Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P4866 - Severe Neurological Impairments Due to Marchiafava-Bignami Disease in the Setting of Chronic and Continued Alcohol Abuse and Malnutrition
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- MH
Michael Harring, MD
St. Luke's University Health Network
Bethlehem, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Michael Harring, MD, Vishal Patel, MD
St. Luke's University Health Network, Bethlehem, PA
Introduction: Marchiafava-Bignami (MBD) disease is a rare disorder characterized by demyelination and necrosis of the corpus callosum and nearby subcortical white matter. Symptoms include dementia, impaired gait, dysarthria, ataxia and seizures. The exact etiology is not completely known, but postulated to be due to a combination of direct neurotoxicity from alcohol as well as B vitamin deficiencies. Above all, alcohol cessation is paramount to significant recovery, and similar to other conditions supplementation with folate and vitamin B complex can lead to improvement in symptoms.
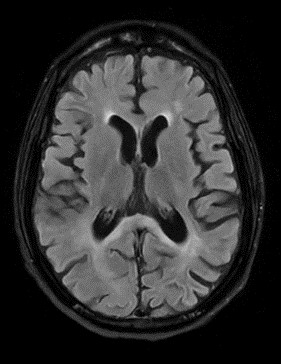
Case Description/Methods: A 44 year old male with history of GERD, tobacco use and cirrhosis due to chronic alcohol use decompensated by ascites presented to the emergency department due to hematemesis at which time he was found to have hemoglobin of 5.6 g/dL. Prior to hospitalization he underwent MRI brain due to difficulty with ambulation, which revealed T2 prolongation/FLAIR signal hyperintensity centered along the splenium of the corpus callosum consistent with Marchiafava-Bignami disease with cerebral volume loss (Figure 1). He was then seen in hepatology clinic, at which time patient reported drinking a 40 oz sized beer as well as well as 2-3 shots of liquor daily for multiple decades. He had developed progressively worsening proximal upper and lower motor dysfunction leading to a persistent wheelchair requirement. Unfortunately, he refused assistance focused towards alcohol cessation leading to recurrence of alcohol abuse.
Discussion: Of utmost importance in Marchiafava-Bignami disease is early detection and absolute cessation of alcohol intake. Many patients do in fact recover with B vitamin supplementation, but this unfortunately is not always the case and sometimes only to a variable degree. Typically, lesions include edematous changes involving the corpus callosum symmetrically with a lesion of increased signal on T2-weighted imaging/FLAIR, but this can change based on the acuity of the condition with atrophy of the affected area developing as the disease becomes chronic. Patients can make significant recovery through early identification of the condition as well as multimodal treatment strategies including vitamin supplementation, behavioral therapy to assist with alcohol cessation and therapy directed towards improvement in neuromuscular complications.
Disclosures:
Michael Harring, MD, Vishal Patel, MD. P4866 - Severe Neurological Impairments Due to Marchiafava-Bignami Disease in the Setting of Chronic and Continued Alcohol Abuse and Malnutrition, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
St. Luke's University Health Network, Bethlehem, PA
Introduction: Marchiafava-Bignami (MBD) disease is a rare disorder characterized by demyelination and necrosis of the corpus callosum and nearby subcortical white matter. Symptoms include dementia, impaired gait, dysarthria, ataxia and seizures. The exact etiology is not completely known, but postulated to be due to a combination of direct neurotoxicity from alcohol as well as B vitamin deficiencies. Above all, alcohol cessation is paramount to significant recovery, and similar to other conditions supplementation with folate and vitamin B complex can lead to improvement in symptoms.
Case Description/Methods: A 44 year old male with history of GERD, tobacco use and cirrhosis due to chronic alcohol use decompensated by ascites presented to the emergency department due to hematemesis at which time he was found to have hemoglobin of 5.6 g/dL. Prior to hospitalization he underwent MRI brain due to difficulty with ambulation, which revealed T2 prolongation/FLAIR signal hyperintensity centered along the splenium of the corpus callosum consistent with Marchiafava-Bignami disease with cerebral volume loss (Figure 1). He was then seen in hepatology clinic, at which time patient reported drinking a 40 oz sized beer as well as well as 2-3 shots of liquor daily for multiple decades. He had developed progressively worsening proximal upper and lower motor dysfunction leading to a persistent wheelchair requirement. Unfortunately, he refused assistance focused towards alcohol cessation leading to recurrence of alcohol abuse.
Discussion: Of utmost importance in Marchiafava-Bignami disease is early detection and absolute cessation of alcohol intake. Many patients do in fact recover with B vitamin supplementation, but this unfortunately is not always the case and sometimes only to a variable degree. Typically, lesions include edematous changes involving the corpus callosum symmetrically with a lesion of increased signal on T2-weighted imaging/FLAIR, but this can change based on the acuity of the condition with atrophy of the affected area developing as the disease becomes chronic. Patients can make significant recovery through early identification of the condition as well as multimodal treatment strategies including vitamin supplementation, behavioral therapy to assist with alcohol cessation and therapy directed towards improvement in neuromuscular complications.

Figure: Figure 1: MRI T2/FLAIR image showing asymmetric corpus callosum lesion
Disclosures:
Michael Harring indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vishal Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Harring, MD, Vishal Patel, MD. P4866 - Severe Neurological Impairments Due to Marchiafava-Bignami Disease in the Setting of Chronic and Continued Alcohol Abuse and Malnutrition, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

