Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P4684 - Missed Opportunities to Screen for Fatty Liver: Improving Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Screening Through a Quality Assessment and Quality Improvement Project
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio
.jpg)
Yazan Abboud, MD
Rutgers New Jersey Medical School
Newark, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Yazan Abboud, MD1, Imran A. Qureshi, MD1, Ritik M. Goyal, MBBS1, Logine Abouzead, MD1, Ahmed Al-Khazraji, MD1, Kaveh Hajifathalian, MD1, Paul Gaglio, MD2, Sima Vossough-Teehan, MD1
1Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ; 2Rutgers NJ Medical School, Newark, NJ
Introduction: MASLD is the fastest-growing indication for liver transplantation in Western countries, including the US. With the escalating obesity epidemic, MASLD incidence is projected to continue rising. Due to its often asymptomatic nature, MASLD frequently goes undiagnosed. Early detection is critical for improving outcomes, particularly with the emergence of newly FDA-approved agents. To facilitate early detection, GI and endocrine societies advocate for MASLD screening in outpatient settings using non-invasive tools such as the FIB4 score and liver elastography. This study aimed to evaluate and improve the adherence of primary care clinic (PCP) providers to MASLD screening guidelines.
Methods: This is a single-center study involving resident-run PCP clinic at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VA). The study was designed based on PDSA cycle with pre- and post-intervention phases. EMRs for consecutive clinic patients between April-July 2023 were reviewed. Thereafter, interventions included creating a FIB4 smart-phrase in the EMR and incorporating it in the clinic note template. Residents were educated to screen eligible patients with metabolic risk factors; this was included in the smart-phrase. Thereafter, EMRs for consecutive clinic patients between August 2023-February 2024 were reviewed. Data collected included whether the patients were screened for MASLD or not. Statistical analysis was performed using Fisher’s exact test (P< 0.05).
Results: There were 280 patients included in this study, majority were males (90.1%) with median age of 62.5 years (Table 1A). Average FIB4 score was 1.44 with most patients being at low risk for fibrosis (60.2%).
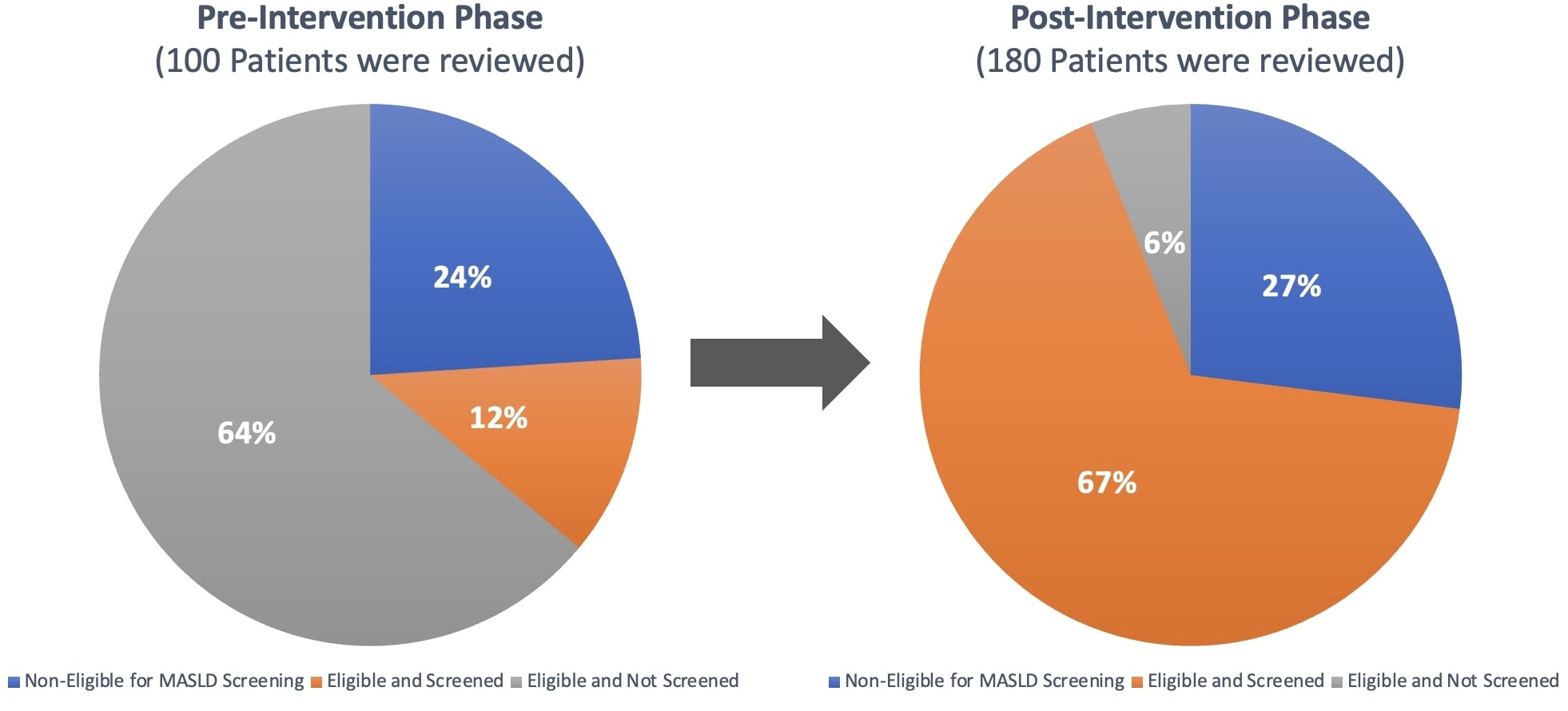
Pre-intervention phase: 100 patients were included; 76 of them were eligible for MASLD screening and only 12 were screened (14%) (Table 1B).
