Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Obesity
P4888 - Tirzepatide and MASLD: Real-World Outcomes in Patients With Overweight and Obesity
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Maria A Espinosa, MD
Mayo Clinic
Rochester, MN
Presenting Author(s)
Maria A Espinosa, MD1, Sima Fansa, MD1, Diego Anazco, MD1, Wissam Ghusn, MD2, Tama Elif, MD3, Lizeth Cifuentes, MD4, Campos Alejandro, MD2, Rene Rivera, MD3, Maria D Hurtado, MD, PhD5, Andres Acosta, MD, PhD1
1Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 2Boston University, Boston, MA; 3Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL; 4University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA; 5Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, MN
Introduction: Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) is a common obesity-associated comorbidity. Tirzepatide, a dual gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP)/ Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist (GLP-1) receptor co-agonist, has demonstrated effectiveness in glycemic control and weight loss outcomes. More recently, it has also shown favorable results on fibrosis and inflammation endpoints in phase 2 clinical trials for MASLD. We aimed to investigate the effect of tirzepatide on liver enzymes and liver fibrosis scores after 12 months of tirzepatide treatment in individuals with MASLD and overweight or obesity in real-world setting.
Methods: This is a multi-center retrospective study of adults with MASLD treated with tirzepatide for weight loss or glycemic control. We excluded patients taking tirzepatide for < 3 months, taking other anti-obesity medications, and those with a history of bariatric surgery, or active malignancy. The primary outcome was changes in the Fib-4 score after 12 months of tirzepatide therapy. Secondary outcomes included changes in liver enzymes, NAFLD Fibrosis Score (NFS), and total body weight loss percentage (TBWL%). Data are presented as mean ± SD. Continuous endpoints were analyzed using paired t-tests.
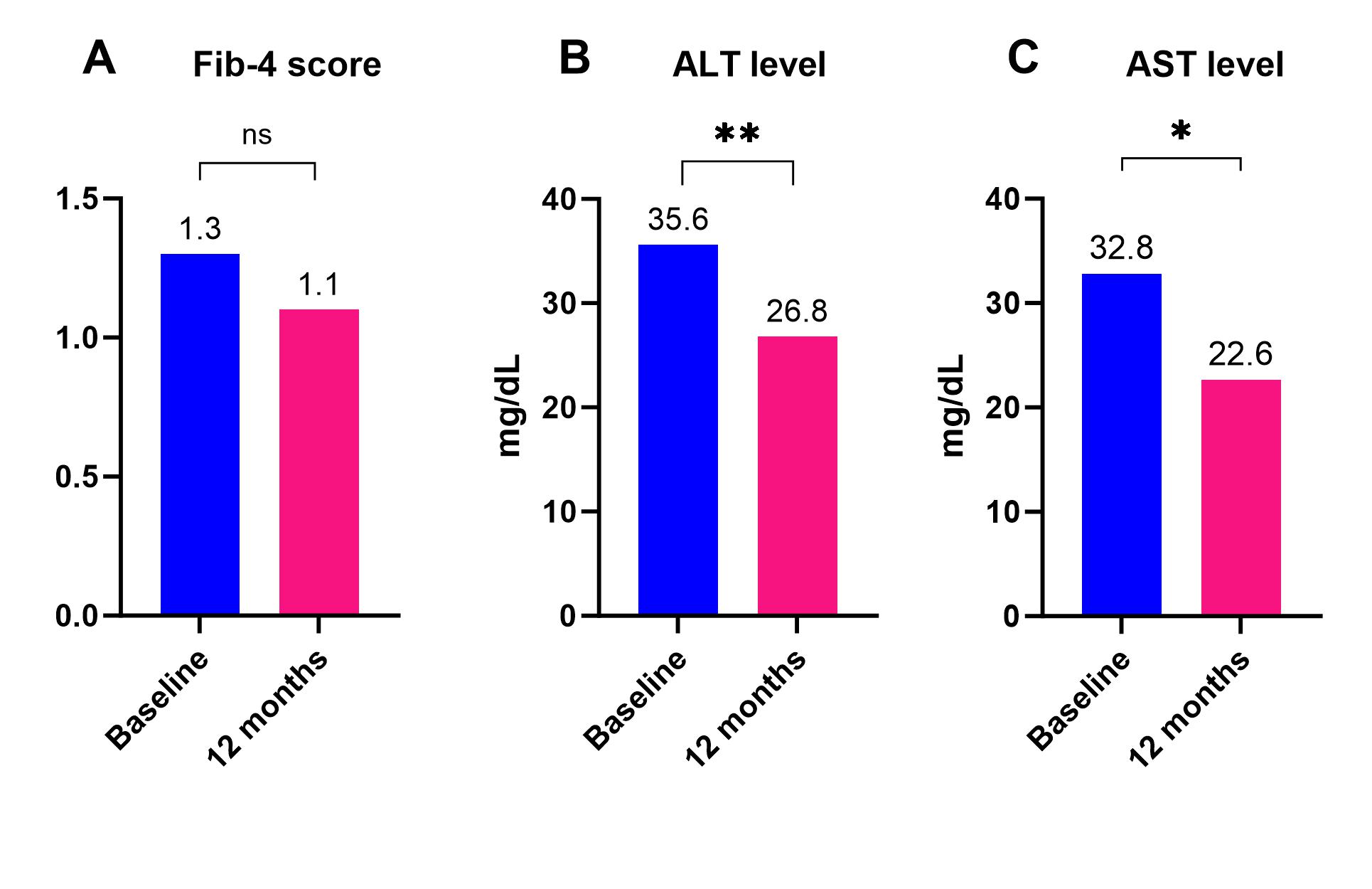
Results: We included 58 participants: 60.3% female, mean age 51.8± 12.6 years, BMI 39.1 ± 7.5 kg/m2, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (56.9%), Table 1. There was a non-significant decrease in the Fib-4 score at 12 months (n=29, mean diff. -0.2, 95%CI -0.7 to 0.4, p= 0.5, Figure 1A). Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) decreased significantly at 12 months with a mean reduction of 8.9 mg/dL (n=34; 95% CI: 3.6 to 14.1; p=0.002, Figure 1B) and 10.2 mg/dL (n=34; 95%CI 0.4 to 19.9; p= 0.04, Figure 1C), respectively. TBWL% at 12 months was 12.4± 1.5. After 12 months, the NFS remained stable in 18 patients (78.3%), improved in 3 (13%), and worsened in 2 (8.7%).
