Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2690 - Impact of Mirikizumab on Clinically Meaningful Improvements in Fatigue as Measured by FACIT-F in Patients With Moderately to Severely Active Crohn’s Disease
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Miguel Regueiro, MD
Cleveland Clinic
Cleveland, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Peter Bossuyt, 1, Miguel D Regueiro, MD2, Monika Fischer, MD, MS3, Kristina Traxler, 4, Guanglei Yu, 4, Marijana Protic, 4, Konstantinos Tsilkos, 4, Aisha Vadhariya, 4, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD5, Pascal Juillerat, 6
1Imelda GI Clinical Research Center, Imelda General Hospital, Bonheiden, Antwerpen, Belgium; 2Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 3Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN; 4Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN; 5Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan; 6Intesto Crohn's and Colitis Center, Bern and Fribourg, Bern, Bern, Switzerland
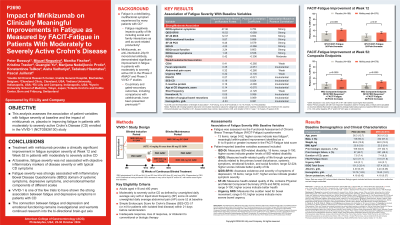
Introduction: This study assesses the impact of mirikizumab (MIRI) vs. placebo (PBO) in improving fatigue among patients with moderate-to-severe active Crohn’s disease (CD) and the correlation of patient variables with baseline (BL) fatigue severity in the Phase 3 VIVID-1 study.
Methods: Patients were randomized 6:3:2 to MIRI (900 mg intravenous at Week [W]0, W4, and W8, then 300 mg subcutaneous every 4W from W12-W52), ustekinumab (UST) or PBO. Fatigue was assessed by the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F) questionnaire. We report the PBO (N=199) and MIRI (N=579) patient proportion achieving W12 FACIT-F ≥6- or ≥9-pt increase from BL. W52 comparisons with PBO used composite (C) endpoints: W12 clinical response by Patient-Reported Outcome (≥30% decrease in stool frequency [SF] or abdominal pain [AP], and neither worse than BL), and W52 FACIT-F increase of either ≥6-pts (C≥6) or ≥9-pts (C≥9). p-Values were calculated via Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test adjusted by biologic-failed status; BL Simple Endoscopic Score for CD (SES-CD) total score (< 12, ≥12); either BL SF ≥7 and/or AP ≥2.5. The pooled population (excluding missing data) with a range of patient variables was analyzed to assess the correlation with fatigue severity. Variables were ranked by importance and Pearson correlation coefficients (r) calculated.
Results: W12: 31.2% PBO vs 43.0% MIRI patients achieved FACIT-F ≥6-pt increase (p< 0.005) and 22.1% PBO vs 32.6% MIRI achieved FACIT-F ≥9-pt increase (p< 0.01). W52: 20.1% PBO vs 34.9% MIRI patients met C≥6 and 15.6% PBO vs 28.5% MIRI met C≥9 (both, p< 0.0005). A strong association (r>0.5) was found between fatigue severity and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire (IBDQ), and with the emotional functioning domain of IBDQ and Mental Component Summary (MCS) of Short Form (SF)-36 (Table). There was a weak association (r=0.1–0.3) with AP score, SF score, and Urgency Numeric Rating Scale, and insubstantial association (r< 0.1) with SES-CD, C-reactive protein, and fecal calprotectin.
Discussion: MIRI showed a clinically significant W12 fatigue improvement vs. PBO and a nominally statistically higher improvement in W52 composite endpoints vs. PBO. At BL, fatigue was not associated with objective inflammatory markers of disease severity or with typical CD symptoms in this model. The strong association between fatigue and MCS of SF-36 and the emotional functioning domain of IBDQ implies bidirectional effects of brain-gut interactions that warrant further exploration.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Peter Bossuyt, 1, Miguel D Regueiro, MD2, Monika Fischer, MD, MS3, Kristina Traxler, 4, Guanglei Yu, 4, Marijana Protic, 4, Konstantinos Tsilkos, 4, Aisha Vadhariya, 4, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD5, Pascal Juillerat, 6. P2690 - Impact of Mirikizumab on Clinically Meaningful Improvements in Fatigue as Measured by FACIT-F in Patients With Moderately to Severely Active Crohn’s Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Imelda GI Clinical Research Center, Imelda General Hospital, Bonheiden, Antwerpen, Belgium; 2Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH; 3Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN; 4Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN; 5Kyorin University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan; 6Intesto Crohn's and Colitis Center, Bern and Fribourg, Bern, Bern, Switzerland
Introduction: This study assesses the impact of mirikizumab (MIRI) vs. placebo (PBO) in improving fatigue among patients with moderate-to-severe active Crohn’s disease (CD) and the correlation of patient variables with baseline (BL) fatigue severity in the Phase 3 VIVID-1 study.
