Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1799 - IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis Presenting as Cholangiocarcinoma: A Diagnostic Challenge
Monday, October 28, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Luke Stachler, MD
University of Florida College of Medicine
Jacksonville, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Luke Stachler, MD, Raafat Makary, MD, PhD, Lauren N.. Stemboroski, DO, Maged A.. Ghali, MD, Neha Agrawal, MD
University of Florida College of Medicine, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a complex immunoinflammatory condition that can affect multiple organs. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) affects the biliary tree and can be mistaken for other inflammatory or malignant processes—mainly pancreatic cancer, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and cholangiocarcinoma (CC). We present a case of a woman with features of obstructive jaundice, highly suspicious for CC.
Case Description/Methods: A 58-year-old woman with hypothyroidism presented with several days of nausea, cola colored urine, and jaundice. Abdominal imaging involving computed tomography and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) revealed a 3.7 cm hepatic duct stricture and a hypo-enhancing lesion of the common hepatic duct at the hilum, causing mass effect on nearby hepatic ducts with associated regional lymphadenopathy—features highly suggestive of CC. Laboratory data included total bilirubin (T bili) of 16.5 mg/dL, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) of 133 IU/L, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) of 104 IU/L, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) of 331 IU/L, and CA 19-9 of 196 U/mL. Diagnosed as CC based on imaging, a left partial hepatectomy and extrahepatic duct resection with Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy were performed. Surgical pathology was negative for CC but showed IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis. Serum IgG4 levels were elevated at 101 mg/dL. The patient had several post-surgical complications including bile leak and sepsis requiring two percutaneous drains and prolonged hospital stays. While biliary drains were in, liver function tests improved. They were removed eight months post-op when her AST, ALT, ALP and T bili began uptrending. She responded well to high dose prednisone and azathioprine (AZA).
Discussion: For accurate diagnosis of IgG4-SC, it is crucial to exclude its most common mimics since management differs. While MRCP may suffice in some cases, most patients require endoscopic ultrasound-guided liver biopsy or fine-needle aspiration of the pancreas, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, or intraductal ultrasound. At present, there are two diagnostic criteria: the HISORt criteria (primarily used in Europe and USA), and the Japan Biliary Association criteria (mainly used in Japan and China). Both criteria require four diagnostic methods: a typical cholangiogram, elevated IgG4 antibodies, systemic involvement, and histopathology. IgG4-SC responds well to steroid therapy. Prognosis is often inversely related to the extent of multi-organ involvement.
Disclosures:
Luke Stachler, MD, Raafat Makary, MD, PhD, Lauren N.. Stemboroski, DO, Maged A.. Ghali, MD, Neha Agrawal, MD. P1799 - IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis Presenting as Cholangiocarcinoma: A Diagnostic Challenge, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
University of Florida College of Medicine, Jacksonville, FL
Introduction: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a complex immunoinflammatory condition that can affect multiple organs. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) affects the biliary tree and can be mistaken for other inflammatory or malignant processes—mainly pancreatic cancer, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and cholangiocarcinoma (CC). We present a case of a woman with features of obstructive jaundice, highly suspicious for CC.
Case Description/Methods: A 58-year-old woman with hypothyroidism presented with several days of nausea, cola colored urine, and jaundice. Abdominal imaging involving computed tomography and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) revealed a 3.7 cm hepatic duct stricture and a hypo-enhancing lesion of the common hepatic duct at the hilum, causing mass effect on nearby hepatic ducts with associated regional lymphadenopathy—features highly suggestive of CC. Laboratory data included total bilirubin (T bili) of 16.5 mg/dL, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) of 133 IU/L, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) of 104 IU/L, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) of 331 IU/L, and CA 19-9 of 196 U/mL. Diagnosed as CC based on imaging, a left partial hepatectomy and extrahepatic duct resection with Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy were performed. Surgical pathology was negative for CC but showed IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis. Serum IgG4 levels were elevated at 101 mg/dL. The patient had several post-surgical complications including bile leak and sepsis requiring two percutaneous drains and prolonged hospital stays. While biliary drains were in, liver function tests improved. They were removed eight months post-op when her AST, ALT, ALP and T bili began uptrending. She responded well to high dose prednisone and azathioprine (AZA).
Discussion: For accurate diagnosis of IgG4-SC, it is crucial to exclude its most common mimics since management differs. While MRCP may suffice in some cases, most patients require endoscopic ultrasound-guided liver biopsy or fine-needle aspiration of the pancreas, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, or intraductal ultrasound. At present, there are two diagnostic criteria: the HISORt criteria (primarily used in Europe and USA), and the Japan Biliary Association criteria (mainly used in Japan and China). Both criteria require four diagnostic methods: a typical cholangiogram, elevated IgG4 antibodies, systemic involvement, and histopathology. IgG4-SC responds well to steroid therapy. Prognosis is often inversely related to the extent of multi-organ involvement.

