Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P4735 - Effective Management of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Nivolumab: A Case Report
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Chineye Brenda Amuchi, MD, MPH
Beth Israel Lahey Health
Burlington, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Chineye Brenda Amuchi, MD, MPH, James Doolin, MD, Carmi Punzalan, MD
Beth Israel Lahey Health, Burlington, MA
Introduction: Historically, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treatment has relied on surgical interventions, liver transplantation, local ablative therapies, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. However, the emergence of immune checkpoint blockade has revolutionized HCC management. Among these approaches, targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway has gained considerable attention. This case report presents an advanced HCC successfully treated with nivolumab, highlighting its potential efficacy.
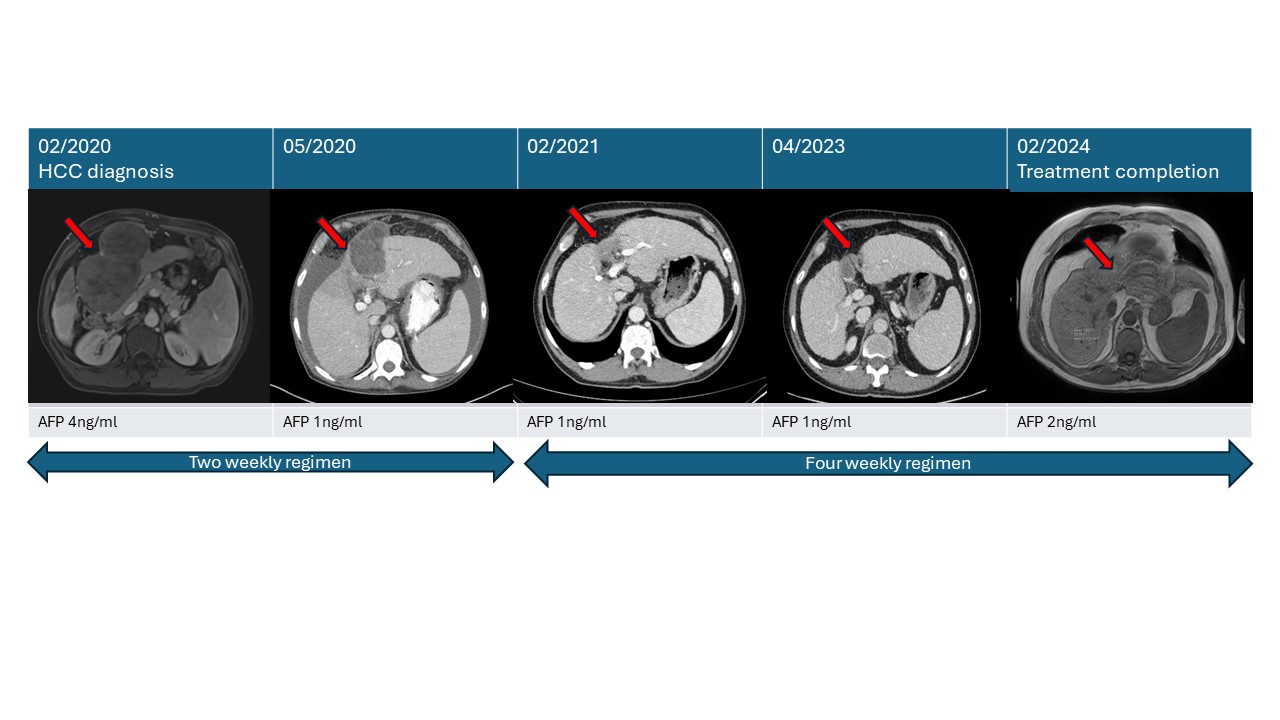
Case Description/Methods: A 59-year-old male with a history of chronic hepatitis B and liver cirrhosis presented with advanced HCC. Diagnosed with hepatitis B in his 20s, he developed cirrhosis in 2012, confirmed by imaging that revealed splenomegaly and a nodular liver contour. He had no follow-up until 2019 when he presented with abdominal pain. MRI showed a bilobed mass in the medial left hepatic lobe with hyperenhancement, washout, and enhancing capsule consistent with an LI-RADS-5 lesion, along with an enteric fistula into one of the tumors. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level was 4 ng/ml. Biopsy confirmed HCC.