Post-intervention phase: 180 patients were included; 132 of them were eligible for MASLD screening and 121 were screened (92%) (Figure 1).
There were significant differences in rates of screening pre- and post-intervention (P< 0.001).
Liver elastography was ordered for all 49 patients with moderate or high FIB4 score.
Discussion: Creating a simple smart phrase on the FIB4 score and incorporating it within the clinic note template at the VA markedly enhanced residents' compliance with screening patients for MASLD and referring them for liver elastography. Our next aim is to incorporate the smart-phrase at our two other residency sites, aiming to improve early detection of MASLD and ultimately patients’ outcomes.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Yazan Abboud, MD1, Imran A. Qureshi, MD1, Ritik M. Goyal, MBBS1, Logine Abouzead, MD1, Ahmed Al-Khazraji, MD1, Kaveh Hajifathalian, MD1, Paul Gaglio, MD2, Sima Vossough-Teehan, MD1. P4684 - Missed Opportunities to Screen for Fatty Liver: Improving Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Screening Through a Quality Assessment and Quality Improvement Project, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ; 2Rutgers NJ Medical School, Newark, NJ
Introduction: MASLD is the fastest-growing indication for liver transplantation in Western countries, including the US. With the escalating obesity epidemic, MASLD incidence is projected to continue rising. Due to its often asymptomatic nature, MASLD frequently goes undiagnosed. Early detection is critical for improving outcomes, particularly with the emergence of newly FDA-approved agents. To facilitate early detection, GI and endocrine societies advocate for MASLD screening in outpatient settings using non-invasive tools such as the FIB4 score and liver elastography. This study aimed to evaluate and improve the adherence of primary care clinic (PCP) providers to MASLD screening guidelines.
Methods: This is a single-center study involving resident-run PCP clinic at the Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VA). The study was designed based on PDSA cycle with pre- and post-intervention phases. EMRs for consecutive clinic patients between April-July 2023 were reviewed. Thereafter, interventions included creating a FIB4 smart-phrase in the EMR and incorporating it in the clinic note template. Residents were educated to screen eligible patients with metabolic risk factors; this was included in the smart-phrase. Thereafter, EMRs for consecutive clinic patients between August 2023-February 2024 were reviewed. Data collected included whether the patients were screened for MASLD or not. Statistical analysis was performed using Fisher’s exact test (P< 0.05).
Results: There were 280 patients included in this study, majority were males (90.1%) with median age of 62.5 years (Table 1A). Average FIB4 score was 1.44 with most patients being at low risk for fibrosis (60.2%).
Pre-intervention phase: 100 patients were included; 76 of them were eligible for MASLD screening and only 12 were screened (14%) (Table 1B).
Post-intervention phase: 180 patients were included; 132 of them were eligible for MASLD screening and 121 were screened (92%) (Figure 1).
There were significant differences in rates of screening pre- and post-intervention (P< 0.001).
Liver elastography was ordered for all 49 patients with moderate or high FIB4 score.
Discussion: Creating a simple smart phrase on the FIB4 score and incorporating it within the clinic note template at the VA markedly enhanced residents' compliance with screening patients for MASLD and referring them for liver elastography. Our next aim is to incorporate the smart-phrase at our two other residency sites, aiming to improve early detection of MASLD and ultimately patients’ outcomes.

Figure: Figure 1: Screening Rates for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLS) pre- and post-intervention.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Yazan Abboud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Imran Qureshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ritik Goyal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Logine Abouzead indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Al-Khazraji indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kaveh Hajifathalian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Gaglio indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sima Vossough-Teehan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yazan Abboud, MD1, Imran A. Qureshi, MD1, Ritik M. Goyal, MBBS1, Logine Abouzead, MD1, Ahmed Al-Khazraji, MD1, Kaveh Hajifathalian, MD1, Paul Gaglio, MD2, Sima Vossough-Teehan, MD1. P4684 - Missed Opportunities to Screen for Fatty Liver: Improving Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Screening Through a Quality Assessment and Quality Improvement Project, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
