Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2562 - Early Sonographic Transmural Remission as a Post-Induction Target Across Advanced Therapies in Crohn’s Disease
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Matthew Smyth, MD
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Vancouver, BC, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Matthew Smyth, MD1, Michael Dolinger, MD, MBA2, Marla C. Dubinsky, MD2
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Vancouver, BC, Canada; 2Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY
Introduction: Intestinal ultrasound (IUS) is becoming an important early target to drive treatment optimization with growing interest in clinical trials. The differential healing rates across advanced therapies (AT) remains unknown. We aimed to determine the rates of early post induction IUS transmural (TM) remission and response across AT in Crohn’s Disease (CD).
Methods: Single center retrospective review of patients initiating AT who underwent IUS pre and post induction and had disease activity and biomarker data available between Aug 2020-Jan 2024. Patients with normal pre-AT IUS or post op were excluded. Primary outcome was post-induction TM response of the most affected segment (segmental response: >25% decrease in bowel wall thickness (BWT) from baseline, absolute BWT decrease >2mm, or absolute decrease >1mm with >1-point improvement in Modified Limberg Score (MLS)). Secondary outcomes were segmental and complete (all bowel segments) TM remission (BWT < 3.0mm and MLS 0). Descriptive statistics summarized data (median [IQR]), univariate analysis compared differences across groups, and binary logistic regression was used for multivariate analysis.
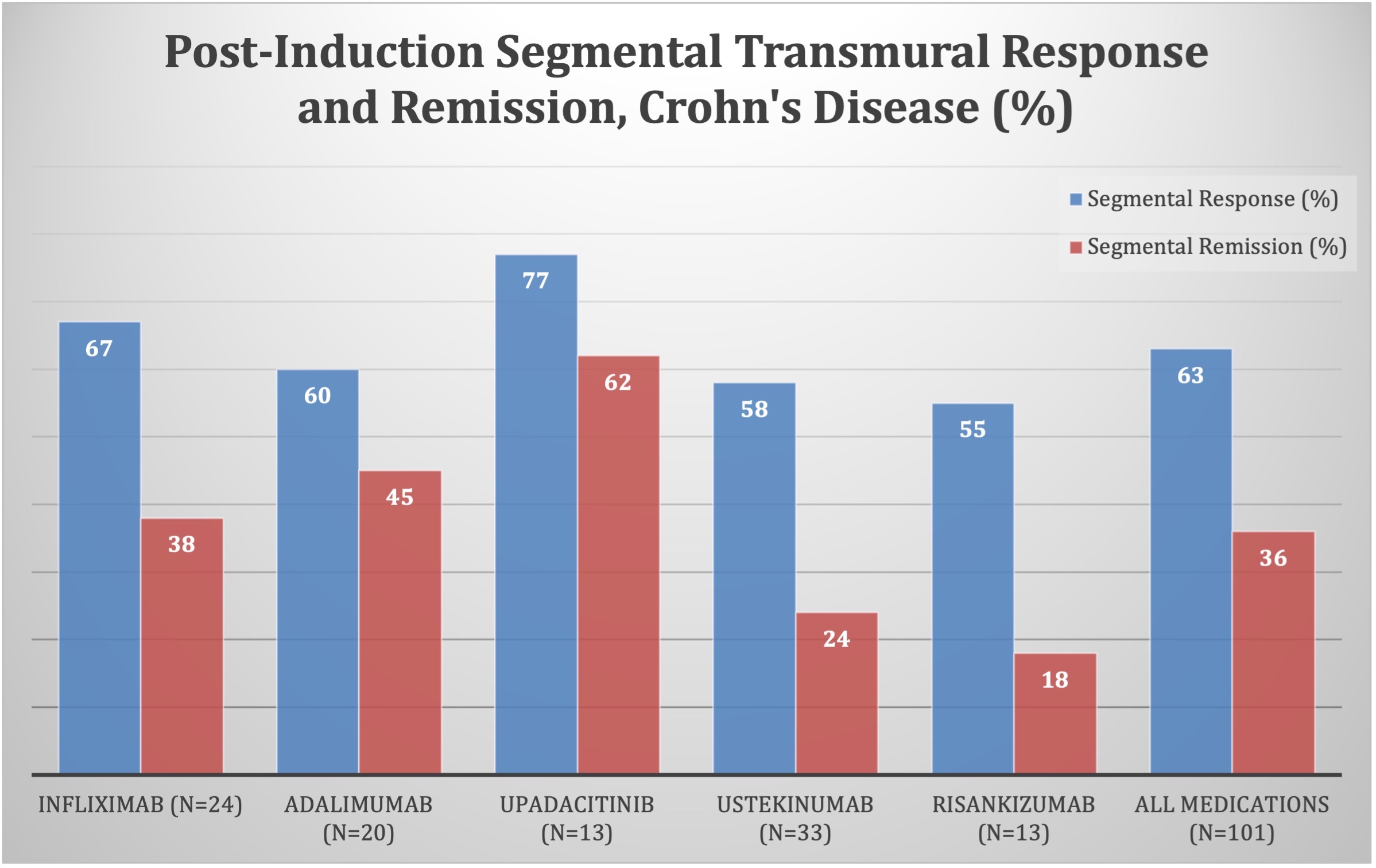
Results: 101 patients (53% female, age 17.4 [15.0-21.1] years); disease duration 0.80 [0.17-3.96] years; post induction IUS 78 [56-102] days on AT. Segmental TM response across all AT was 63%. Segmental and complete TM remission was 36% and 35% (figure). Complete TM remission was seen at a higher rate with upadacitinib (UPA) than ustekinumab (UST) (p=0.009) and risankizumab (RZB) (p=0.032) but not anti-TNF (NS). Patients with severe IUS inflammation (MLS 3) at baseline were less likely to achieve TM remission independent of AT (aOR 0.21 [0.059-0.76]). After controlling for baseline IUS severity, CRP, and individual therapies; infliximab (IFX) (aOR 11.7 [2.2-62.4]) and UPA (aOR 5.22 [1.0-27.2]) were associated with complete TM remission. Rates of segmental TM response were greater for colonic than ileal disease in UST/RZB (88% vs 47%, p=0.038), but no different in TNF/UPA. Patients started on UST/RZB after >1 failed prior AT had a trend for lower rates of TM outcomes (NS), while number of prior therapies had no impact on UPA response or remission rates.
