Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P2873 - Comparative Analysis of Clinical Outcomes in Hepatitis B/Delta Virus Co-infection vs Hepatitis B Mono-Infection in a Large Integrated Healthcare System
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Xiaoran Li, MD
Kaiser Permanente
San Francisco, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Xiaoran Li, MD1, Lue-Yen Tucker, BA2, Krisna P. Chai, MD3, Suk Seo, 4, Nizar Mukhtar, MD1, Grace M. Chee, PharmD5, Kyung Kwon, MD6, Sripriya Balasubramanian, MD, MPH7, Brock Macdonald, MD8, Julie Schmittdiel, PhD, MA2, Varun Saxena, MD, MAS9
1Kaiser Permanente, San Francisco, CA; 2Kaiser Permanente, Pleasanton, CA; 3Kaiser Permanente, Santa Clara, CA; 4Kaiser Permanente, Moraga, CA; 5Gilead Sciences, Inc., Foster City, CA; 6Gilead Sciences, Inc., Gilead, CA; 7Kaiser Permanente, Roseville, CA; 8Kaiser Permanente, San Rafael, CA; 9Kaiser Permanente, South San Francisco, CA
Introduction: Clinical observation has suggested Hepatitis B virus (HBV)/Hepatitis Delta virus (HDV) co-infection may lead to worse prognosis compared to HBV mono-infection. However, conclusive evidence of poorer outcomes in HBV/HDV co-infected patients remains elusive due to under-estimation of HBV/HDV co-infection stemming from low HDV screening rates. In this study, we aim to compare clinical outcomes of patients with HBV/HDV co-infection vs. HBV mono-infection in a large integrated healthcare system, underscoring the importance of routine HDV screening and necessity for tailored therapeutic interventions.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study at Kaiser Permanente Northern California, all adult HBV-infected patients identified between 2009 and 2021 were included. Two study groups were identified: HBV/HDV co-infected (anti-HDV positive with/without HDV RNA tested/detected) and HBV mono-infected (HBV surface antigen positive; anti-HDV negative or never checked). Both groups were followed until the occurrence of outcomes of interest (cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma [HCC], liver transplant, and all-cause mortality), membership loss, or study conclusion on December 31, 2022. Patient characteristics and outcomes were compared between the two groups. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used to estimate the cumulative incidence of the outcome; the multivariable Cox proportional-hazards model was utilized to assess association between risk factors and the outcome.
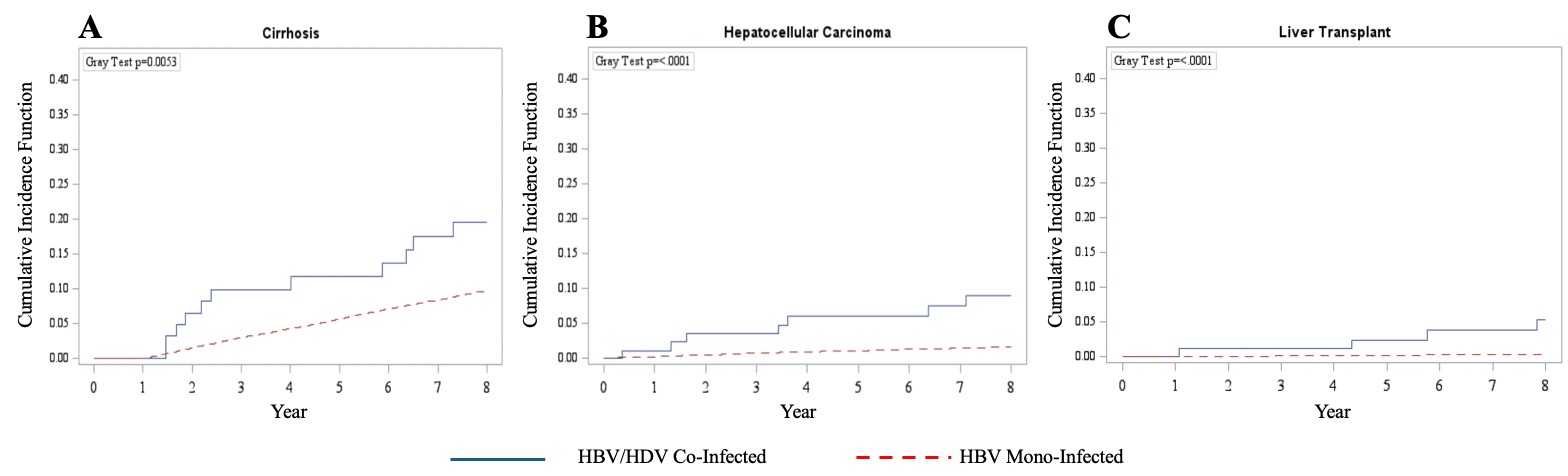
Results: Final cohort included 94 HBV/HDV co-infected and 17700 HBV mono-infected patients. The median ages were 58 and 48 years, the body mass index 26.4 and 24.7, and the baseline MELD scores 8.0 and 7.0 in the HBV/HDV co-infected group and HBV mono-infected group, respectively. HBV/HDV co-infection was associated with higher incidences of cirrhosis, HCC, and liver transplant (Figure 1). While all-cause mortality rates were elevated beyond year 4 in HBV/HDV co-infected patients, statistical significance was not reached. When controlling for demographic factors and medical conditions, HBV/HDV (vs. HBV mono-infected) was an independent risk factor for HCC and liver transplant but not cirrhosis or all-cause mortality (Table 1).
