Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P4314 - Mirikizumab as an Induction and Maintenance Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Control Trials
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Abbas Bader, BA
University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine
Kansas City, MO
Presenting Author(s)
Noor Hassan, MD1, Islam Mohamed, MD2, Maya Mahmoud, MD3, Abbas Bader, BA2, Rishabh Gaur, BA2, Mohamed Refaat, BA2, Ahmed Naeem, MD4, Mir Zulqarnain, DO2, Hassan Ghoz, MD2
1University of Missouri Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 2University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 3SSM Health Saint Louis University Hospital, St. Louis, MO; 4Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Al Qahirah, Egypt
Introduction: Mirikizumab is an IgG4-variant monoclonal antibody that blocks interleukin-23 cytokine activity. This drug was approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration in October 2023 for use in patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis. Our study aimed to determine the efficacy of mirikizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis.
Methods: We searched PubMed, SCOPUS, Embase, and Cochrane from inception through November 2023. All randomized control trials (RCTs) comparing the efficacy of mirikizumab to placebo in adults with ulcerative colitis were included. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine endoscopic improvement, endoscopic remission, and histologic remission in patients with ulcerative colitis who received maintenance and induction mirikizumab. We used the fixed-effect model to pool dichotomous data using risk ratio (RR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI). We also examined the heterogeneity between studies.
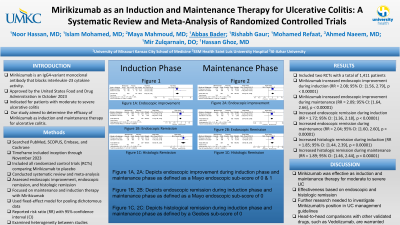
Results: We included two RCTs with a total of 1,411 patients. Mirikizumab was associated with an increased endoscopic improvement rate compared to placebo during the induction phase (Relative Risk [RR] = 2.08; 95% Confidence Interval [CI]: [1.56, 2.79], p < 0.00001) and in the maintenance phase (RR = 2.09; 95% CI: [1.64, 2.66], p < 0.00001). Also, mirikizumab was associated with an increased endoscopic remission rate during both induction (RR = 1.72; 95% CI: [1.36, 2.18], p < 0.00001) and maintenance phases (RR = 2.04; 95% CI: [1.60, 2.60], p < 0.00001). Increased histologic remission rate during both induction (RR = 1.85; 95% CI: [1.44, 2.39], p < 0.00001) and maintenance phases (RR = 1.89; 95% CI: [1.46, 2.44], p < 0.00001) was noted with the use of mirikizumab. Figures 1 and 2 demonstrate this data.
Discussion: Mirikizumab is effective as both induction and maintenance therapy for moderate to severe ulcerative colitis based on endoscopic and histologic remission. Further research is warranted to investigate the position of mirikizumab in ulcerative colitis management guidelines by head-to-head comparisons with other validated drugs, such as vedolizumab.

Disclosures:
Noor Hassan, MD1, Islam Mohamed, MD2, Maya Mahmoud, MD3, Abbas Bader, BA2, Rishabh Gaur, BA2, Mohamed Refaat, BA2, Ahmed Naeem, MD4, Mir Zulqarnain, DO2, Hassan Ghoz, MD2. P4314 - Mirikizumab as an Induction and Maintenance Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Control Trials, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Missouri Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 2University of Missouri - Kansas City School of Medicine, Kansas City, MO; 3SSM Health Saint Louis University Hospital, St. Louis, MO; 4Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Al Qahirah, Egypt
Introduction: Mirikizumab is an IgG4-variant monoclonal antibody that blocks interleukin-23 cytokine activity. This drug was approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration in October 2023 for use in patients with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis. Our study aimed to determine the efficacy of mirikizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis.
Methods: We searched PubMed, SCOPUS, Embase, and Cochrane from inception through November 2023. All randomized control trials (RCTs) comparing the efficacy of mirikizumab to placebo in adults with ulcerative colitis were included. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine endoscopic improvement, endoscopic remission, and histologic remission in patients with ulcerative colitis who received maintenance and induction mirikizumab. We used the fixed-effect model to pool dichotomous data using risk ratio (RR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI). We also examined the heterogeneity between studies.
Results: We included two RCTs with a total of 1,411 patients. Mirikizumab was associated with an increased endoscopic improvement rate compared to placebo during the induction phase (Relative Risk [RR] = 2.08; 95% Confidence Interval [CI]: [1.56, 2.79], p < 0.00001) and in the maintenance phase (RR = 2.09; 95% CI: [1.64, 2.66], p < 0.00001). Also, mirikizumab was associated with an increased endoscopic remission rate during both induction (RR = 1.72; 95% CI: [1.36, 2.18], p < 0.00001) and maintenance phases (RR = 2.04; 95% CI: [1.60, 2.60], p < 0.00001). Increased histologic remission rate during both induction (RR = 1.85; 95% CI: [1.44, 2.39], p < 0.00001) and maintenance phases (RR = 1.89; 95% CI: [1.46, 2.44], p < 0.00001) was noted with the use of mirikizumab. Figures 1 and 2 demonstrate this data.
Discussion: Mirikizumab is effective as both induction and maintenance therapy for moderate to severe ulcerative colitis based on endoscopic and histologic remission. Further research is warranted to investigate the position of mirikizumab in ulcerative colitis management guidelines by head-to-head comparisons with other validated drugs, such as vedolizumab.

Figure: Figure 1 depicting endoscopic improvement, endoscopic remission, and histologic remission in the induction phase.
Figure 2 depicting endoscopic improvement, endoscopic remission, and histologic remission in maintenance phase.
Figure 2 depicting endoscopic improvement, endoscopic remission, and histologic remission in maintenance phase.
Disclosures:
Noor Hassan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Islam Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maya Mahmoud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abbas Bader indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rishabh Gaur indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Refaat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Naeem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mir Zulqarnain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hassan Ghoz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noor Hassan, MD1, Islam Mohamed, MD2, Maya Mahmoud, MD3, Abbas Bader, BA2, Rishabh Gaur, BA2, Mohamed Refaat, BA2, Ahmed Naeem, MD4, Mir Zulqarnain, DO2, Hassan Ghoz, MD2. P4314 - Mirikizumab as an Induction and Maintenance Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Control Trials, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
