Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0068 - A Study of Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Proof-of-Concept Efficacy of a Liquid Oral Formulation of NHS7108: A Novel Recombinant Lipase for the Treatment of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- CD
Carmine D'Urzo, MD
Nestlé Health Science
Lausanne, Vaud, Switzerland
Presenting Author(s)
Carmine D'Urzo, MD1, Chris Wynne, MD2, John Windsor, MD3, Edward Edson, BSc4, Hans-Juergen Woerle, MD4
1Nestlé Health Science, Lausanne, Vaud, Switzerland; 2New Zealand Clinical Research, Christchurch, Canterbury, New Zealand; 3University of New Zealand, Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand; 4Nestle Health Science, Lausanne, Vaud, Switzerland
Introduction: Porcine-derived pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy for patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) involves a high daily pill burden, often affecting compliance and resulting in suboptimal outcomes. NHS7108 is an oral, pH-stable, gastric-acid-resistant, highly potent, recombinant lipase derived from Bacillus thermoamylovans with the potential to optimize convenience, compliance and efficacy.
Methods: This phase 1a/1b randomized, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled study comprised three parts. Part A, single ascending dose in Healthy Volunteers (HV); Part B, multiple ascending doses in HV; Part C, single-dose, two-way crossover in severe EPI patients. Dose escalation and transition across study parts was dependent on safety and pharmacokinetic (PK) data. 13C-mixed triglyceride breath test served as the proof-of-concept (PoC) efficacy readout in Part C. The primary endpoints were safety parameters including adverse events (AEs) and changes in clinical laboratory tests, vital signs, 12-lead ECG, and physical examination from baseline.
Results: Part A. Of 30 subjects (mean [SD] age 28.9 [9.13] years, 6 male, mean [SD] BMI 23.99 [3.332] kg/m2), 12 (40%) had ≥1 AE (NHS7108=10; PBO=2; all mild except for 1 moderate AE in the NHS7108 group). The most frequent drug-related AE was headache.
Part B. Of 18 subjects, (mean [SD] age 31.1 [8.47] years, 6 male, mean [SD] BMI 25.22 [3.166] kg/m2), 15 (83.3%) had ≥1 AE (NHS7108=10; PBO=5), all mild or moderate. The most frequent drug-related AE was nausea.
Part C. For the 6 subjects, (mean [SD] age 62.3 [13.00] years, 2 male, mean [SD] BMI 22.87 [3.233] kg/m2) more AEs (6 events in 5 subjects) were observed when receiving PBO than when receiving NHS7108 (2 events in 1 subject). All were mild; no drug-related AE was reported.
Adverse Events: Overall, there were no severe AEs, serious AEs, or AEs requiring discontinuation; and no evident dose dependency.
PK analysis: NHS7108 was not detectable in blood at any of the administered doses.
Breath test:
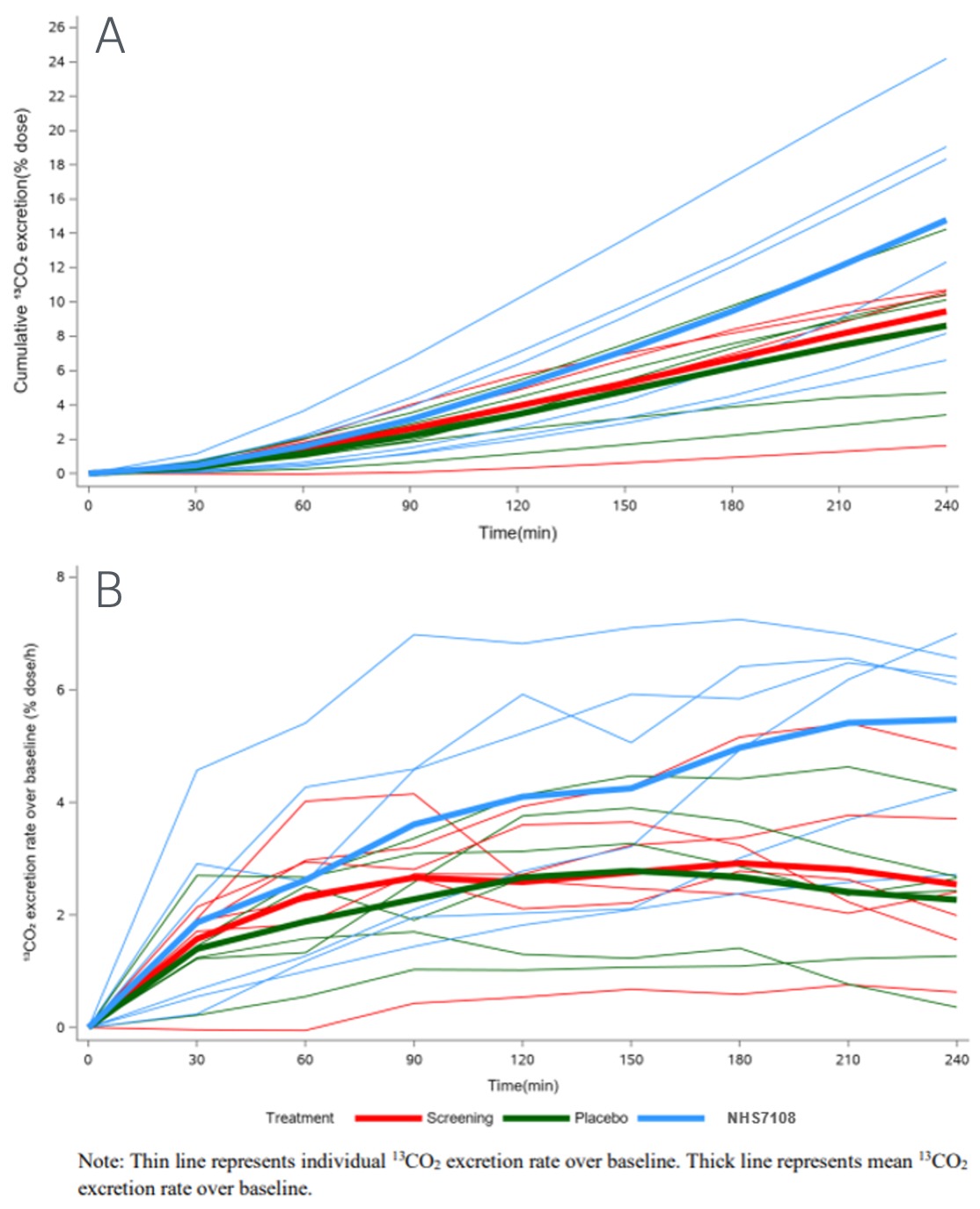
The mean 240min cumulative 13CO2 excretion in the NHS7108 group (14.8% dose) was 72% higher than PBO (8.6% dose). Excretion rate curves showed generally larger and more sustained lipid absorption profiles with NHS7108 than PBO.
