Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P4320 - Effectiveness, Treatment Pattern, and Safety of Ustekinumab Among Bio-Naïve Patients With Crohn’s Disease in Real-World Clinical Settings in China
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Lingya Yao, MD
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China (People's Republic)
Presenting Author(s)
Lingya Yao, MD1, Xiaoqing Lin, MD2, Jian Tang, MD3, Han Gao, 4, Xiang Gao, MD3, Qian Cao, MD, PhD1, Minhu Chen, MD, PhD2
1Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China; 3The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China; 4Medical Affairs, Johnson & Johnson Innovative Medicine, Beijing, Beijing, China
Introduction: Ustekinumab (UST) is a human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody. Clinical trials have shown UST’s efficacy and safety in Crohn’s disease (CD). However, relevant real-world evidence in China is scarce particularly among bio-naïve patients with CD. This study evaluates UST’s endoscopic and clinical effectiveness, treatment pattern, and safety among bio-naïve patients with CD in real-world clinical settings in China.
Methods: A multicentre, retrospective observational study was performed in bio-naïve patients with CD initiating UST between 05/20/2020 and 09/16/2022. Effectiveness was assessed at week 24 (± 4 weeks), including endoscopic remission, endoscopic response, (steroid-free) clinical remission, and (steroid-free) clinical response. Treatment pattern was evaluated by the UST treatment persistence and the CD-related concomitant treatment. Safety was measured by the frequency of adverse events (AEs).
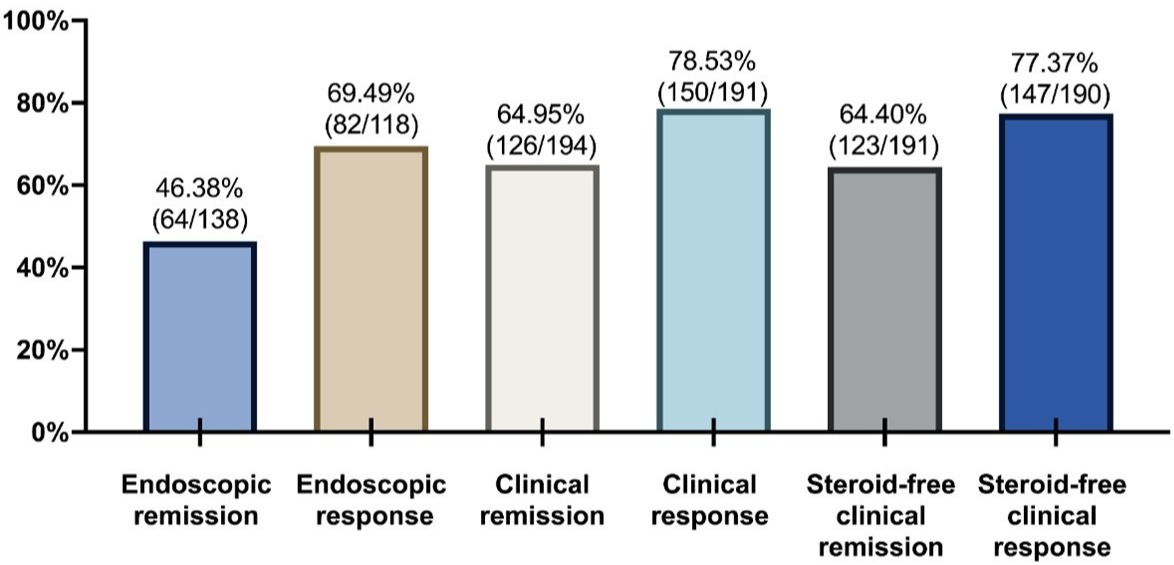
Results: A total of 200 patients initiating UST as 1st-line were included; 44.5% were < 30 years old, 66% had CD for ≤2 years, and 53.5% had moderately-to-severely active CD at baseline. Of patients with endoscopic/clinical outcomes available, at week 24 (± 4 weeks), 46.38% and 69.49% achieved endoscopic remission and response, respectively; 64.95% and 78.53% achieved clinical remission and response, respectively; and 64.4% and 77.37% achieved steroid-free clinical remission and response, respectively (Figure 1). Of 200 patients, most (93%) persisted in UST while 14 (7%) discontinued UST due to a lack of response (n=7; switched to other biologics), surgery (n=5), AE (n=1; switched to other biologics), and patient’s decision (n=1). Two (1%) patients received concomitant immunosuppressants and nine (4.5%) received concomitant steroids during observation. Fifteen patients reported 15 AEs, with fatigue (n=3) and mild infusion reaction (n=3) being most common.
