Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P4550 - Dual Endoscopic Myotomy for Concurrent Achalasia and Esophageal Diverticulum: An Innovative Approach
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
.jpg)
Mark Tawfik, DO
Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health
Staten Island, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Mark Tawfik, DO1, Angelica Rozenfeld, BA2, Hassan Al Moussawi, MD1, Sherif Andrawes, MD1
1Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY; 2Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine, Staten Island, NY
Introduction: Achalasia is a rare esophageal motility disorder marked by impaired relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter and lack of peristalsis, often presenting with symptoms such as dysphagia, regurgitation, and nocturnal choking. Pulsion diverticula may form due to increased intraluminal pressure, leading to herniation of the esophageal wall at weak points. Epiphrenic diverticula is a rare type of false diverticula occurring in the distal esophagus and are almost always associated with an underlying motility disorder like achalasia. Symptomatic achalasia and diverticula necessitate intervention, traditionally through surgical methods or, more recently, the minimally invasive per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM)
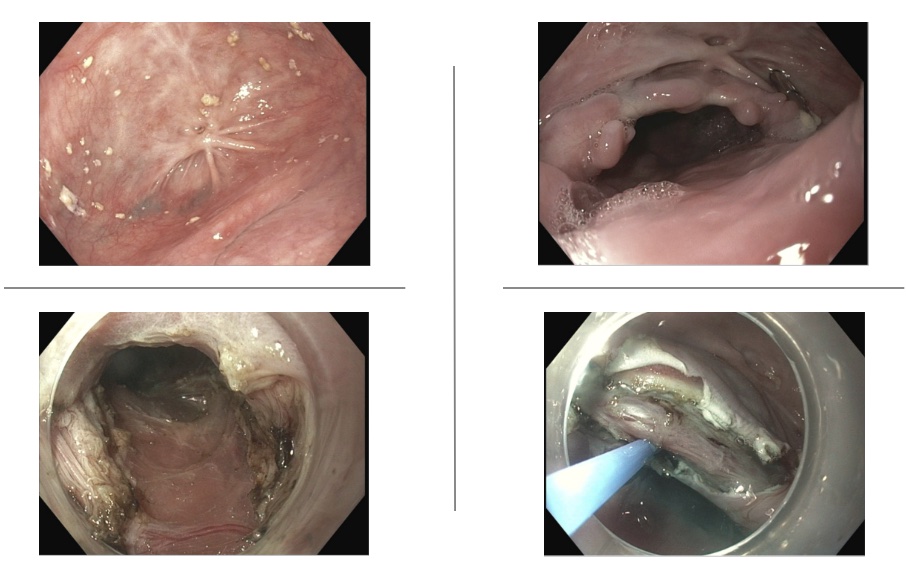
Case Description/Methods: A 65-year-old female presented to the gastroenterology service with worsening dysphagia to solids and liquids. She had recently received an outpatient diagnosis of achalasia, spastic type. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) upon admission revealed a dilated proximal esophagus with distal contraction above the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ), along with residual liquid food consistent with achalasia. Additionally, an epiphrenic diverticulum was identified, with a diverticular edge obstructing the esophagus and impeding the passage of food into the stomach (Figure 1).
The decision was made to perform both an Esophageal Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (E-POEM) to target the achalasia and a Diverticular Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (D-POEM) to target the diverticulum obstructing the esophagus (Figure 1). Following the procedure, the patient experienced relief, and her diet was gradually advanced. A one-week follow-up revealed persistent relief, and the patient was able to tolerate solid food without any dysphagia.
Discussion: Esophageal POEM (E-POEM) addresses achalasia. A mucosal incision is made to create a submucosal tunnel, allowing for the selective cutting of the circular muscle layer while preserving the longitudinal muscle layer. This effectively reduces the LES pressure, alleviating the outflow obstruction at the gastroesophageal junction.
Diverticular POEM (D-POEM) targets diverticula. It involves creating a submucosal tunnel followed by myotomy at the side of the diverticulum to facilitate opening and drainage, thereby relieving the obstruction and associated symptoms. To treat our case, we approached it in a unique way by performing two POEM’s: an E-POEM and D-POEM. Further research is warranted to assess long term outcomes of doing these two procedures simultaneously.
Disclosures:
Mark Tawfik, DO1, Angelica Rozenfeld, BA2, Hassan Al Moussawi, MD1, Sherif Andrawes, MD1. P4550 - Dual Endoscopic Myotomy for Concurrent Achalasia and Esophageal Diverticulum: An Innovative Approach, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Mark Tawfik, DO1, Angelica Rozenfeld, BA2, Hassan Al Moussawi, MD1, Sherif Andrawes, MD1
1Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY; 2Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine, Staten Island, NY
Introduction: Achalasia is a rare esophageal motility disorder marked by impaired relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter and lack of peristalsis, often presenting with symptoms such as dysphagia, regurgitation, and nocturnal choking. Pulsion diverticula may form due to increased intraluminal pressure, leading to herniation of the esophageal wall at weak points. Epiphrenic diverticula is a rare type of false diverticula occurring in the distal esophagus and are almost always associated with an underlying motility disorder like achalasia. Symptomatic achalasia and diverticula necessitate intervention, traditionally through surgical methods or, more recently, the minimally invasive per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM)
Case Description/Methods: A 65-year-old female presented to the gastroenterology service with worsening dysphagia to solids and liquids. She had recently received an outpatient diagnosis of achalasia, spastic type. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) upon admission revealed a dilated proximal esophagus with distal contraction above the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ), along with residual liquid food consistent with achalasia. Additionally, an epiphrenic diverticulum was identified, with a diverticular edge obstructing the esophagus and impeding the passage of food into the stomach (Figure 1).
The decision was made to perform both an Esophageal Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (E-POEM) to target the achalasia and a Diverticular Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (D-POEM) to target the diverticulum obstructing the esophagus (Figure 1). Following the procedure, the patient experienced relief, and her diet was gradually advanced. A one-week follow-up revealed persistent relief, and the patient was able to tolerate solid food without any dysphagia.
Discussion: Esophageal POEM (E-POEM) addresses achalasia. A mucosal incision is made to create a submucosal tunnel, allowing for the selective cutting of the circular muscle layer while preserving the longitudinal muscle layer. This effectively reduces the LES pressure, alleviating the outflow obstruction at the gastroesophageal junction.
Diverticular POEM (D-POEM) targets diverticula. It involves creating a submucosal tunnel followed by myotomy at the side of the diverticulum to facilitate opening and drainage, thereby relieving the obstruction and associated symptoms. To treat our case, we approached it in a unique way by performing two POEM’s: an E-POEM and D-POEM. Further research is warranted to assess long term outcomes of doing these two procedures simultaneously.

Figure: FIgure 1: Top left: Epiphrenic diverticulum with achalasia. Bottom Left: E-POEM. bottom right: D-POEM. Top right: Esophageal lumen now open
Disclosures:
Mark Tawfik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Angelica Rozenfeld indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hassan Al Moussawi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sherif Andrawes indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mark Tawfik, DO1, Angelica Rozenfeld, BA2, Hassan Al Moussawi, MD1, Sherif Andrawes, MD1. P4550 - Dual Endoscopic Myotomy for Concurrent Achalasia and Esophageal Diverticulum: An Innovative Approach, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

