Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2545 - Fecal Calprotectin Decreases Following Transition to Subcutaneous CT-P13 in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases on Escalated Intravenous Infliximab Maintenance Therapy
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Zhigang Wang, MSc, PharmD
Katholieke Universiteit Leuven
Leuven, Vlaams-Brabant, Belgium
Presenting Author(s)
Zhigang Wang, MSc, PharmD1, Marc Ferrante, MD, PhD2, Séverine Vermeire, MD, PhD3, Erwin Dreesen, PharmD; PhD1
1Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Leuven, Vlaams-Brabant, Belgium; 2University Hospitals, Leuven, Vlaams-Brabant, Belgium; 3University Hospitals Leuven, Leuven, Vlaams-Brabant, Belgium
Introduction: The subcutaneous (SC) formulation of infliximab (IFX) CT-P13 has shown non-inferior pharmacokinetics (PK) and comparable efficacy to the intravenous (IV) formulation in clinical trials. However, it remains unclear whether patients on escalated IV dosing regimens can safely transition to standard SC dosing without losing therapeutic response. This study aims to elucidate the dose-exposure-response relationship during IFX IV-to-SC switch in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) through population PK-pharmacodynamic (popPK-PD) modeling and simulation.
Methods: Data were collected from healthy volunteers in two single-dose Phase I studies (CT-P13 1.5 and 1.9) and patients with IBD in a two-part Phase I study (CT-P13 1.6). In patients with IBD, frequent PK sampling was conducted during switching from 5 mg/kg IV IFX to bi-weekly (Q2W) SC IFX injections of 120/180/240mg in Part 1 and 120/240mg in Part 2. Fecal calprotectin (FC) was measured at baseline, week(w) 2 and w6, and then Q8W until w30 and w54 in Part 1 and 2 of the study, respectively. PopPK-PD modeling and simulation using NONMEM 7.5 were conducted on 2000 virtual patients to evaluate the FC evolution post-switch from escalated IV to standard 120mg Q2W SC IFX dosing.
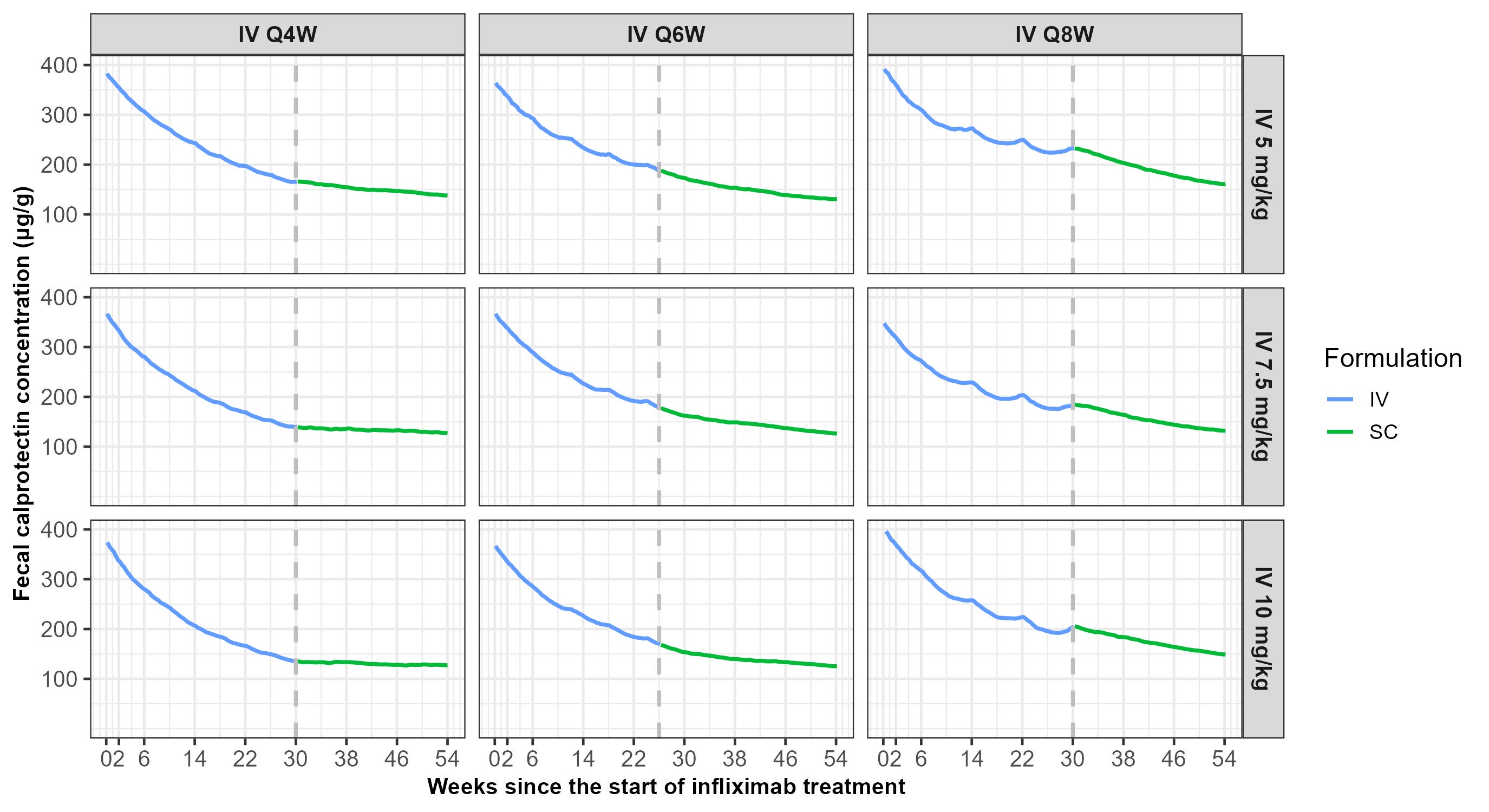
Results: The analysis included 253 healthy volunteers and 179 IBD patients, contributing to 7351 IFX concentrations and 1201 FC concentrations. A simultaneous popPK-PD model was developed, comprising a 2-compartment popPK model linking IFX dose to exposure, and an indirect response popPD model describing the inhibitory effect of IFX exposure on the production rate constant of FC. IFX clearance decreased with increasing serum albumin, decreasing body weight, and the absence of neutralizing anti-drug antibodies (NAb). The