Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P4325 - Real World Characteristics and Treatment Patterns of Patients With Crohn’s Disease (CD) Treated With Risankizumab: A US Claims Database Study
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E


Bincy Abraham, MD, MS, FACG
Houston Methodist-Weill Cornell
Houston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Gil Y. Melmed, MD1, Casey Chapman, MD2, Bincy P. Abraham, MD, MS, FACG3, Jenny Griffith, PharmD4, Nidhi Shukla, PhD, MBA5, Javier A. Zambrano, MD6, Brooke Kim, RN, BSN, MS5, Tianzhou Yu, PhD, MS, MPH5, Corey A. Siegel, MD, MS7
1Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA; 2GI Alliance, Baton Rouge, LA; 3Houston Methodist-Weill Cornell, Houston, TX; 4AbbVie, Edwardsville, IL; 5AbbVie, Mettawa, IL; 6AbbVie, Inc., Scottsdale, AZ; 7Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, NH
Introduction: Risankizumab (RZB), an interleukin-23 p19-specific humanized monoclonal antibody, was approved by the United States (US) Food and Drug Administration (June 2022) for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe Crohn’s disease (CD). Here, we describe the characteristics and initial treatment patterns of patients with CD in the US who have been treated with RZB.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study was conducted from June 2022 to January 2024 using US insurance claims data from the Merative MarketScan database. Eligible patients were ≥18 years of age, had a diagnosis of CD (at least 1 inpatient or 2 outpatient claims), received 600 mg intravenous RZB induction, and were continuously enrolled in pharmacy and medical benefits for 6 months prior to (baseline) and 6 months (follow-up) after the first RZB claim. Patient demographics, disease characteristics, treatment history, and RZB treatment patterns are described.
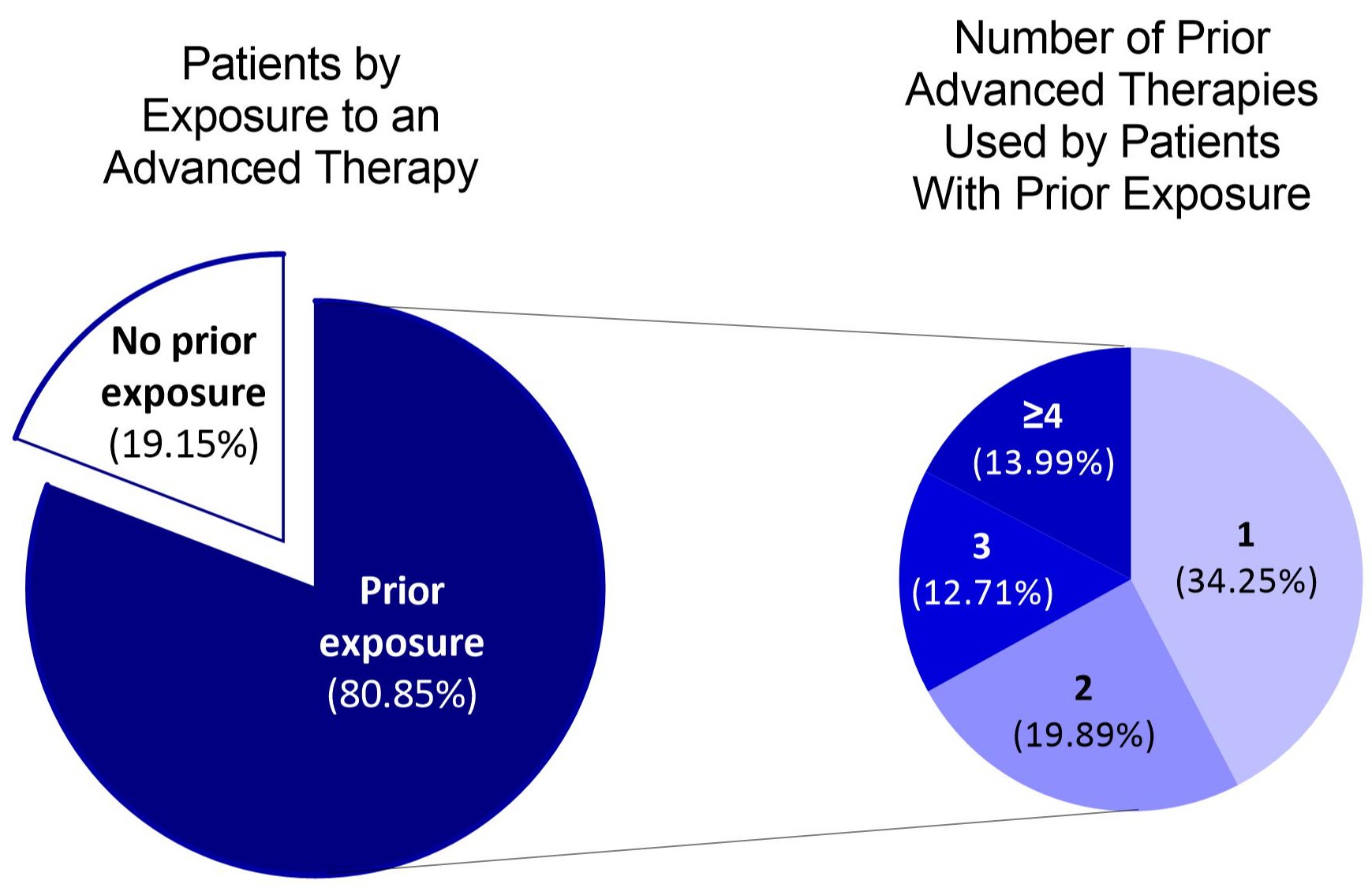
Results: A total of 543 eligible patients were identified (average age 39.8 years [range 18-80]; 54.9% female) (Table). The greatest proportion of patients had ileal colonic disease (29.3%), followed by ileal disease (26.0%), and colonic disease (14.9%); disease location was unspecified for 29.8% of patients. During baseline, 9.2% and 7.4% of patients had claims for fistulizing disease and stricturing disease, respectively, and 10.3% of patients had undergone surgery for CD. Most patients (80.9%) had prior exposure to advanced therapy (34.3% with prior exposure to 1 advanced therapy, 19.9% to 2, and 26.7% to ≥3) (Figure) and most had previously used an anti-tumor necrosis factor agent (63.2%). At the initiation of RZB induction, 8.7% of patients were using an immunomodulator, 76.6% of whom were using a thiopurine, and 41.1% were using systemic steroids. Over 90% of patients (490/543) received a RZB maintenance dose following induction, and 95.7% of these patients received the 360 mg RZB maintenance dose.
