Monday Poster Session
Category: GI Bleeding
P2541 - Metastatic Ovarian Cancer - A Rare Cause of Lower GI Bleeding
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Mena Tawfik, MD
Parkview Health Center
Pueblo, CO
Presenting Author(s)
Mena Tawfik, MD1, Ramy Sekla, MD2, Aleena Sammar, MD1, Sung K. Yang, MD2
1Parkview Health Center, Pueblo, CO; 2Parkview Medical Center, Pueblo, CO
Introduction: Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death from gynecological malignancies among women. The most common cause of death is cancer metastases. Ovarian cancer metastasis to the colon is a rare entity that occurs mainly via direct invasion or intraperitoneal seeding and rarely via hematogenous dissemination. We present a case of an 85 year-old female with ovarian cancer metastasis to the colon 7 years after initial diagnosis and debulking surgery.
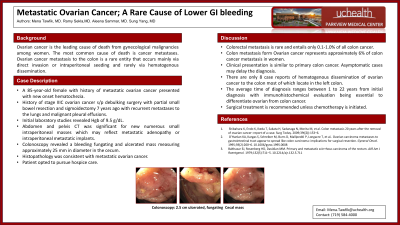
Case Description/Methods: An 85-year-old female with history of chronic anemia, metastatic ovarian cancer presented to the hospital with new onset hematochezia. Patient was initially diagnosed with stage IIIC ovarian cancer and underwent debulking surgery with partial small bowel resection and sigmoidectomy 7 years ago. Two years ago she had recurrent metastatic disease to the lungs with malignant pleural effusions. Initial laboratory studies revealed hemoglobin of 9.5 g/dL which is around patient’s baseline. Abdomen and pelvis CT was significant for new numerous small intraperitoneal masses which may reflect metastatic adenopathy or intraperitoneal metastatic implants with no evidence of bowel wall thickening. Colonoscopy revealed a bleeding fungating and ulcerated mass measuring approximately 25 mm in diameter in the cecum. Biopsies were performed with histopathology consistent with metastatic ovarian cancer. Given disease progression, patient opted to go home on hospice care.
Discussion: Colorectal metastasis is rare and entails only 0.1-1.0% of all colon cancer. [3] Colon metastasis form Ovarian cancer represents approximately 6% of colon cancer metastasis in women. Clinical presentation is similar to primary colon cancer with new onset anemia, lower GI bleeding or bowel obstruction. Asymptomatic cases may delay the diagnosis. There are only 8 case reports of hematogenous dissemination of ovarian cancer to the colon most of which locate in the left colon. The average time of diagnosis ranges between 1 to 22 years from initial diagnosis. Immunohistochemical evaluation is essential to differentiate ovarian from colon cancer. Surgical treatment is recommended unless chemotherapy is initiated.
Disclosures:
Mena Tawfik, MD1, Ramy Sekla, MD2, Aleena Sammar, MD1, Sung K. Yang, MD2. P2541 - Metastatic Ovarian Cancer - A Rare Cause of Lower GI Bleeding, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Parkview Health Center, Pueblo, CO; 2Parkview Medical Center, Pueblo, CO
Introduction: Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death from gynecological malignancies among women. The most common cause of death is cancer metastases. Ovarian cancer metastasis to the colon is a rare entity that occurs mainly via direct invasion or intraperitoneal seeding and rarely via hematogenous dissemination. We present a case of an 85 year-old female with ovarian cancer metastasis to the colon 7 years after initial diagnosis and debulking surgery.
Case Description/Methods: An 85-year-old female with history of chronic anemia, metastatic ovarian cancer presented to the hospital with new onset hematochezia. Patient was initially diagnosed with stage IIIC ovarian cancer and underwent debulking surgery with partial small bowel resection and sigmoidectomy 7 years ago. Two years ago she had recurrent metastatic disease to the lungs with malignant pleural effusions. Initial laboratory studies revealed hemoglobin of 9.5 g/dL which is around patient’s baseline. Abdomen and pelvis CT was significant for new numerous small intraperitoneal masses which may reflect metastatic adenopathy or intraperitoneal metastatic implants with no evidence of bowel wall thickening. Colonoscopy revealed a bleeding fungating and ulcerated mass measuring approximately 25 mm in diameter in the cecum. Biopsies were performed with histopathology consistent with metastatic ovarian cancer. Given disease progression, patient opted to go home on hospice care.
Discussion: Colorectal metastasis is rare and entails only 0.1-1.0% of all colon cancer. [3] Colon metastasis form Ovarian cancer represents approximately 6% of colon cancer metastasis in women. Clinical presentation is similar to primary colon cancer with new onset anemia, lower GI bleeding or bowel obstruction. Asymptomatic cases may delay the diagnosis. There are only 8 case reports of hematogenous dissemination of ovarian cancer to the colon most of which locate in the left colon. The average time of diagnosis ranges between 1 to 22 years from initial diagnosis. Immunohistochemical evaluation is essential to differentiate ovarian from colon cancer. Surgical treatment is recommended unless chemotherapy is initiated.
Disclosures:
Mena Tawfik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ramy Sekla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aleena Sammar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sung Yang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mena Tawfik, MD1, Ramy Sekla, MD2, Aleena Sammar, MD1, Sung K. Yang, MD2. P2541 - Metastatic Ovarian Cancer - A Rare Cause of Lower GI Bleeding, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