Discussion: Post-induction TM outcomes are achievable across AT: 2/3 of patients achieve segmental TM response and 1/3 achieve complete TM remission. While TM outcomes should be used to guide therapy optimization, post-induction thresholds should be customized based on each AT and baseline IUS severity.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Matthew Smyth, MD1, Michael Dolinger, MD, MBA2, Marla C. Dubinsky, MD2. P2562 - Early Sonographic Transmural Remission as a Post-Induction Target Across Advanced Therapies in Crohn’s Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Vancouver, BC, Canada; 2Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY
Introduction: Intestinal ultrasound (IUS) is becoming an important early target to drive treatment optimization with growing interest in clinical trials. The differential healing rates across advanced therapies (AT) remains unknown. We aimed to determine the rates of early post induction IUS transmural (TM) remission and response across AT in Crohn’s Disease (CD).
Methods: Single center retrospective review of patients initiating AT who underwent IUS pre and post induction and had disease activity and biomarker data available between Aug 2020-Jan 2024. Patients with normal pre-AT IUS or post op were excluded. Primary outcome was post-induction TM response of the most affected segment (segmental response: >25% decrease in bowel wall thickness (BWT) from baseline, absolute BWT decrease >2mm, or absolute decrease >1mm with >1-point improvement in Modified Limberg Score (MLS)). Secondary outcomes were segmental and complete (all bowel segments) TM remission (BWT < 3.0mm and MLS 0). Descriptive statistics summarized data (median [IQR]), univariate analysis compared differences across groups, and binary logistic regression was used for multivariate analysis.
Results: 101 patients (53% female, age 17.4 [15.0-21.1] years); disease duration 0.80 [0.17-3.96] years; post induction IUS 78 [56-102] days on AT. Segmental TM response across all AT was 63%. Segmental and complete TM remission was 36% and 35% (figure). Complete TM remission was seen at a higher rate with upadacitinib (UPA) than ustekinumab (UST) (p=0.009) and risankizumab (RZB) (p=0.032) but not anti-TNF (NS). Patients with severe IUS inflammation (MLS 3) at baseline were less likely to achieve TM remission independent of AT (aOR 0.21 [0.059-0.76]). After controlling for baseline IUS severity, CRP, and individual therapies; infliximab (IFX) (aOR 11.7 [2.2-62.4]) and UPA (aOR 5.22 [1.0-27.2]) were associated with complete TM remission. Rates of segmental TM response were greater for colonic than ileal disease in UST/RZB (88% vs 47%, p=0.038), but no different in TNF/UPA. Patients started on UST/RZB after >1 failed prior AT had a trend for lower rates of TM outcomes (NS), while number of prior therapies had no impact on UPA response or remission rates.
Discussion: Post-induction TM outcomes are achievable across AT: 2/3 of patients achieve segmental TM response and 1/3 achieve complete TM remission. While TM outcomes should be used to guide therapy optimization, post-induction thresholds should be customized based on each AT and baseline IUS severity.

Figure: Post Induction Segmental Transmural Response and Remissio
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Matthew Smyth indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Dolinger: Neurologica – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant.
Marla Dubinsky: AbbVie – Consultant. Abivax – Consultant. Arena – Consultant. AstraZeneca – Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Eli Lilly – Consultant. Genentech – Consultant. Gilead – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant. Pfizer Inc – Consultant. Prometheus Labs – Consultant. Takeda – Consultant.
Matthew Smyth, MD1, Michael Dolinger, MD, MBA2, Marla C. Dubinsky, MD2. P2562 - Early Sonographic Transmural Remission as a Post-Induction Target Across Advanced Therapies in Crohn’s Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

