Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P4409 - Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis Triggered by Secukinumab: Insights Into IL-17 Pathway Complications
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- RP
Rahul Patel, DO
Jefferson Health
Washington Township, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Rahul Patel, DO1, Joshua Soliman, DO1, Sanket Patel, DO2
1Jefferson Health, Washington Township, NJ; 2Virtua Health System, Voorhees, NJ
Introduction: Secukinumab, an anti-IL-17A agent used in treating psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis, has a poorly understood pathophysiologic role in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). We present a case of severe acute ulcerative colitis after treatment with secukinumab.
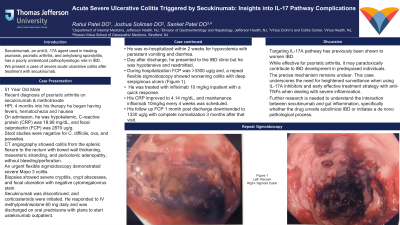
Case Description/Methods: A 51-year-old male with a recent diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis on secukinumab and methotrexate presented 4 months into his treatment course with hematochezia, nausea, and fevers. He had an unremarkable colonoscopy 7 years prior. On arrival, he was hypokalemic, C-reactive protein (CRP) was 18.98 mg/dL, and fecal calprotectin (FCP) was 2870 ug/g. Stool studies were negative for C. difficile, ova, and parasites. CT angiography showed colitis from the splenic flexure to the rectum with bowel wall thickening, mesenteric stranding, and pericolonic adenopathy, without bleeding/perforation. An urgent flexible sigmoidoscopy demonstrated severe Mayo 3 colitis. Biopsies showed severe cryptitis, crypt abscesses, and focal ulceration with negative cytomegalovirus stain. Secukinumab was discontinued, and corticosteroids were initiated. He responded to IV methylprednisolone 60 mg daily and was discharged on oral prednisone with plans to start ustekinumab outpatient. He was re-hospitalized within 2 weeks for hypovolemia with persistent vomiting and diarrhea. Day after discharge, he presented to the IBD clinic but he was hypotensive and readmitted. During hospitalization FCP was >3300 ug/g and, a repeat flexible sigmoidoscopy showed worsening colitis with deep serpiginous ulcers (figure 1). He was treated with infliximab 10 mg/kg inpatient with a quick response. His CRP improved to 4.14 mg/dL, and maintenance infliximab 10mg/kg every 4 weeks was scheduled. His follow up FCP 1 month post discharge downtrended to 1330 ug/g with complete normalization 3 months after that visit.
Discussion: Targeting IL-17A pathway has previously been shown to worsen IBD. While effective for psoriatic arthritis, it may paradoxically contribute to IBD development in predisposed individuals. The precise mechanism remains unclear. This case underscores the need for heightened surveillance when using IL-17A inhibitors and early effective treatment strategy with anti-TNFs when dealing with severe inflammation. Further research is needed to understand the interaction between secukinumab and gut inflammation, specifically whether the drug unveils subclinical IBD or initiates a de novo pathological process.

Disclosures:
Rahul Patel, DO1, Joshua Soliman, DO1, Sanket Patel, DO2. P4409 - Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis Triggered by Secukinumab: Insights Into IL-17 Pathway Complications, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Jefferson Health, Washington Township, NJ; 2Virtua Health System, Voorhees, NJ
Introduction: Secukinumab, an anti-IL-17A agent used in treating psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis, has a poorly understood pathophysiologic role in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). We present a case of severe acute ulcerative colitis after treatment with secukinumab.
Case Description/Methods: A 51-year-old male with a recent diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis on secukinumab and methotrexate presented 4 months into his treatment course with hematochezia, nausea, and fevers. He had an unremarkable colonoscopy 7 years prior. On arrival, he was hypokalemic, C-reactive protein (CRP) was 18.98 mg/dL, and fecal calprotectin (FCP) was 2870 ug/g. Stool studies were negative for C. difficile, ova, and parasites. CT angiography showed colitis from the splenic flexure to the rectum with bowel wall thickening, mesenteric stranding, and pericolonic adenopathy, without bleeding/perforation. An urgent flexible sigmoidoscopy demonstrated severe Mayo 3 colitis. Biopsies showed severe cryptitis, crypt abscesses, and focal ulceration with negative cytomegalovirus stain. Secukinumab was discontinued, and corticosteroids were initiated. He responded to IV methylprednisolone 60 mg daily and was discharged on oral prednisone with plans to start ustekinumab outpatient. He was re-hospitalized within 2 weeks for hypovolemia with persistent vomiting and diarrhea. Day after discharge, he presented to the IBD clinic but he was hypotensive and readmitted. During hospitalization FCP was >3300 ug/g and, a repeat flexible sigmoidoscopy showed worsening colitis with deep serpiginous ulcers (figure 1). He was treated with infliximab 10 mg/kg inpatient with a quick response. His CRP improved to 4.14 mg/dL, and maintenance infliximab 10mg/kg every 4 weeks was scheduled. His follow up FCP 1 month post discharge downtrended to 1330 ug/g with complete normalization 3 months after that visit.
Discussion: Targeting IL-17A pathway has previously been shown to worsen IBD. While effective for psoriatic arthritis, it may paradoxically contribute to IBD development in predisposed individuals. The precise mechanism remains unclear. This case underscores the need for heightened surveillance when using IL-17A inhibitors and early effective treatment strategy with anti-TNFs when dealing with severe inflammation. Further research is needed to understand the interaction between secukinumab and gut inflammation, specifically whether the drug unveils subclinical IBD or initiates a de novo pathological process.

Figure: Figure 1: Flexible Sigmoidoscopy demonstrating deep serpiginous ulcers with mucosal friability.
(A) Rectum
(B) Sigmoid Colon
(A) Rectum
(B) Sigmoid Colon
Disclosures:
Rahul Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joshua Soliman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sanket Patel: Abbvie – Speakers Bureau. BMS – Speakers Bureau. Eli Lilly – Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Speakers Bureau.
Rahul Patel, DO1, Joshua Soliman, DO1, Sanket Patel, DO2. P4409 - Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis Triggered by Secukinumab: Insights Into IL-17 Pathway Complications, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