Discussion: This study demonstrated HBV/HDV co-infection is associated with poorer clinical outcomes within a large integrated healthcare system. Our study highlights the importance of routine HDV screening and the need for tailored therapeutic interventions.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Xiaoran Li, MD1, Lue-Yen Tucker, BA2, Krisna P. Chai, MD3, Suk Seo, 4, Nizar Mukhtar, MD1, Grace M. Chee, PharmD5, Kyung Kwon, MD6, Sripriya Balasubramanian, MD, MPH7, Brock Macdonald, MD8, Julie Schmittdiel, PhD, MA2, Varun Saxena, MD, MAS9. P2873 - Comparative Analysis of Clinical Outcomes in Hepatitis B/Delta Virus Co-infection vs Hepatitis B Mono-Infection in a Large Integrated Healthcare System, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Kaiser Permanente, San Francisco, CA; 2Kaiser Permanente, Pleasanton, CA; 3Kaiser Permanente, Santa Clara, CA; 4Kaiser Permanente, Moraga, CA; 5Gilead Sciences, Inc., Foster City, CA; 6Gilead Sciences, Inc., Gilead, CA; 7Kaiser Permanente, Roseville, CA; 8Kaiser Permanente, San Rafael, CA; 9Kaiser Permanente, South San Francisco, CA
Introduction: Clinical observation has suggested Hepatitis B virus (HBV)/Hepatitis Delta virus (HDV) co-infection may lead to worse prognosis compared to HBV mono-infection. However, conclusive evidence of poorer outcomes in HBV/HDV co-infected patients remains elusive due to under-estimation of HBV/HDV co-infection stemming from low HDV screening rates. In this study, we aim to compare clinical outcomes of patients with HBV/HDV co-infection vs. HBV mono-infection in a large integrated healthcare system, underscoring the importance of routine HDV screening and necessity for tailored therapeutic interventions.
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study at Kaiser Permanente Northern California, all adult HBV-infected patients identified between 2009 and 2021 were included. Two study groups were identified: HBV/HDV co-infected (anti-HDV positive with/without HDV RNA tested/detected) and HBV mono-infected (HBV surface antigen positive; anti-HDV negative or never checked). Both groups were followed until the occurrence of outcomes of interest (cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma [HCC], liver transplant, and all-cause mortality), membership loss, or study conclusion on December 31, 2022. Patient characteristics and outcomes were compared between the two groups. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used to estimate the cumulative incidence of the outcome; the multivariable Cox proportional-hazards model was utilized to assess association between risk factors and the outcome.
Results: Final cohort included 94 HBV/HDV co-infected and 17700 HBV mono-infected patients. The median ages were 58 and 48 years, the body mass index 26.4 and 24.7, and the baseline MELD scores 8.0 and 7.0 in the HBV/HDV co-infected group and HBV mono-infected group, respectively. HBV/HDV co-infection was associated with higher incidences of cirrhosis, HCC, and liver transplant (Figure 1). While all-cause mortality rates were elevated beyond year 4 in HBV/HDV co-infected patients, statistical significance was not reached. When controlling for demographic factors and medical conditions, HBV/HDV (vs. HBV mono-infected) was an independent risk factor for HCC and liver transplant but not cirrhosis or all-cause mortality (Table 1).
Discussion: This study demonstrated HBV/HDV co-infection is associated with poorer clinical outcomes within a large integrated healthcare system. Our study highlights the importance of routine HDV screening and the need for tailored therapeutic interventions.

Figure: Figure 1 A-C. Kaplan-Meier curves of outcomes of interest in HBV/HDV co-infected and HBV mono-infected patients.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Xiaoran Li indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lue-Yen Tucker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krisna Chai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Suk Seo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nizar Mukhtar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Grace Chee: Gilead Sciences – Employee.
Kyung Kwon: Gilead – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Sripriya Balasubramanian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brock Macdonald: Gilead Pharmeceuticals – Grant/Research Support.
Julie Schmittdiel: Gilead – Grant/Research Support.
Varun Saxena: Gilead Sciences – Grant/Research Support.
Xiaoran Li, MD1, Lue-Yen Tucker, BA2, Krisna P. Chai, MD3, Suk Seo, 4, Nizar Mukhtar, MD1, Grace M. Chee, PharmD5, Kyung Kwon, MD6, Sripriya Balasubramanian, MD, MPH7, Brock Macdonald, MD8, Julie Schmittdiel, PhD, MA2, Varun Saxena, MD, MAS9. P2873 - Comparative Analysis of Clinical Outcomes in Hepatitis B/Delta Virus Co-infection vs Hepatitis B Mono-Infection in a Large Integrated Healthcare System, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
