Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P4510 - Successful Management of Pancreatic Insulinoma by Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Radio Frequency Ablation
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Mark Solinski, MD
McGaw Medical Center of Northwestern University
Chicago, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Mark Solinski, MD1, Grant R. Whitmer, MD1, Hannah Soltani, BS2, Sukrit Jain, MD1, Jonathan Xia, MD, PhD2, Rajesh Keswani, MD, MS3
1McGaw Medical Center of Northwestern University, Chicago, IL; 2Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL; 3Northwestern Medicine, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors have an incidence of approximately 5 in 100,000 individuals. The majority of functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors are Insulinomas which account for roughly 21% of cases. Current first line treatment is surgical resection, however age and/or comorbidities preclude many patients from being candidates. EUS guided radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a promising non-invasive alternative.
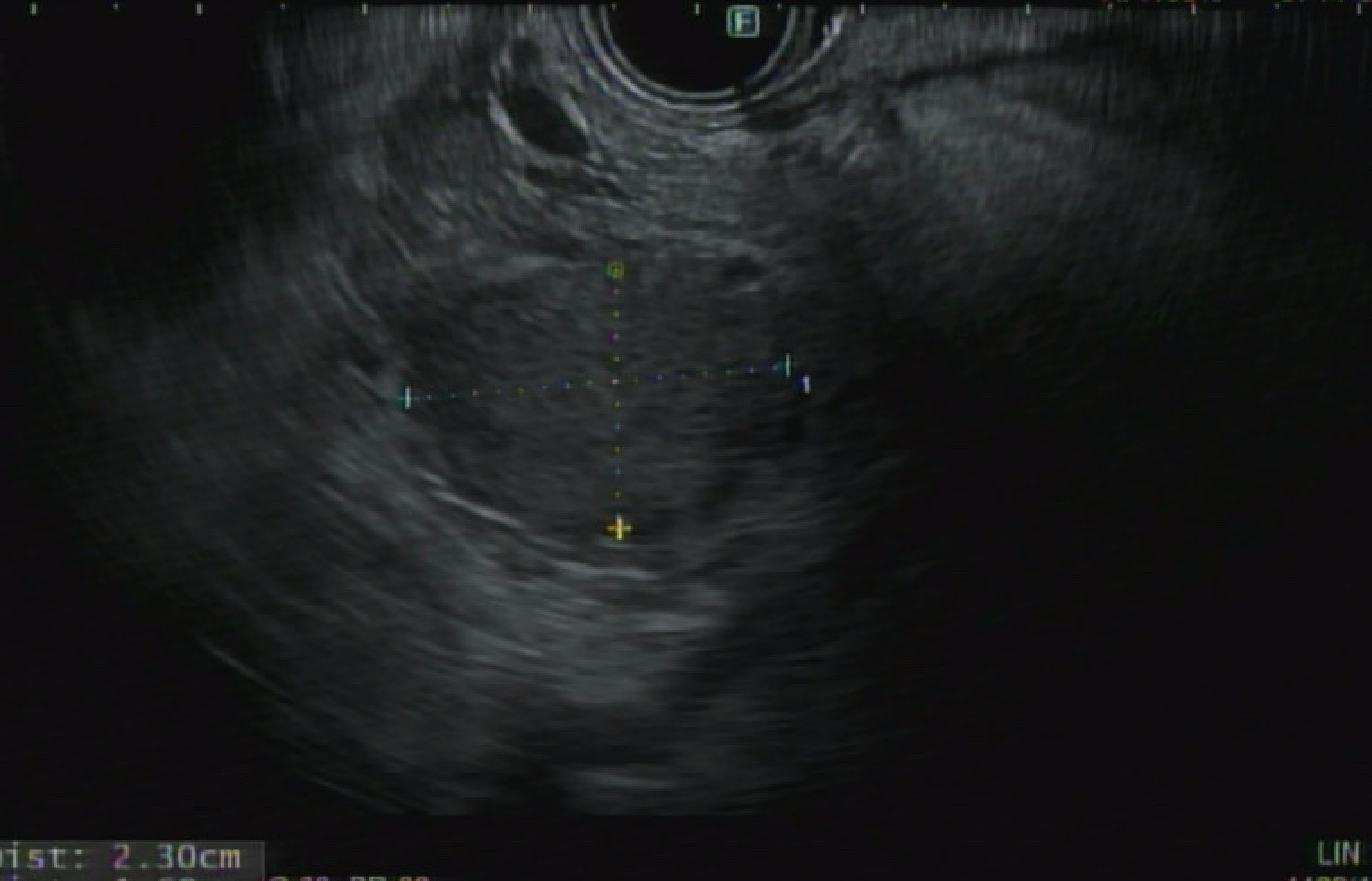
Case Description/Methods: A 63-year-old male presented to the hospital after a fall and was subsequently found to be hypoglycemic to 39. Patient ate high sugar foods when feeling symptomatic, which led to a 70-pound unintentional weight gain (BMI: 41.63). Evaluation revealed HbA1c 4.9%, TSH 1.30mIU/L, glucose 45mg/dl corresponding to C-peptide 14.00ng/ml, proinsulin 174.2pmol/L, IGF-1 10ng/ml, insulin 388.4mIU/ml, insulin autoantibodies < 0.4nU/ml, prolactin 22.2ng/mL, total testosterone 8ng/dL, free testosterone 2.3pg/mL. Patient had an unremarkable abdominal CT, but PET Dotate scan showed a 28mm lesion in the pancreatic head concerning for an insulinoma, and a 34mm lesion concerning for pituitary macroadenoma. Patient was treated with off-label Pasireotide/diazoxide for glycemic control. His course was complicated by small bowel obstruction requiring high dextrose TPN to maintain glucose level. Surgical oncology evaluated the patient and determined he was not a surgical candidate due to BMI >35.0 and concern for pulmonary HTN, prompting referral for EUS RFA. On EUS, a round hypoechoic mass measuring 23 mm x 16 mm was visualized in the head of the pancreas. The lesion received 6 cycles of 20-watt radiofrequency ablation from a 7 mm catheter. Immunostaining of the biopsy was positive for synaptophysin, Chromagranin A, and INSM1, all consistent with a well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumor.
