Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Practice Management
P4931 - Advancements in AI for Gastroenterology Education: An Assessment of OpenAI's GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 in MKSAP Question Interpretation
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Isha Samreen, MBBS, MPH
Hemet Global Medical Center
Murrieta, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Akash Patel, MD1, Isha Samreen, MBBS, MPH2, Imran Ahmed, MA3
1Eisenhower Medical Center, Riverside Community Hospital, Palm Desert, CA; 2Hemet Global Medical Center, Murrieta, CA; 3Burrell College of Osteopathic Medicine, Anaheim, CA
Introduction: The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in medical education represents a transformative shift, offering substantial support for residents preparing for board exams. This study evaluates and compares the accuracy of OpenAI's GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 language models in answering gastroenterology-related Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) from the widely used Medical Knowledge Self-Assessment Program (MKSAP) question bank. The MKSAP was chosen for its comprehensive, validated content and is widely regarded as the gold standard for board preparation.
Methods: We presented 126 MKSAP MCQs, covering eight key gastroenterology topics, to both GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models. The questions were further categorized into Diagnosis (N=54) and Management (N=72) types. Performance comparisons were made against the average accuracy of medical professional MKSAP users, reflecting the percentage of correct answers given by MKSAP users.
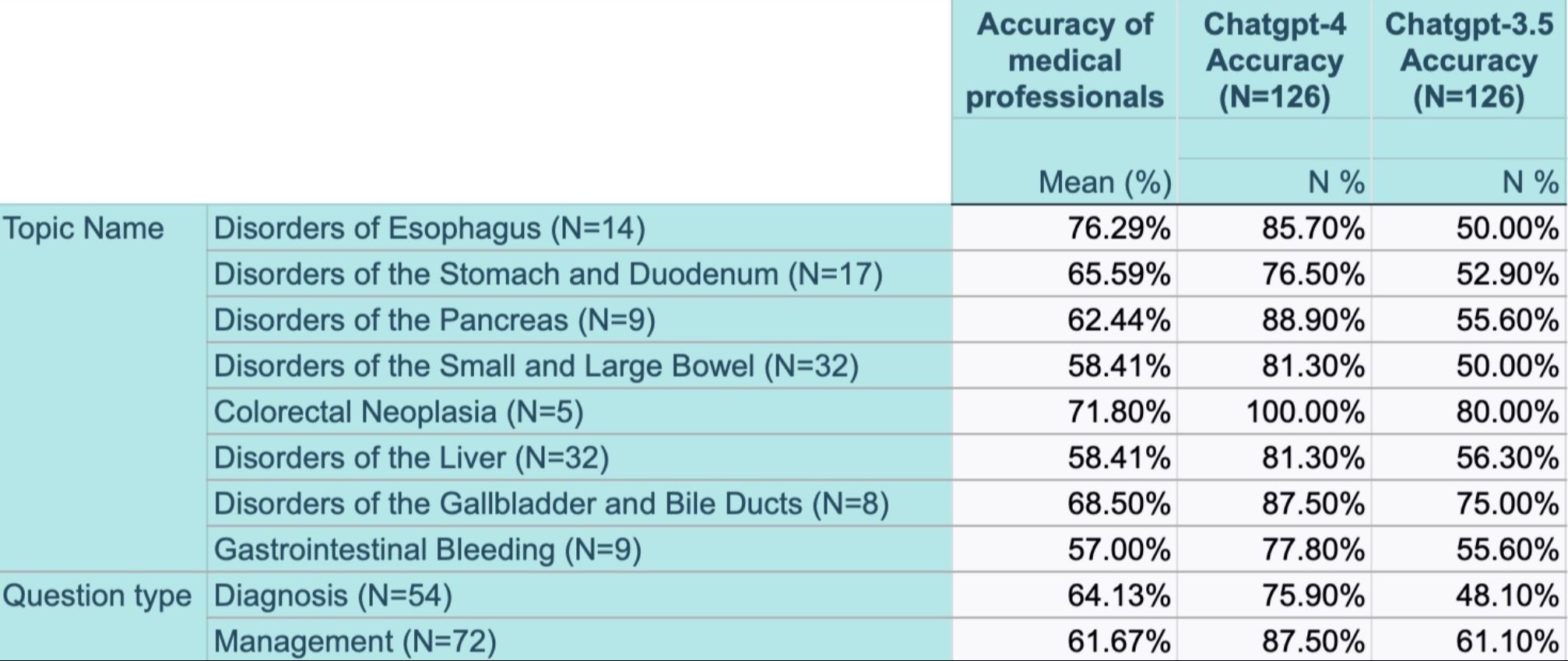
Results: Our findings reveal a notable advancement in AI capabilities, with GPT-4 outperforming GPT-3.5 and even human professionals across all gastroenterology topics. GPT-4 excelled in each tested category, including Disorders of the Esophagus, Disorders of the Stomach and Duodenum, Disorders of the Pancreas, Disorders of the Small and Large Bowel, Colorectal Neoplasia, Disorders of the Liver, Disorders of the Gallbladder and Bile Ducts, and Gastrointestinal Bleeding. For instance, in Disorders of the Esophagus, GPT-4 achieved an accuracy of 85.7%, surpassing the 76.29% accuracy of human professionals and the 50% accuracy of GPT-3.5. In Colorectal Neoplasia, GPT-4 reached 100% accuracy, compared to 71.8% for human professionals and 80% for GPT-3.5. GPT-4 also excelled in both Diagnosis and Management categories, demonstrating its advanced capability in medical education.