Discussion: Since FDA approval, real-world evidence demonstrates that most patients who received induction with RZB also received RZB maintenance dosing following induction, and nearly 1 out of every 5 patients who started RZB were naïve to prior treatment with an advanced therapy. Most patient demographics and disease characteristic reported to date are consistent with the phase 3 RZB clinical trial program.. Future analyses will evaluate longer-term outcomes, including the impact of RZB treatment on steroid utilization.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Gil Y. Melmed, MD1, Casey Chapman, MD2, Bincy P. Abraham, MD, MS, FACG3, Jenny Griffith, PharmD4, Nidhi Shukla, PhD, MBA5, Javier A. Zambrano, MD6, Brooke Kim, RN, BSN, MS5, Tianzhou Yu, PhD, MS, MPH5, Corey A. Siegel, MD, MS7. P4325 - Real World Characteristics and Treatment Patterns of Patients With Crohn’s Disease (CD) Treated With Risankizumab: A US Claims Database Study, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA; 2GI Alliance, Baton Rouge, LA; 3Houston Methodist-Weill Cornell, Houston, TX; 4AbbVie, Edwardsville, IL; 5AbbVie, Mettawa, IL; 6AbbVie, Inc., Scottsdale, AZ; 7Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, Lebanon, NH
Introduction: Risankizumab (RZB), an interleukin-23 p19-specific humanized monoclonal antibody, was approved by the United States (US) Food and Drug Administration (June 2022) for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe Crohn’s disease (CD). Here, we describe the characteristics and initial treatment patterns of patients with CD in the US who have been treated with RZB.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study was conducted from June 2022 to January 2024 using US insurance claims data from the Merative MarketScan database. Eligible patients were ≥18 years of age, had a diagnosis of CD (at least 1 inpatient or 2 outpatient claims), received 600 mg intravenous RZB induction, and were continuously enrolled in pharmacy and medical benefits for 6 months prior to (baseline) and 6 months (follow-up) after the first RZB claim. Patient demographics, disease characteristics, treatment history, and RZB treatment patterns are described.