Discussion: EUS RFA appears to be just as effective and safer than surgical resection of pancreatic insulinomas. Prior studies have recommended EUS RFA for insulinomas < 2.0 cm in patients without concern for associated genetic syndrome. This case demonstrates the feasibility of EUS RFA in patients with insulinomas > 2.0 cm and concern for genetic syndrome (MEN-1) in a patient deemed not a surgical candidate due to obesity caused by defensive eating to manage his hypoglycemia. This case provides an example of the expanding role for EUS RFA to treat pancreatic insulinomas, and should encourage expansion of inclusion criteria for any pending head-to-head trials of EUS RFA vs surgical resection.
Disclosures:
Mark Solinski, MD1, Grant R. Whitmer, MD1, Hannah Soltani, BS2, Sukrit Jain, MD1, Jonathan Xia, MD, PhD2, Rajesh Keswani, MD, MS3. P4510 - Successful Management of Pancreatic Insulinoma by Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Radio Frequency Ablation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1McGaw Medical Center of Northwestern University, Chicago, IL; 2Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL; 3Northwestern Medicine, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors have an incidence of approximately 5 in 100,000 individuals. The majority of functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors are Insulinomas which account for roughly 21% of cases. Current first line treatment is surgical resection, however age and/or comorbidities preclude many patients from being candidates. EUS guided radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a promising non-invasive alternative.
Case Description/Methods: A 63-year-old male presented to the hospital after a fall and was subsequently found to be hypoglycemic to 39. Patient ate high sugar foods when feeling symptomatic, which led to a 70-pound unintentional weight gain (BMI: 41.63). Evaluation revealed HbA1c 4.9%, TSH 1.30mIU/L, glucose 45mg/dl corresponding to C-peptide 14.00ng/ml, proinsulin 174.2pmol/L, IGF-1 10ng/ml, insulin 388.4mIU/ml, insulin autoantibodies < 0.4nU/ml, prolactin 22.2ng/mL, total testosterone 8ng/dL, free testosterone 2.3pg/mL. Patient had an unremarkable abdominal CT, but PET Dotate scan showed a 28mm lesion in the pancreatic head concerning for an insulinoma, and a 34mm lesion concerning for pituitary macroadenoma. Patient was treated with off-label Pasireotide/diazoxide for glycemic control. His course was complicated by small bowel obstruction requiring high dextrose TPN to maintain glucose level. Surgical oncology evaluated the patient and determined he was not a surgical candidate due to BMI >35.0 and concern for pulmonary HTN, prompting referral for EUS RFA. On EUS, a round hypoechoic mass measuring 23 mm x 16 mm was visualized in the head of the pancreas. The lesion received 6 cycles of 20-watt radiofrequency ablation from a 7 mm catheter. Immunostaining of the biopsy was positive for synaptophysin, Chromagranin A, and INSM1, all consistent with a well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumor.
Discussion: EUS RFA appears to be just as effective and safer than surgical resection of pancreatic insulinomas. Prior studies have recommended EUS RFA for insulinomas < 2.0 cm in patients without concern for associated genetic syndrome. This case demonstrates the feasibility of EUS RFA in patients with insulinomas > 2.0 cm and concern for genetic syndrome (MEN-1) in a patient deemed not a surgical candidate due to obesity caused by defensive eating to manage his hypoglycemia. This case provides an example of the expanding role for EUS RFA to treat pancreatic insulinomas, and should encourage expansion of inclusion criteria for any pending head-to-head trials of EUS RFA vs surgical resection.

Figure: A 23mm x 16mm Insulinoma seen on EUS.
Disclosures:
Mark Solinski indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Grant Whitmer: Baxter International – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds). Biomarin Pharmaceuticals – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds). Edwards Lifesciences – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds). Oncolytics Biotech – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Hannah Soltani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sukrit Jain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jonathan Xia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rajesh Keswani: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Medtronic – Consultant.
Mark Solinski, MD1, Grant R. Whitmer, MD1, Hannah Soltani, BS2, Sukrit Jain, MD1, Jonathan Xia, MD, PhD2, Rajesh Keswani, MD, MS3. P4510 - Successful Management of Pancreatic Insulinoma by Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Radio Frequency Ablation, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