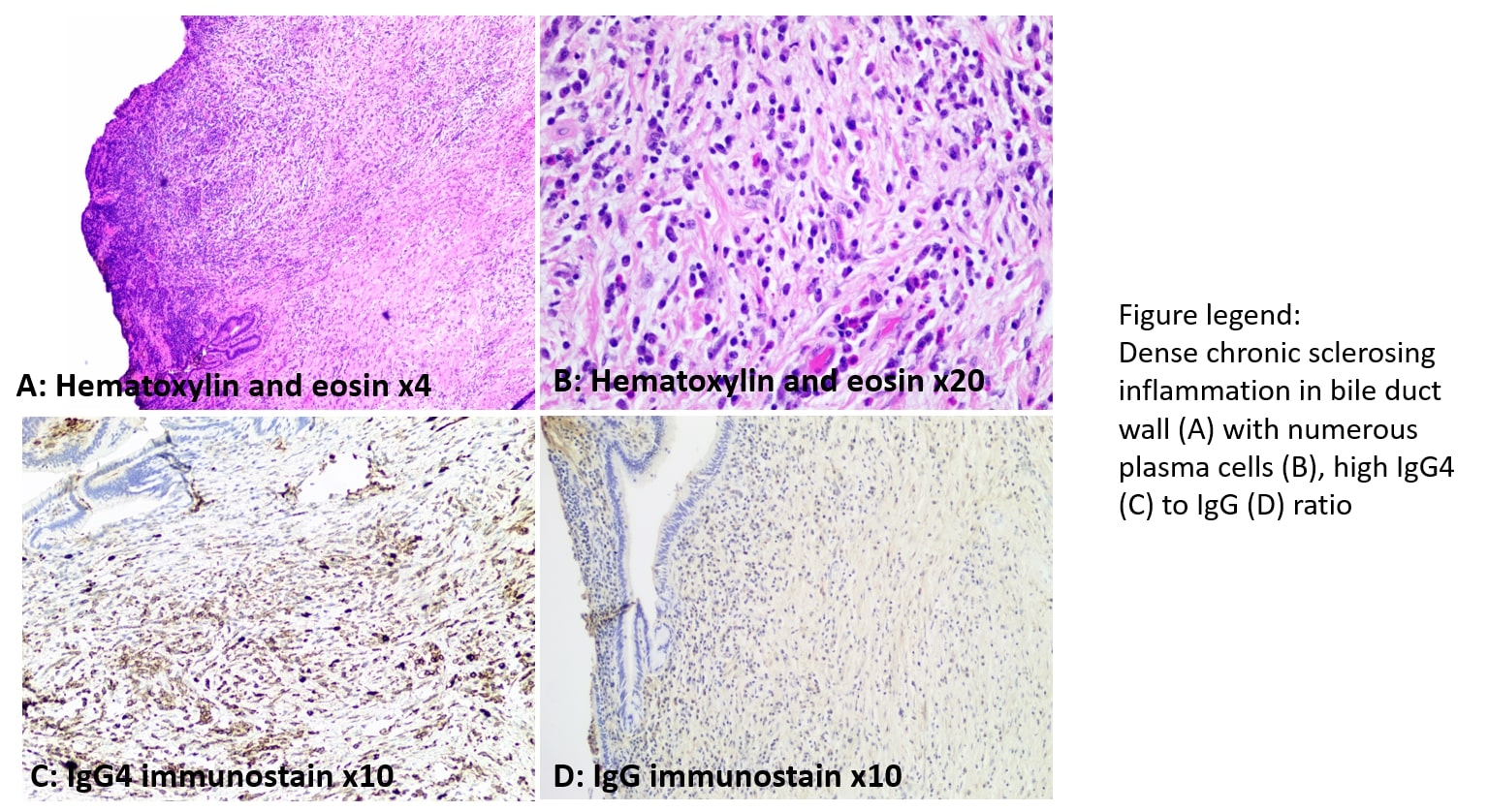
Figure: Excised bile duct tissue sample. Dense chronic sclerosing inflammation in bile duct wall (A) with numerous plasma cells (B), high IgG4 (C) to IgG (D) ratio
Disclosures:
Luke Stachler indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raafat Makary indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lauren Stemboroski indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maged Ghali: Gilead – Grant/Research Support. Madrigal – Grant/Research Support. Novo Nordisk – Grant/Research Support.
Neha Agrawal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Luke Stachler, MD, Raafat Makary, MD, PhD, Lauren N.. Stemboroski, DO, Maged A.. Ghali, MD, Neha Agrawal, MD. P1799 - IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis Presenting as Cholangiocarcinoma: A Diagnostic Challenge, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