Discussion: In patients with MASLD, treatment with tirzepatide for 12 months was associated with decreased ALT and AST. Further studies are needed to assess the effects of tirzepatide on MASLD parameters.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Maria A Espinosa, MD1, Sima Fansa, MD1, Diego Anazco, MD1, Wissam Ghusn, MD2, Tama Elif, MD3, Lizeth Cifuentes, MD4, Campos Alejandro, MD2, Rene Rivera, MD3, Maria D Hurtado, MD, PhD5, Andres Acosta, MD, PhD1. P4888 - Tirzepatide and MASLD: Real-World Outcomes in Patients With Overweight and Obesity, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 2Boston University, Boston, MA; 3Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, FL; 4University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, PA; 5Mayo Clinic, Jacksonville, MN
Introduction: Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) is a common obesity-associated comorbidity. Tirzepatide, a dual gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP)/ Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist (GLP-1) receptor co-agonist, has demonstrated effectiveness in glycemic control and weight loss outcomes. More recently, it has also shown favorable results on fibrosis and inflammation endpoints in phase 2 clinical trials for MASLD. We aimed to investigate the effect of tirzepatide on liver enzymes and liver fibrosis scores after 12 months of tirzepatide treatment in individuals with MASLD and overweight or obesity in real-world setting.
Methods: This is a multi-center retrospective study of adults with MASLD treated with tirzepatide for weight loss or glycemic control. We excluded patients taking tirzepatide for < 3 months, taking other anti-obesity medications, and those with a history of bariatric surgery, or active malignancy. The primary outcome was changes in the Fib-4 score after 12 months of tirzepatide therapy. Secondary outcomes included changes in liver enzymes, NAFLD Fibrosis Score (NFS), and total body weight loss percentage (TBWL%). Data are presented as mean ± SD. Continuous endpoints were analyzed using paired t-tests.
Results: We included 58 participants: 60.3% female, mean age 51.8± 12.6 years, BMI 39.1 ± 7.5 kg/m2, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (56.9%), Table 1. There was a non-significant decrease in the Fib-4 score at 12 months (n=29, mean diff. -0.2, 95%CI -0.7 to 0.4, p= 0.5, Figure 1A). Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) decreased significantly at 12 months with a mean reduction of 8.9 mg/dL (n=34; 95% CI: 3.6 to 14.1; p=0.002, Figure 1B) and 10.2 mg/dL (n=34; 95%CI 0.4 to 19.9; p= 0.04, Figure 1C), respectively. TBWL% at 12 months was 12.4± 1.5. After 12 months, the NFS remained stable in 18 patients (78.3%), improved in 3 (13%), and worsened in 2 (8.7%).
Discussion: In patients with MASLD, treatment with tirzepatide for 12 months was associated with decreased ALT and AST. Further studies are needed to assess the effects of tirzepatide on MASLD parameters.

Figure: Figure 1: Change in Fib-4 score, ALT, and AST from baseline to 12 months after treatment.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Maria A Espinosa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sima Fansa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Diego Anazco indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wissam Ghusn indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tama Elif indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lizeth Cifuentes indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Campos Alejandro indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rene Rivera indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maria D Hurtado indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andres Acosta: Amgen – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Busch Health – Consultant. Currax Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. General Mills – Consultant. Gila Therapeutics – Consultant. Nestle – Consultant. Phenomix Sciences Inc. – Intellectual Property/Patents. RareDiseases – Consultant. Rhythm pharmaceutical – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Satiogen Pharmaceutical – Grant/Research Support. Vivus Inc – Grant/Research Support.
Maria A Espinosa, MD1, Sima Fansa, MD1, Diego Anazco, MD1, Wissam Ghusn, MD2, Tama Elif, MD3, Lizeth Cifuentes, MD4, Campos Alejandro, MD2, Rene Rivera, MD3, Maria D Hurtado, MD, PhD5, Andres Acosta, MD, PhD1. P4888 - Tirzepatide and MASLD: Real-World Outcomes in Patients With Overweight and Obesity, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