Discussion: Among these patients who were relatively young and had short CD duration, almost half achieved endoscopic remission at week 24 after UST initiation. Multiple clinical outcomes consistently improved, and the magnitude of improvement appeared more prominent than in registrational trials. Most patients persisted in UST without switching to other biologics and were treated without concomitant medications. No serious AEs or unexpected safety signals occurred. Findings of this study support the consideration of UST as 1st-line biologics for CD.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Lingya Yao, MD1, Xiaoqing Lin, MD2, Jian Tang, MD3, Han Gao, 4, Xiang Gao, MD3, Qian Cao, MD, PhD1, Minhu Chen, MD, PhD2. P4320 - Effectiveness, Treatment Pattern, and Safety of Ustekinumab Among Bio-Naïve Patients With Crohn’s Disease in Real-World Clinical Settings in China, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China; 3The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China; 4Medical Affairs, Johnson & Johnson Innovative Medicine, Beijing, Beijing, China
Introduction: Ustekinumab (UST) is a human interleukin-12/23 monoclonal antibody. Clinical trials have shown UST’s efficacy and safety in Crohn’s disease (CD). However, relevant real-world evidence in China is scarce particularly among bio-naïve patients with CD. This study evaluates UST’s endoscopic and clinical effectiveness, treatment pattern, and safety among bio-naïve patients with CD in real-world clinical settings in China.
Methods: A multicentre, retrospective observational study was performed in bio-naïve patients with CD initiating UST between 05/20/2020 and 09/16/2022. Effectiveness was assessed at week 24 (± 4 weeks), including endoscopic remission, endoscopic response, (steroid-free) clinical remission, and (steroid-free) clinical response. Treatment pattern was evaluated by the UST treatment persistence and the CD-related concomitant treatment. Safety was measured by the frequency of adverse events (AEs).
Results: A total of 200 patients initiating UST as 1st-line were included; 44.5% were < 30 years old, 66% had CD for ≤2 years, and 53.5% had moderately-to-severely active CD at baseline. Of patients with endoscopic/clinical outcomes available, at week 24 (± 4 weeks), 46.38% and 69.49% achieved endoscopic remission and response, respectively; 64.95% and 78.53% achieved clinical remission and response, respectively; and 64.4% and 77.37% achieved steroid-free clinical remission and response, respectively (Figure 1). Of 200 patients, most (93%) persisted in UST while 14 (7%) discontinued UST due to a lack of response (n=7; switched to other biologics), surgery (n=5), AE (n=1; switched to other biologics), and patient’s decision (n=1). Two (1%) patients received concomitant immunosuppressants and nine (4.5%) received concomitant steroids during observation. Fifteen patients reported 15 AEs, with fatigue (n=3) and mild infusion reaction (n=3) being most common.
Discussion: Among these patients who were relatively young and had short CD duration, almost half achieved endoscopic remission at week 24 after UST initiation. Multiple clinical outcomes consistently improved, and the magnitude of improvement appeared more prominent than in registrational trials. Most patients persisted in UST without switching to other biologics and were treated without concomitant medications. No serious AEs or unexpected safety signals occurred. Findings of this study support the consideration of UST as 1st-line biologics for CD.

Figure: Figure 1 Summary of Endoscopic and Clinical Effectiveness at Week 24 (± 4 Weeks)
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Lingya Yao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Xiaoqing Lin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jian Tang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Han Gao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Xiang Gao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Qian Cao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Minhu Chen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lingya Yao, MD1, Xiaoqing Lin, MD2, Jian Tang, MD3, Han Gao, 4, Xiang Gao, MD3, Qian Cao, MD, PhD1, Minhu Chen, MD, PhD2. P4320 - Effectiveness, Treatment Pattern, and Safety of Ustekinumab Among Bio-Naïve Patients With Crohn’s Disease in Real-World Clinical Settings in China, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
