Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P5006 - Isolated Collagenous Sprue in an Elderly Female With a New Diagnosis of Celiac Disease
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- HD
Hunter Chance Dickson, DO
USA Health, University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Presenting Author(s)
Hunter Chance Dickson, DO1, Cesar Moreno, MD1, Benjamin Niland, MD2
1USA Health, University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL; 2University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL
Introduction: Collagenous sprue (CS) is a rare form of small bowel enteropathy caused by subepithelial deposition of collagen and mucosal inflammation. CS has been associated with celiac disease. Less than 100 cases of isolated CS have been reported in medical literature. We present the case of a 74-year-old female who presented with chronic diarrhea and a new diagnosis of celiac disease and isolated collagenous sprue.
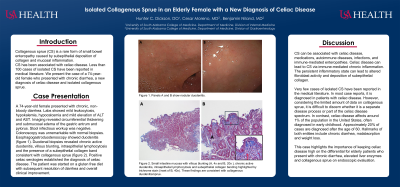
Case Description/Methods: A 74-year-old female presented with chronic, non-bloody diarrhea, up to 20 episodes daily. Laboratory evaluation showed mild leukocytosis, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia and mild elevation of ALT and AST. Imaging revealed circumferential thickening and submucosal edema of the gastric antrum and pylorus. Extensive stool infectious workup was negative. Colonoscopy was unremarkable with normal biopsies. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed duodenitis. Duodenal biopsies revealed chronic active duodenitis, villous blunting, intraepithelial lymphocytosis and the presence of a subepithelial collagen band consistent with collagenous sprue. Positive celiac serologies established the diagnosis of celiac disease. The patient was started on a gluten free diet with subsequent resolution of diarrhea and overall clinical improvement.
Discussion: CS can be associated with celiac disease, medications, autoimmune diseases, infections, and immune-mediated enteropathies. Celiac disease can lead to CS via immune-mediated chronic inflammation. The persistent inflammatory state can lead to altered fibroblast activity and deposition of subepithelial collagen. Very few cases of isolated CS have been reported in the medical literature. In most case reports, it is diagnosed in patients with celiac disease. However, considering the limited amount of data on collagenous sprue, it is difficult to discern whether it is a separate disease process or part of the celiac disease spectrum. In contrast, celiac disease affects around 1% of the population in the United States, often diagnosed in early childhood. Approximately 20% of cases are diagnosed after the age of 60. Hallmarks of both entities include chronic diarrhea, malabsorption and weight loss. This case highlights the importance of keeping celiac disease high in the differential for elderly patients who present with chronic diarrhea, elevated liver enzymes and collagenous sprue on endoscopic evaluation.
Disclosures:
Hunter Chance Dickson, DO1, Cesar Moreno, MD1, Benjamin Niland, MD2. P5006 - Isolated Collagenous Sprue in an Elderly Female With a New Diagnosis of Celiac Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1USA Health, University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL; 2University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL
Introduction: Collagenous sprue (CS) is a rare form of small bowel enteropathy caused by subepithelial deposition of collagen and mucosal inflammation. CS has been associated with celiac disease. Less than 100 cases of isolated CS have been reported in medical literature. We present the case of a 74-year-old female who presented with chronic diarrhea and a new diagnosis of celiac disease and isolated collagenous sprue.
Case Description/Methods: A 74-year-old female presented with chronic, non-bloody diarrhea, up to 20 episodes daily. Laboratory evaluation showed mild leukocytosis, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia and mild elevation of ALT and AST. Imaging revealed circumferential thickening and submucosal edema of the gastric antrum and pylorus. Extensive stool infectious workup was negative. Colonoscopy was unremarkable with normal biopsies. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy showed duodenitis. Duodenal biopsies revealed chronic active duodenitis, villous blunting, intraepithelial lymphocytosis and the presence of a subepithelial collagen band consistent with collagenous sprue. Positive celiac serologies established the diagnosis of celiac disease. The patient was started on a gluten free diet with subsequent resolution of diarrhea and overall clinical improvement.
Discussion: CS can be associated with celiac disease, medications, autoimmune diseases, infections, and immune-mediated enteropathies. Celiac disease can lead to CS via immune-mediated chronic inflammation. The persistent inflammatory state can lead to altered fibroblast activity and deposition of subepithelial collagen. Very few cases of isolated CS have been reported in the medical literature. In most case reports, it is diagnosed in patients with celiac disease. However, considering the limited amount of data on collagenous sprue, it is difficult to discern whether it is a separate disease process or part of the celiac disease spectrum. In contrast, celiac disease affects around 1% of the population in the United States, often diagnosed in early childhood. Approximately 20% of cases are diagnosed after the age of 60. Hallmarks of both entities include chronic diarrhea, malabsorption and weight loss. This case highlights the importance of keeping celiac disease high in the differential for elderly patients who present with chronic diarrhea, elevated liver enzymes and collagenous sprue on endoscopic evaluation.
Disclosures:
Hunter Chance Dickson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cesar Moreno indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Benjamin Niland indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hunter Chance Dickson, DO1, Cesar Moreno, MD1, Benjamin Niland, MD2. P5006 - Isolated Collagenous Sprue in an Elderly Female With a New Diagnosis of Celiac Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