Results: A total of 543 eligible patients were identified (average age 39.8 years [range 18-80]; 54.9% female) (Table). The greatest proportion of patients had ileal colonic disease (29.3%), followed by ileal disease (26.0%), and colonic disease (14.9%); disease location was unspecified for 29.8% of patients. During baseline, 9.2% and 7.4% of patients had claims for fistulizing disease and stricturing disease, respectively, and 10.3% of patients had undergone surgery for CD. Most patients (80.9%) had prior exposure to advanced therapy (34.3% with prior exposure to 1 advanced therapy, 19.9% to 2, and 26.7% to ≥3) (Figure) and most had previously used an anti-tumor necrosis factor agent (63.2%). At the initiation of RZB induction, 8.7% of patients were using an immunomodulator, 76.6% of whom were using a thiopurine, and 41.1% were using systemic steroids. Over 90% of patients (490/543) received a RZB maintenance dose following induction, and 95.7% of these patients received the 360 mg RZB maintenance dose.
Discussion: Since FDA approval, real-world evidence demonstrates that most patients who received induction with RZB also received RZB maintenance dosing following induction, and nearly 1 out of every 5 patients who started RZB were naïve to prior treatment with an advanced therapy. Most patient demographics and disease characteristic reported to date are consistent with the phase 3 RZB clinical trial program.. Future analyses will evaluate longer-term outcomes, including the impact of RZB treatment on steroid utilization.

Figure: Figure. Prior Exposure to Advanced Therapy
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Gil Y. Melmed: AbbVie – Consultant. Arena Biopharmaceuticals – Consultant. Boehringer-Ingelheim – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb-Celgene – Consultant. Dieta – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant. Genentech – Consultant. Gilead – Consultant. Janssen Immunology – Consultant. Oshi Health – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Prometheus Labs – Consultant. Samsung Bioepis – Consultant. Shionogi – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant. Techlab – Consultant. Viatris – Consultant.
Casey Chapman: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – Speakers Bureau. El Lilly and Company – Consultant. Janssen – Speakers Bureau. Medtronic – Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau.
Bincy P. Abraham: AbbVie – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Celltrion – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Fresenius Kabi – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Medtronic – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Prometheus – Consultant. Samsung Bioepis – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Speakers Bureau.
Jenny Griffith: AbbVie – Employee, Stock Options, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Nidhi Shukla: AbbVie – Independent Contractor, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Javier Zambrano: AbbVie – Employee, Stock Options.
Brooke Kim: AbbVie – Employee.
Tianzhou Yu: AbbVie – Fellowship sponsored by the company.
Corey Siegel: Abbvie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speaker for CME activities. BMS – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Boomerang – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Buhlman – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speaker for CME activities. Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Napo pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaker for CME activities. Prometheus Biosciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Prometheus Labs – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Roivant – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, speaker for CME activities. Trellus Health – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant.
Gil Y. Melmed, MD1, Casey Chapman, MD2, Bincy P. Abraham, MD, MS, FACG3, Jenny Griffith, PharmD4, Nidhi Shukla, PhD, MBA5, Javier A. Zambrano, MD6, Brooke Kim, RN, BSN, MS5, Tianzhou Yu, PhD, MS, MPH5, Corey A. Siegel, MD, MS7. P4325 - Real World Characteristics and Treatment Patterns of Patients With Crohn’s Disease (CD) Treated With Risankizumab: A US Claims Database Study, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