Nivolumab therapy was commenced at 240 mg intravenously (IV) every two weeks for eight doses. A follow-up CT scan in May showed a reduction in the size of the bilobed mass to 5.2 by 7.8 cm, representing a treatment response. The dose was then adjusted to 480 mg IV every four weeks between May 2020 to February 2023. Follow-up imaging continued to show improvement in the tumor size. Imaging in February 2024 revealed no liver lesions. The patient has been off nivolumab for a year with no recurrence of liver masses. His latest MRI in March 2024 confirmed the resolution of HCC, with AFP levels at 1 ng/mL. He continues entecavir for hepatitis B treatment.
Discussion: This case illustrates the potential of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody, in treating advanced HCC. Nivolumab enhances T-cell-mediated immune responses against tumor cells, significantly advancing HCC therapy. The patient's initial presentation with large hepatic lesions and an enteric fistula posed significant therapeutic challenges, necessitating innovative approaches. In this case, Nivolumab's efficacy in reducing tumor burden and achieving sustained remission is noteworthy. This case reinforces the promise of immune checkpoint inhibitors in transforming the landscape of HCC treatment, offering hope for improved outcomes in patients with advanced disease.
Disclosures:
Chineye Brenda Amuchi, MD, MPH, James Doolin, MD, Carmi Punzalan, MD. P4735 - Effective Management of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Nivolumab: A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Beth Israel Lahey Health, Burlington, MA
Introduction: Historically, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treatment has relied on surgical interventions, liver transplantation, local ablative therapies, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. However, the emergence of immune checkpoint blockade has revolutionized HCC management. Among these approaches, targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway has gained considerable attention. This case report presents an advanced HCC successfully treated with nivolumab, highlighting its potential efficacy.
Case Description/Methods: A 59-year-old male with a history of chronic hepatitis B and liver cirrhosis presented with advanced HCC. Diagnosed with hepatitis B in his 20s, he developed cirrhosis in 2012, confirmed by imaging that revealed splenomegaly and a nodular liver contour. He had no follow-up until 2019 when he presented with abdominal pain. MRI showed a bilobed mass in the medial left hepatic lobe with hyperenhancement, washout, and enhancing capsule consistent with an LI-RADS-5 lesion, along with an enteric fistula into one of the tumors. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level was 4 ng/ml. Biopsy confirmed HCC.
Nivolumab therapy was commenced at 240 mg intravenously (IV) every two weeks for eight doses. A follow-up CT scan in May showed a reduction in the size of the bilobed mass to 5.2 by 7.8 cm, representing a treatment response. The dose was then adjusted to 480 mg IV every four weeks between May 2020 to February 2023. Follow-up imaging continued to show improvement in the tumor size. Imaging in February 2024 revealed no liver lesions. The patient has been off nivolumab for a year with no recurrence of liver masses. His latest MRI in March 2024 confirmed the resolution of HCC, with AFP levels at 1 ng/mL. He continues entecavir for hepatitis B treatment.
Discussion: This case illustrates the potential of nivolumab, an anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody, in treating advanced HCC. Nivolumab enhances T-cell-mediated immune responses against tumor cells, significantly advancing HCC therapy. The patient's initial presentation with large hepatic lesions and an enteric fistula posed significant therapeutic challenges, necessitating innovative approaches. In this case, Nivolumab's efficacy in reducing tumor burden and achieving sustained remission is noteworthy. This case reinforces the promise of immune checkpoint inhibitors in transforming the landscape of HCC treatment, offering hope for improved outcomes in patients with advanced disease.

Figure: Images showing HCC progression
Disclosures:
Chineye Brenda Amuchi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
James Doolin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Carmi Punzalan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chineye Brenda Amuchi, MD, MPH, James Doolin, MD, Carmi Punzalan, MD. P4735 - Effective Management of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Nivolumab: A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