terminal half-life of IFX in a median patient (body weight 75 kg, serum albumin 45 mg/L, without NAb) was 9.3 days. FC levels decreased with increasing IFX exposure. Simulations showed that patients on escalated IV maintenance therapy can safely switch to 120mg Q2W SC IFX without an increase in FC (switch from Q4W IV) or even further decreases in FC (switch from Q6W/Q8W IV) (Figure 1).
Discussion: Standard SC CT-P13 dosing offers an improved biomarker response as compared to standard and escalated IV dosing. Real-world data are awaited to confirm clinical benefits of transitioning from escalated IV to standard SC dosing. Furthermore, our model may facilitate personalized dosing based on combined IFX and FC monitoring.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Zhigang Wang, MSc, PharmD1, Marc Ferrante, MD, PhD2, Séverine Vermeire, MD, PhD3, Erwin Dreesen, PharmD; PhD1. P2545 - Fecal Calprotectin Decreases Following Transition to Subcutaneous CT-P13 in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases on Escalated Intravenous Infliximab Maintenance Therapy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Leuven, Vlaams-Brabant, Belgium; 2University Hospitals, Leuven, Vlaams-Brabant, Belgium; 3University Hospitals Leuven, Leuven, Vlaams-Brabant, Belgium
Introduction: The subcutaneous (SC) formulation of infliximab (IFX) CT-P13 has shown non-inferior pharmacokinetics (PK) and comparable efficacy to the intravenous (IV) formulation in clinical trials. However, it remains unclear whether patients on escalated IV dosing regimens can safely transition to standard SC dosing without losing therapeutic response. This study aims to elucidate the dose-exposure-response relationship during IFX IV-to-SC switch in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) through population PK-pharmacodynamic (popPK-PD) modeling and simulation.
Methods: Data were collected from healthy volunteers in two single-dose Phase I studies (CT-P13 1.5 and 1.9) and patients with IBD in a two-part Phase I study (CT-P13 1.6). In patients with IBD, frequent PK sampling was conducted during switching from 5 mg/kg IV IFX to bi-weekly (Q2W) SC IFX injections of 120/180/240mg in Part 1 and 120/240mg in Part 2. Fecal calprotectin (FC) was measured at baseline, week(w) 2 and w6, and then Q8W until w30 and w54 in Part 1 and 2 of the study, respectively. PopPK-PD modeling and simulation using NONMEM 7.5 were conducted on 2000 virtual patients to evaluate the FC evolution post-switch from escalated IV to standard 120mg Q2W SC IFX dosing.
