Fluticasone Propionate for Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis, After Intra-Esophageal Injection in Mini-Pigs
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- AM
Amanda Malone, PhD
Eupraxia Pharmaceuticals
Victoria, BC, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Murray Webb, PhD, Anastasia Litke, MSc, LIam MacFarlane, PhD, Amanda Malone, PhD
Eupraxia Pharmaceuticals, Victoria, BC, Canada
Introduction: EP-104GI is an extended-release formulation of Fluticasone Propionate (FP) in development for treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. We report results from a 6-week study in mini-pigs comparing the pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and local safety of intra-esophageal injection of EP-104GI with an oral gavage of an FP solution.
Methods: Twelve male mini-pigs received EP-104GI by 4 circumferential 2.5 mg sub-mucosal injections 5 cm from the gastroesophageal junction, a total dose of 10 mg FP. Twelve other male mini-pigs received 10 mg of an FP solution by oral gavage. Blood was collected at 1, 4, 24 hrs and days 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 14, 21, 28 and 42 and plasma FP measured by an LC/MS-MS method. On days 1, 7, 21 and 42 after dosing, 3 animals per group were euthanized and esophageal tissue was recovered from the injection site and 1, 2, 3 and 4 cm from the injection site. FP in esophageal tissue was measured by LC/MS-MS and tissue biopsy samples examined for histopathology.
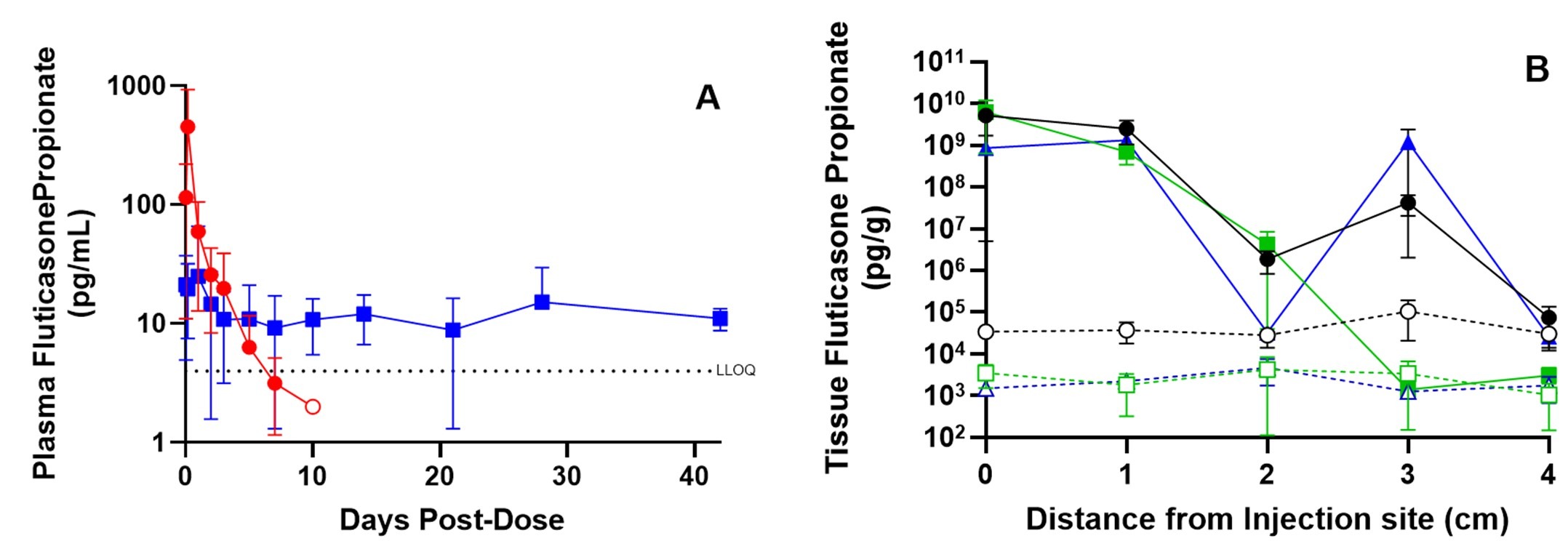
Results: A plasma Cmax of 25 pg/mL was observed 1 day after sub-mucosal injection of EP-104GI in the esophagus. After that, plasma FP was stable from 9-15 pg/mL for the next 6 weeks, showing EP-104GI achieved extended FP release. For an FP solution given by oral gavage, Cmax of 454 pg/mL was at 4 hours and thereafter decreased rapidly with concentrations below 4 pg/mL by Day 10. FP concentrations in esophageal tissues achieved by EP-104GI were 10 to 10,000-fold higher than oral gavage of FP for the entire 6-week study. Tissue FP levels decreased with distance from the injection site but were still 10 to 100-fold higher than achieved by oral gavage of FP even at 4 cm from the injection site and for up to 6 weeks after dosing. The FP-releasing depot of EP-104GI was readily visible by histopathology.
