Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2686 - Timing of Index Ileocolic Resection is Associated With Radiographic Recurrence in Patients With Crohn’s Disease
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- EL
Elizabeth S. Li, BSc
NYU Grossman School of Medicine
New York, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Elizabeth S. Li, BSc1, Terry Li, MD2, Ravi Shah, MD3, Benjamin Click, MD4, Delaney R. Ryan, MPH5, Benjamin L. Cohen, MD6, Edward Barnes, MD, MPH, FACG7, Abel Joseph, MD8, Salam Bachour, MD9, Jessica Hu, BS7, Susell Contreras, BA2, Jordan Axelrad, MD, MPH1
1NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY; 2NYU Langone Health, New York, NY; 3Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 4University of Colorado, Aurora, CO; 5Cleveland Clinic Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland, OH; 6Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 7University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 8Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, CA; 9Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA
Introduction: Surgical resection in Crohn’s disease (CD) is often reserved for complicated or refractory disease, though studies have suggested a role for early primary ileocolic resection (ICR). We aimed to compare the risk of CD recurrence in patients undergoing early versus late ileocolic resection.
Methods: In a multicenter, retrospective cohort study, patients > 18 years old with CD and an index ICR with available postoperative endoscopy were included. Those with prior ICR or permanent ileostomy were excluded. Baseline and demographic variables were compared using Chi square and Kruskal Wallis. Univariable Cox analysis of endoscopic (Rutgeerts ≥ i2b), radiographic (active inflammation), surgical (repeat ICR), and composite CD recurrence were performed and stratified by timing of ICR from CD diagnosis (≤ 1, 2-5, or ≥ 6 years). Multivariate Cox analysis of CD recurrence by timing of < 1 vs ≥ 1 year was done using established risk factors for recurrence.
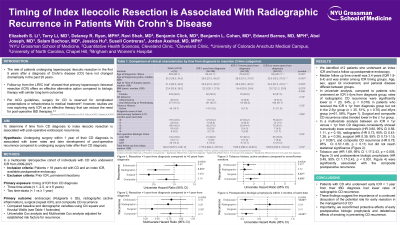
Results: A total of 412 patients were included. Median follow up time overall was 3.4 years (IQR 1.9-6.4) and was similar among ICR timing groups, with 109 (26%), 122 (30%), and 181 (44%) patients in the ≤ 1, 2-5, or ≥ 6yrs from diagnosis groups, respectively. In the univariate analysis, compared to patients who received ICR ≥ 6yrs from diagnosis group, rates of radiographic CD recurrence were significantly lower (n = 20, 34%, p = 0.018) in the ≤ 1yr group but not in the 2-5yr group (n = 35, 51%, p = 0.70, Table 1). Endoscopic, surgical, and composite CD recurrence rates also trended lower in the ≤ 1yr group. Multivariate analysis between ICR ≤ 1yr versus > 1yr from CD diagnosis consistently showed numerically lower endoscopic (HR 0.80, 95% CI 0.58-1.11, p = 0.18), radiographic (HR 0.73, 95% CI 0.43-1.26, p = 0.26), surgical (HR 0.39, 95% CI 0.13-1.15, p = 0.087), and composite CD recurrence (HR 0.78, 95% CI 0.57-1.06, p = 0.11) but did not reach statistical significance. Tobacco use (HR 1.69, 95% CI 1.17-2.43, p = 0.005) and postoperative biologic prophylaxis (HR 0.49, 95% CI 1.17-2.43, p < 0.001) were significantly associated with composite postoperative recurrence.
Discussion: Early ICR had lower rates of CD recurrence, though the sample was underpowered to reach statistical significance. These findings suggest the importance of a continued discussion of the potential role for early resection in the management of CD. Importantly, the data reconfirmed the protective effects of early postoperative biologic prophylaxis in preventing CD recurrence.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Elizabeth S. Li, BSc1, Terry Li, MD2, Ravi Shah, MD3, Benjamin Click, MD4, Delaney R. Ryan, MPH5, Benjamin L. Cohen, MD6, Edward Barnes, MD, MPH, FACG7, Abel Joseph, MD8, Salam Bachour, MD9, Jessica Hu, BS7, Susell Contreras, BA2, Jordan Axelrad, MD, MPH1. P2686 - Timing of Index Ileocolic Resection is Associated With Radiographic Recurrence in Patients With Crohn’s Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Elizabeth S. Li, BSc1, Terry Li, MD2, Ravi Shah, MD3, Benjamin Click, MD4, Delaney R. Ryan, MPH5, Benjamin L. Cohen, MD6, Edward Barnes, MD, MPH, FACG7, Abel Joseph, MD8, Salam Bachour, MD9, Jessica Hu, BS7, Susell Contreras, BA2, Jordan Axelrad, MD, MPH1
1NYU Grossman School of Medicine, New York, NY; 2NYU Langone Health, New York, NY; 3Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 4University of Colorado, Aurora, CO; 5Cleveland Clinic Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland, OH; 6Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 7University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC; 8Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, CA; 9Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA
Introduction: Surgical resection in Crohn’s disease (CD) is often reserved for complicated or refractory disease, though studies have suggested a role for early primary ileocolic resection (ICR). We aimed to compare the risk of CD recurrence in patients undergoing early versus late ileocolic resection.
