Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P4467 - Role of Artificial Intelligence to Assess Malignant Potential in Intraductal - Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Amna Iqbal, MD
University of Toledo Medical Center
Toledo, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Amna Iqbal, MD1, Iqra Arshad, MD2, Rehmat Ullah Awan, MD3, Zohaib Ahmed, MD1, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD4, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD5, Umar Hayat, MD6, Babu Mohan, MD7, Shailendra Singh, MD3, Yaseen Alastal, MD1, Hafiz Muhammad Sharjeel Arshad, MD8
1University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 2SSM Health Saint Louis University Hospital, St. Louis, MO; 3West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV; 4The University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS; 5University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 6Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 7Orlando Gastroenterology PA, Orlando, FL; 8Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IL
Introduction: All Pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) have a malignancy risk which varies significantly based on which ducts are involved, the IPMN size, growth rate, the presence of mural nodules or solid component and cytology on fluid aspiration. There is emerging role of AI in improving identification of premalignant pancreatic lesions to avoid misdiagnosis, over-diagnosis, and unnecessary surgical intervention. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess role of AI to identify malignant potential in IPMN.
Methods: A systematic search of multiple databases was undertaken through May 25, 2024 to identify relevant studies comparing use of AI in IPMN. We performed a meta-analysis of the included studies using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (Biostat, Englewood, USA). The random-effects model was used to calculate the weighted pooled risk with the corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) of our desired outcome.
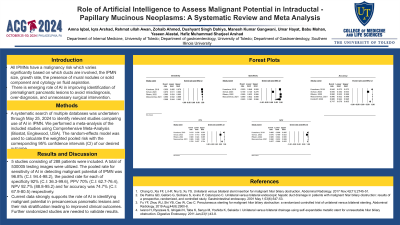
Results: 5 studies consisting of 288 patients were included. A total of 530005 testing images were utilized. The pooled rate for sensitivity of AI in detecting malignant potential of IPMN was 96.8% (C.I: 94.4-98.2), the pooled rate for each of specificity 92% (C.I: 36.3-99.6), PPV 70% (C.I: 62.7-76.4), NPV 92.7% (88.8-95.2) and for accuracy was 74.7% (C.I: 67.9-80.5) respectively.
Discussion: IPMNs are divided into main-duct IPMN (MD-IPMN), branch-duct (BD-IPMN) and mixed-type IPMN. Current standard of care for the diagnosis and classification of pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs) involves cross-sectional imaging studies and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and, when indicated, EUS-guided fine needle aspiration and cyst fluid analysis. However, this is suboptimal for the identification and risk stratification of PCLs, with accuracy of only 65–75% for detecting mucinous PCLs. Careful surveillance of patients with IPMN may therefore lead to early detection of pancreatic cancer. Joanna et al. developed EUS-confocal laser endomicroscopy based AI algorithms to risk-stratify BD-IPMNs (predict advanced neoplasia versus low- grade dysplasia), AI models showed higher accuracy (82%) for the detection of high-grade dysplasia or adenocarcinoma than the AGA guidelines (68.6%) and Fukuoka criteria (74.3%). Current data strongly supports the role of AI in identifying malignant potential in precancerous pancreatic lesions and their risk stratification leading to improved clinical outcomes. Further randomized studies are needed to validate results.

Disclosures:
Amna Iqbal, MD1, Iqra Arshad, MD2, Rehmat Ullah Awan, MD3, Zohaib Ahmed, MD1, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD4, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD5, Umar Hayat, MD6, Babu Mohan, MD7, Shailendra Singh, MD3, Yaseen Alastal, MD1, Hafiz Muhammad Sharjeel Arshad, MD8. P4467 - Role of Artificial Intelligence to Assess Malignant Potential in Intraductal - Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 2SSM Health Saint Louis University Hospital, St. Louis, MO; 3West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV; 4The University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS; 5University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 6Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 7Orlando Gastroenterology PA, Orlando, FL; 8Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IL
Introduction: All Pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) have a malignancy risk which varies significantly based on which ducts are involved, the IPMN size, growth rate, the presence of mural nodules or solid component and cytology on fluid aspiration. There is emerging role of AI in improving identification of premalignant pancreatic lesions to avoid misdiagnosis, over-diagnosis, and unnecessary surgical intervention. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess role of AI to identify malignant potential in IPMN.
Methods: A systematic search of multiple databases was undertaken through May 25, 2024 to identify relevant studies comparing use of AI in IPMN. We performed a meta-analysis of the included studies using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (Biostat, Englewood, USA). The random-effects model was used to calculate the weighted pooled risk with the corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) of our desired outcome.
Results: 5 studies consisting of 288 patients were included. A total of 530005 testing images were utilized. The pooled rate for sensitivity of AI in detecting malignant potential of IPMN was 96.8% (C.I: 94.4-98.2), the pooled rate for each of specificity 92% (C.I: 36.3-99.6), PPV 70% (C.I: 62.7-76.4), NPV 92.7% (88.8-95.2) and for accuracy was 74.7% (C.I: 67.9-80.5) respectively.
Discussion: IPMNs are divided into main-duct IPMN (MD-IPMN), branch-duct (BD-IPMN) and mixed-type IPMN. Current standard of care for the diagnosis and classification of pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs) involves cross-sectional imaging studies and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and, when indicated, EUS-guided fine needle aspiration and cyst fluid analysis. However, this is suboptimal for the identification and risk stratification of PCLs, with accuracy of only 65–75% for detecting mucinous PCLs. Careful surveillance of patients with IPMN may therefore lead to early detection of pancreatic cancer. Joanna et al. developed EUS-confocal laser endomicroscopy based AI algorithms to risk-stratify BD-IPMNs (predict advanced neoplasia versus low- grade dysplasia), AI models showed higher accuracy (82%) for the detection of high-grade dysplasia or adenocarcinoma than the AGA guidelines (68.6%) and Fukuoka criteria (74.3%). Current data strongly supports the role of AI in identifying malignant potential in precancerous pancreatic lesions and their risk stratification leading to improved clinical outcomes. Further randomized studies are needed to validate results.

Figure: Figure1. Forest plots demonstrating role of AI in detecting malignant potential of IPMN.
Disclosures:
Amna Iqbal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iqra Arshad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rehmat Ullah Awan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zohaib Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dushyant Dahiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manesh Kumar Gangwani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umar Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Babu Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shailendra Singh: Apollo Endosurgery – Consultant. Boston Scientific – Consultant. Fujifilm Endoscopy – Consultant.
Yaseen Alastal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hafiz Muhammad Sharjeel Arshad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amna Iqbal, MD1, Iqra Arshad, MD2, Rehmat Ullah Awan, MD3, Zohaib Ahmed, MD1, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD4, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD5, Umar Hayat, MD6, Babu Mohan, MD7, Shailendra Singh, MD3, Yaseen Alastal, MD1, Hafiz Muhammad Sharjeel Arshad, MD8. P4467 - Role of Artificial Intelligence to Assess Malignant Potential in Intraductal - Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms: A Systematic Review and Meta Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