Methods: Patients were randomized 6:3:2 to MIRI (900 mg intravenous at Week [W]0, W4, and W8, then 300 mg subcutaneous every 4W from W12-W52), ustekinumab (UST) or PBO. Fatigue was assessed by the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F) questionnaire. We report the PBO (N=199) and MIRI (N=579) patient proportion achieving W12 FACIT-F ≥6- or ≥9-pt increase from BL. W52 comparisons with PBO used composite (C) endpoints: W12 clinical response by Patient-Reported Outcome (≥30% decrease in stool frequency [SF] or abdominal pain [AP], and neither worse than BL), and W52 FACIT-F increase of either ≥6-pts (C≥6) or ≥9-pts (C≥9). p-Values were calculated via Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test adjusted by biologic-failed status; BL Simple Endoscopic Score for CD (SES-CD) total score (< 12, ≥12); either BL SF ≥7 and/or AP ≥2.5. The pooled population (excluding missing data) with a range of patient variables was analyzed to assess the correlation with fatigue severity. Variables were ranked by importance and Pearson correlation coefficients (r) calculated.
Results: W12: 31.2% PBO vs 43.0% MIRI patients achieved FACIT-F ≥6-pt increase (p< 0.005) and 22.1% PBO vs 32.6% MIRI achieved FACIT-F ≥9-pt increase (p< 0.01). W52: 20.1% PBO vs 34.9% MIRI patients met C≥6 and 15.6% PBO vs 28.5% MIRI met C≥9 (both, p< 0.0005). A strong association (r>0.5) was found between fatigue severity and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire (IBDQ), and with the emotional functioning domain of IBDQ and Mental Component Summary (MCS) of Short Form (SF)-36 (Table). There was a weak association (r=0.1–0.3) with AP score, SF score, and Urgency Numeric Rating Scale, and insubstantial association (r< 0.1) with SES-CD, C-reactive protein, and fecal calprotectin.
Discussion: MIRI showed a clinically significant W12 fatigue improvement vs. PBO and a nominally statistically higher improvement in W52 composite endpoints vs. PBO. At BL, fatigue was not associated with objective inflammatory markers of disease severity or with typical CD symptoms in this model. The strong association between fatigue and MCS of SF-36 and the emotional functioning domain of IBDQ implies bidirectional effects of brain-gut interactions that warrant further exploration.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Peter Bossuyt: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Amgen – Grant/Research Support. Arena pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Benelux – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecture fees. CAG – Lecture fees. Celltrion – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecture fees. CiRC Biosciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Dr. Falk Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Eli Lilly and Company – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. EPGS – Lecture fees. Galapagos NV – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecture fees. Globalport – Lecture fees. Hospira – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support, Lecture fees. Materia Prima – Lecture fees. Merck – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Mundipharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Grant/Research Support. Mylan – Grant/Research Support. Pentax – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecture fees. Pfizer – Grant/Research Support, Advisory board fees. PSI CRO – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Roche – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Sandoz – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Scope – Lecture fees. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Lecture fees. Tetrameros – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Viatris – Grant/Research Support.
Miguel D Regueiro: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau.
Monika Fischer: AbbVie – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Eli Lilly and Company – Consultant. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant. Rebiotix – Consultant. Scioto Biosciences – Consultant. Seres Therapeutics – Consultant.
Kristina Traxler: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Guanglei Yu: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Marijana Protic: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Konstantinos Tsilkos: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Aisha Vadhariya: Eli Lilly and Company – Employee, Stock Options.
Tadakazu Hisamatsu: AbbVie – Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Daiichi-Sankyo – Grant/Research Support. EA Pharma – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant. JIMRO – Grant/Research Support. Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation – Grant/Research Support, lecture fees. Mochida Pharmaceutical – Grant/Research Support. Nippon Kayaku – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Grant/Research Support. Takeda Pharmaceutical – Grant/Research Support, lecture fees.
Pascal Juillerat: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Eli Lilly and Company – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Ferring Pharmaceuticals – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Gilead Sciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Merck Sharp & Dohme – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pierre Fabre – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Roche – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Sandoz – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Tillots Pharma AG – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. UCB Pharma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Vifor Pharma – Grant/Research Support.
Peter Bossuyt, 1, Miguel D Regueiro, MD2, Monika Fischer, MD, MS3, Kristina Traxler, 4, Guanglei Yu, 4, Marijana Protic, 4, Konstantinos Tsilkos, 4, Aisha Vadhariya, 4, Tadakazu Hisamatsu, MD, PhD5, Pascal Juillerat, 6. P2690 - Impact of Mirikizumab on Clinically Meaningful Improvements in Fatigue as Measured by FACIT-F in Patients With Moderately to Severely Active Crohn’s Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