Results: The analysis included 253 healthy volunteers and 179 IBD patients, contributing to 7351 IFX concentrations and 1201 FC concentrations. A simultaneous popPK-PD model was developed, comprising a 2-compartment popPK model linking IFX dose to exposure, and an indirect response popPD model describing the inhibitory effect of IFX exposure on the production rate constant of FC. IFX clearance decreased with increasing serum albumin, decreasing body weight, and the absence of neutralizing anti-drug antibodies (NAb). The terminal half-life of IFX in a median patient (body weight 75 kg, serum albumin 45 mg/L, without NAb) was 9.3 days. FC levels decreased with increasing IFX exposure. Simulations showed that patients on escalated IV maintenance therapy can safely switch to 120mg Q2W SC IFX without an increase in FC (switch from Q4W IV) or even further decreases in FC (switch from Q6W/Q8W IV) (Figure 1).
Discussion: Standard SC CT-P13 dosing offers an improved biomarker response as compared to standard and escalated IV dosing. Real-world data are awaited to confirm clinical benefits of transitioning from escalated IV to standard SC dosing. Furthermore, our model may facilitate personalized dosing based on combined IFX and FC monitoring.

Figure: Figure 1. Fecal calprotectin over time following the transition from various escalated intravenous (IV) dosing regimens to standard bi-weekly 120mg subcutaneous (SC) dosing of infliximab CT-P13. The vertical dashed lines indicate the timepoint when the standard SC dose starts. Virtual patients who were on every 4 and 8 weeks (Q4W and Q8W) IV dosing regimen were switched at week 30. Virtual patients who were on Q6W IV dosing regimen were switched at week 26.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Zhigang Wang: Celltrion – Sponsorship of travel and accomendation cost for ACG2024 conference.
Marc Ferrante: AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Agomab – Consultant. Amgen – Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Biogen – Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. Dr Falk Pharma – Speakers Bureau. EG Pharmaceuticals – Grant/Research Support. Eli Lilly and Company – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Ferring – Speakers Bureau. Janssen – Grant/Research Support. Janssen-Cilag – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Lamepro – Speakers Bureau. Medtronic – Consultant. MRM Health – Consultant. MSD – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. Regeneron – Consultant. Samsung Bioepis – Consultant. Sandoz – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau. ThermoFisher – Consultant. Truvion Healthcare – Speakers Bureau. Viatris – Grant/Research Support, Speakers Bureau.
Séverine Vermeire: AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Abivax – Consultant. AbolerlsPharma – Consultant. AgomAb – Consultant. Alimentiv – Consultant. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant. BioraTherapeutics – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Cytoki Pharma – Consultant. Dr Falk Pharma – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant. Galapagos – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Genentech Roche – Consultant. Gilead – Consultant. GSK – Consultant. Hospira – Consultant. J&J – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Janssen – Consultant. lmidomics – Consultant. Materia Prima – Consultant. Mestag Therapeutics – Consultant. Microbiotica – Consultant. MiroBio – Consultant. Morphic – Consultant. MrMHealth – Consultant. MSD – Consultant. Mundipharma – Consultant. Pfizer Inc – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Prodigest – Consultant. Progenity – Consultant. Prometheus – Consultant. Robarts Clinical Trials – Consultant. Surrozen – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Theravance – Consultant. Tillots Pharma AG – Consultant. VectivBio – Consultant. Ventyx – Consultant. Zealand Pharma – Consultant.
Erwin Dreesen: Alimentiv – Consultant. argenx – Consultant. Celltrion – Speakers Bureau. Galapagos – Speakers Bureau. Janssen – Grant/Research Support. Prometheus – Grant/Research Support. Sandoz – Grant/Research Support.
Zhigang Wang, MSc, PharmD1, Marc Ferrante, MD, PhD2, Séverine Vermeire, MD, PhD3, Erwin Dreesen, PharmD; PhD1. P2545 - Fecal Calprotectin Decreases Following Transition to Subcutaneous CT-P13 in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases on Escalated Intravenous Infliximab Maintenance Therapy, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