Discussion: EP-104GI, an extended-release formulation of FP, achieves continuous payout of FP for at least 6 weeks after sub-mucosal injection in the esophagus. FP release provides both high local FP concentrations and minimal systemic drug exposure. Plasma FP has been observed for up to 6 months after a single injection in patients in a parallel clinical trial. Tissue concentrations of FP are orders of magnitude higher than achieved by FP given orally, even at distances up to 4 cm from the injection sites. Sub-mucosal injection of EP-104GI in the esophagus was well tolerated. These data show that EP-104GI has significant potential as a safe, effective and long-duration treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis.
Disclosures:
Murray Webb, PhD, Anastasia Litke, MSc, LIam MacFarlane, PhD, Amanda Malone, PhD. P2209 - Pharmacokinetics and Local Tolerability of EP-104GI, an Extended-Release Formulation of Fluticasone Propionate for Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis, After Intra-Esophageal Injection in Mini-Pigs, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Murray Webb, PhD, Anastasia Litke, MSc, LIam MacFarlane, PhD, Amanda Malone, PhD
Eupraxia Pharmaceuticals, Victoria, BC, Canada
Introduction: EP-104GI is an extended-release formulation of Fluticasone Propionate (FP) in development for treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis. We report results from a 6-week study in mini-pigs comparing the pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and local safety of intra-esophageal injection of EP-104GI with an oral gavage of an FP solution.
Methods: Twelve male mini-pigs received EP-104GI by 4 circumferential 2.5 mg sub-mucosal injections 5 cm from the gastroesophageal junction, a total dose of 10 mg FP. Twelve other male mini-pigs received 10 mg of an FP solution by oral gavage. Blood was collected at 1, 4, 24 hrs and days 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 14, 21, 28 and 42 and plasma FP measured by an LC/MS-MS method. On days 1, 7, 21 and 42 after dosing, 3 animals per group were euthanized and esophageal tissue was recovered from the injection site and 1, 2, 3 and 4 cm from the injection site. FP in esophageal tissue was measured by LC/MS-MS and tissue biopsy samples examined for histopathology.
Results: A plasma Cmax of 25 pg/mL was observed 1 day after sub-mucosal injection of EP-104GI in the esophagus. After that, plasma FP was stable from 9-15 pg/mL for the next 6 weeks, showing EP-104GI achieved extended FP release. For an FP solution given by oral gavage, Cmax of 454 pg/mL was at 4 hours and thereafter decreased rapidly with concentrations below 4 pg/mL by Day 10. FP concentrations in esophageal tissues achieved by EP-104GI were 10 to 10,000-fold higher than oral gavage of FP for the entire 6-week study. Tissue FP levels decreased with distance from the injection site but were still 10 to 100-fold higher than achieved by oral gavage of FP even at 4 cm from the injection site and for up to 6 weeks after dosing. The FP-releasing depot of EP-104GI was readily visible by histopathology.
Discussion: EP-104GI, an extended-release formulation of FP, achieves continuous payout of FP for at least 6 weeks after sub-mucosal injection in the esophagus. FP release provides both high local FP concentrations and minimal systemic drug exposure. Plasma FP has been observed for up to 6 months after a single injection in patients in a parallel clinical trial. Tissue concentrations of FP are orders of magnitude higher than achieved by FP given orally, even at distances up to 4 cm from the injection sites. Sub-mucosal injection of EP-104GI in the esophagus was well tolerated. These data show that EP-104GI has significant potential as a safe, effective and long-duration treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis.

Figure: Panel A: Mean plasma concentrations of after FP oral gavage (red circle) or sub-mucosal injection of EP-104GI (blue square). Panel B: Mean concentrations of FP in esophageal tissue with distance from the injection site at 1 day (black circles), 3 weeks (green squares) and 6 weeks (blue triangles) after dosing of either EP-104GI (filled symbols) or oral FP (open symbols).
Disclosures:
Murray Webb: Eupraxia Pharmaceuticals – Employee, Stock Options.
Anastasia Litke: Eupraxia Pharmaceuticals – Employee.
LIam MacFarlane: Eupraxia Pharmaceuticals Inc – Employee.
Amanda Malone: Eupraxia Pharmaceuticals – Employee, Intellectual Property/Patents, Owner/Ownership Interest, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds). GuideStar Medical Devices – Stock-privately held company.
Murray Webb, PhD, Anastasia Litke, MSc, LIam MacFarlane, PhD, Amanda Malone, PhD. P2209 - Pharmacokinetics and Local Tolerability of EP-104GI, an Extended-Release Formulation of Fluticasone Propionate for Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis, After Intra-Esophageal Injection in Mini-Pigs, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