Methods: In a multicenter, retrospective cohort study, patients > 18 years old with CD and an index ICR with available postoperative endoscopy were included. Those with prior ICR or permanent ileostomy were excluded. Baseline and demographic variables were compared using Chi square and Kruskal Wallis. Univariable Cox analysis of endoscopic (Rutgeerts ≥ i2b), radiographic (active inflammation), surgical (repeat ICR), and composite CD recurrence were performed and stratified by timing of ICR from CD diagnosis (≤ 1, 2-5, or ≥ 6 years). Multivariate Cox analysis of CD recurrence by timing of < 1 vs ≥ 1 year was done using established risk factors for recurrence.
Results: A total of 412 patients were included. Median follow up time overall was 3.4 years (IQR 1.9-6.4) and was similar among ICR timing groups, with 109 (26%), 122 (30%), and 181 (44%) patients in the ≤ 1, 2-5, or ≥ 6yrs from diagnosis groups, respectively. In the univariate analysis, compared to patients who received ICR ≥ 6yrs from diagnosis group, rates of radiographic CD recurrence were significantly lower (n = 20, 34%, p = 0.018) in the ≤ 1yr group but not in the 2-5yr group (n = 35, 51%, p = 0.70, Table 1). Endoscopic, surgical, and composite CD recurrence rates also trended lower in the ≤ 1yr group. Multivariate analysis between ICR ≤ 1yr versus > 1yr from CD diagnosis consistently showed numerically lower endoscopic (HR 0.80, 95% CI 0.58-1.11, p = 0.18), radiographic (HR 0.73, 95% CI 0.43-1.26, p = 0.26), surgical (HR 0.39, 95% CI 0.13-1.15, p = 0.087), and composite CD recurrence (HR 0.78, 95% CI 0.57-1.06, p = 0.11) but did not reach statistical significance. Tobacco use (HR 1.69, 95% CI 1.17-2.43, p = 0.005) and postoperative biologic prophylaxis (HR 0.49, 95% CI 1.17-2.43, p < 0.001) were significantly associated with composite postoperative recurrence.
Discussion: Early ICR had lower rates of CD recurrence, though the sample was underpowered to reach statistical significance. These findings suggest the importance of a continued discussion of the potential role for early resection in the management of CD. Importantly, the data reconfirmed the protective effects of early postoperative biologic prophylaxis in preventing CD recurrence.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Elizabeth Li indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Terry Li indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ravi Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Benjamin Click: AbbVie – Consultant. BMS – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant. Prometheus – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. TARGET-RWE – Consultant.
Delaney Ryan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Benjamin L. Cohen: Abbvie – Consultant, support and/or funding, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – support and/or funding. Celgene – support and/or funding. Emmes – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Janssen – Consultant, support and/or funding, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – support and/or funding. Takeda – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Target RWE – Consultant, Speakers Bureau.
Edward Barnes: AbbVie, Inc. – Consultant. Boomerang – Consultant. Bristol-Meyers Squibb – Consultant. Direct Biologics – Consultant. Eli Lilly and Company – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Pfizer – Consultant. Target RWE – Consultant.
Abel Joseph indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Salam Bachour indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jessica Hu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Susell Contreras indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jordan Axelrad: Abbvie – Consultant. Adiso – Consultant. Biomerieux – Consultant. BMS – Consultant. Fresenius – Consultant. Genentech – Grant/Research Support. Janssen – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant.
Elizabeth S. Li, BSc1, Terry Li, MD2, Ravi Shah, MD3, Benjamin Click, MD4, Delaney R. Ryan, MPH5, Benjamin L. Cohen, MD6, Edward Barnes, MD, MPH, FACG7, Abel Joseph, MD8, Salam Bachour, MD9, Jessica Hu, BS7, Susell Contreras, BA2, Jordan Axelrad, MD, MPH1. P2686 - Timing of Index Ileocolic Resection is Associated With Radiographic Recurrence in Patients With Crohn’s Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.