Discussion: NHS7108, a novel oral recombinant lipase, was well tolerated at all tested doses and without systemic absorption. Breath testing confirmed improved fat absorption in patients with severe EPI.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Carmine D'Urzo, MD1, Chris Wynne, MD2, John Windsor, MD3, Edward Edson, BSc4, Hans-Juergen Woerle, MD4. P0068 - A Study of Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Proof-of-Concept Efficacy of a Liquid Oral Formulation of NHS7108: A Novel Recombinant Lipase for the Treatment of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Nestlé Health Science, Lausanne, Vaud, Switzerland; 2New Zealand Clinical Research, Christchurch, Canterbury, New Zealand; 3University of New Zealand, Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand; 4Nestle Health Science, Lausanne, Vaud, Switzerland
Introduction: Porcine-derived pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy for patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI) involves a high daily pill burden, often affecting compliance and resulting in suboptimal outcomes. NHS7108 is an oral, pH-stable, gastric-acid-resistant, highly potent, recombinant lipase derived from Bacillus thermoamylovans with the potential to optimize convenience, compliance and efficacy.
Methods: This phase 1a/1b randomized, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled study comprised three parts. Part A, single ascending dose in Healthy Volunteers (HV); Part B, multiple ascending doses in HV; Part C, single-dose, two-way crossover in severe EPI patients. Dose escalation and transition across study parts was dependent on safety and pharmacokinetic (PK) data. 13C-mixed triglyceride breath test served as the proof-of-concept (PoC) efficacy readout in Part C. The primary endpoints were safety parameters including adverse events (AEs) and changes in clinical laboratory tests, vital signs, 12-lead ECG, and physical examination from baseline.
Results: Part A. Of 30 subjects (mean [SD] age 28.9 [9.13] years, 6 male, mean [SD] BMI 23.99 [3.332] kg/m2), 12 (40%) had ≥1 AE (NHS7108=10; PBO=2; all mild except for 1 moderate AE in the NHS7108 group). The most frequent drug-related AE was headache.
Part B. Of 18 subjects, (mean [SD] age 31.1 [8.47] years, 6 male, mean [SD] BMI 25.22 [3.166] kg/m2), 15 (83.3%) had ≥1 AE (NHS7108=10; PBO=5), all mild or moderate. The most frequent drug-related AE was nausea.
Part C. For the 6 subjects, (mean [SD] age 62.3 [13.00] years, 2 male, mean [SD] BMI 22.87 [3.233] kg/m2) more AEs (6 events in 5 subjects) were observed when receiving PBO than when receiving NHS7108 (2 events in 1 subject). All were mild; no drug-related AE was reported.
Adverse Events: Overall, there were no severe AEs, serious AEs, or AEs requiring discontinuation; and no evident dose dependency.
PK analysis: NHS7108 was not detectable in blood at any of the administered doses.
Breath test:
The mean 240min cumulative 13CO2 excretion in the NHS7108 group (14.8% dose) was 72% higher than PBO (8.6% dose). Excretion rate curves showed generally larger and more sustained lipid absorption profiles with NHS7108 than PBO.
Discussion: NHS7108, a novel oral recombinant lipase, was well tolerated at all tested doses and without systemic absorption. Breath testing confirmed improved fat absorption in patients with severe EPI.

Figure: Cumulative 13CO2 excretion (A) and excretion rate over baseline (B)
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Carmine D'Urzo: Nestlé Health Science – Employee.
Chris Wynne indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Windsor indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Edward Edson: Nestlé Health Science – Employee.
Hans-Juergen Woerle: Nestlé Health Science – Employee.
Carmine D'Urzo, MD1, Chris Wynne, MD2, John Windsor, MD3, Edward Edson, BSc4, Hans-Juergen Woerle, MD4. P0068 - A Study of Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Proof-of-Concept Efficacy of a Liquid Oral Formulation of NHS7108: A Novel Recombinant Lipase for the Treatment of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