Discussion: These findings suggest that GPT-4 not only surpasses its predecessor but also consistently outperforms human professionals across a wide range of gastroenterology topics. The results indicate that AI, specifically GPT-4, holds substantial potential as an educational tool and support system in medical practice, providing high accuracy in diagnosing and managing gastroenterological conditions. This could lead to enhanced learning experiences for medical professionals and possibly improve patient care outcomes.
Disclosures:
Akash Patel, MD1, Isha Samreen, MBBS, MPH2, Imran Ahmed, MA3. P4931 - Advancements in AI for Gastroenterology Education: An Assessment of OpenAI's GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 in MKSAP Question Interpretation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Eisenhower Medical Center, Riverside Community Hospital, Palm Desert, CA; 2Hemet Global Medical Center, Murrieta, CA; 3Burrell College of Osteopathic Medicine, Anaheim, CA
Introduction: The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in medical education represents a transformative shift, offering substantial support for residents preparing for board exams. This study evaluates and compares the accuracy of OpenAI's GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 language models in answering gastroenterology-related Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) from the widely used Medical Knowledge Self-Assessment Program (MKSAP) question bank. The MKSAP was chosen for its comprehensive, validated content and is widely regarded as the gold standard for board preparation.
Methods: We presented 126 MKSAP MCQs, covering eight key gastroenterology topics, to both GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models. The questions were further categorized into Diagnosis (N=54) and Management (N=72) types. Performance comparisons were made against the average accuracy of medical professional MKSAP users, reflecting the percentage of correct answers given by MKSAP users.
Results: Our findings reveal a notable advancement in AI capabilities, with GPT-4 outperforming GPT-3.5 and even human professionals across all gastroenterology topics. GPT-4 excelled in each tested category, including Disorders of the Esophagus, Disorders of the Stomach and Duodenum, Disorders of the Pancreas, Disorders of the Small and Large Bowel, Colorectal Neoplasia, Disorders of the Liver, Disorders of the Gallbladder and Bile Ducts, and Gastrointestinal Bleeding. For instance, in Disorders of the Esophagus, GPT-4 achieved an accuracy of 85.7%, surpassing the 76.29% accuracy of human professionals and the 50% accuracy of GPT-3.5. In Colorectal Neoplasia, GPT-4 reached 100% accuracy, compared to 71.8% for human professionals and 80% for GPT-3.5. GPT-4 also excelled in both Diagnosis and Management categories, demonstrating its advanced capability in medical education.
Discussion: These findings suggest that GPT-4 not only surpasses its predecessor but also consistently outperforms human professionals across a wide range of gastroenterology topics. The results indicate that AI, specifically GPT-4, holds substantial potential as an educational tool and support system in medical practice, providing high accuracy in diagnosing and managing gastroenterological conditions. This could lead to enhanced learning experiences for medical professionals and possibly improve patient care outcomes.

Figure: Comparison of average MSKAP questions answered by MSKAP users vs Chatgpt4 vs Chatgpt3.5
Disclosures:
Akash Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Isha Samreen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Imran Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akash Patel, MD1, Isha Samreen, MBBS, MPH2, Imran Ahmed, MA3. P4931 - Advancements in AI for Gastroenterology Education: An Assessment of OpenAI's GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 in MKSAP Question Interpretation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
