Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0176 - IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis Mimicking a Gallbladder Mass With Biliary Infiltration
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- DA
Daksh Ahluwalia, MD
John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County
Chicago, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Daksh Ahluwalia, MD, Victor Udechukwu, MD, Bhanu Siva Mohan Pinnam, MD
John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL
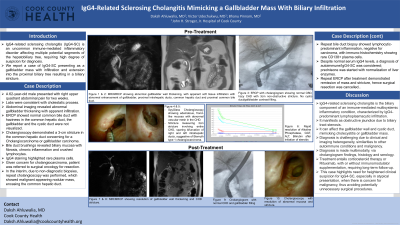
Introduction: IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) is an uncommon immune-mediated inflammatory disorder affecting multiple potential segments of the hepatobiliary tree, requiring high degree of suspicion for diagnosis. We report a case of IgG4-SC presenting as a gallbladder mass with infiltration and extension into the proximal biliary tree resulting in a biliary stricture.
Case Description/Methods: A 62-year-old male presented with right upper quadrant abdominal pain for two weeks. Labs were consistent with cholestatic process. Abdominal imaging revealed abnormal gallbladder thickening with apparent infiltration. ERCP showed normal common bile duct with haziness in the common hepatic duct, the gallbladder and the cystic duct were not visualized. Cholangioscopy demonstrated a 3-cm stricture in the common hepatic duct concerning for a Cholangiocarcinoma or gallbladder carcinoma. Bile duct brushings revealed biliary mucosa with fibrosis, chronic inflammation and crushed lymphocytes. IgG4 staining highlighted rare plasma cells. He was referred to surgery for resection. Due to non-diagnostic biopsies, repeat cholangioscopy showed malignant appearing nodular mass, encasing the common hepatic duct. Bile duct biopsy showed lymphocytic-predominant inflammation, negative for carcinoma, with immuno-histochemistry showing rare CD138+ plasma cells. Despite normal IgG4 levels, a diagnosis of autoimmune/IgG4-SC was considered; prednisone was started with normalization of liver enzymes. Repeat ERCP after treatment demonstrated remission of mass and stricture, hence surgical resection was cancelled.
Discussion: IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis is the biliary component of an immune-mediated multisystemic inflammatory condition, characterized by IgG4-predominant lymphoplasmacytic infiltration. It manifests as obstructive jaundice due to biliary tract stenosis. It can affect the gallbladder wall and cystic duct, mimicking cholecystitis or gallbladder mass. Diagnosis is challenging due to clinical and imaging heterogeneity, similarities to other autoimmune conditions and malignancy. Diagnosis is made multimodally, via cholangiogram findings, histology and serology. Treatment entails corticosteroid therapy or Rituximab, with or without immunomodulator supplementation, requiring long-term follow-up. This case highlights need for heightened clinical suspicion for IgG4-SC, especially in atypical presentation, when there is concern for malignancy, thus avoiding potentially unnecessary surgical procedures.
Disclosures:
Daksh Ahluwalia, MD, Victor Udechukwu, MD, Bhanu Siva Mohan Pinnam, MD. P0176 - IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis Mimicking a Gallbladder Mass With Biliary Infiltration, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL
Introduction: IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) is an uncommon immune-mediated inflammatory disorder affecting multiple potential segments of the hepatobiliary tree, requiring high degree of suspicion for diagnosis. We report a case of IgG4-SC presenting as a gallbladder mass with infiltration and extension into the proximal biliary tree resulting in a biliary stricture.
Case Description/Methods: A 62-year-old male presented with right upper quadrant abdominal pain for two weeks. Labs were consistent with cholestatic process. Abdominal imaging revealed abnormal gallbladder thickening with apparent infiltration. ERCP showed normal common bile duct with haziness in the common hepatic duct, the gallbladder and the cystic duct were not visualized. Cholangioscopy demonstrated a 3-cm stricture in the common hepatic duct concerning for a Cholangiocarcinoma or gallbladder carcinoma. Bile duct brushings revealed biliary mucosa with fibrosis, chronic inflammation and crushed lymphocytes. IgG4 staining highlighted rare plasma cells. He was referred to surgery for resection. Due to non-diagnostic biopsies, repeat cholangioscopy showed malignant appearing nodular mass, encasing the common hepatic duct. Bile duct biopsy showed lymphocytic-predominant inflammation, negative for carcinoma, with immuno-histochemistry showing rare CD138+ plasma cells. Despite normal IgG4 levels, a diagnosis of autoimmune/IgG4-SC was considered; prednisone was started with normalization of liver enzymes. Repeat ERCP after treatment demonstrated remission of mass and stricture, hence surgical resection was cancelled.
Discussion: IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis is the biliary component of an immune-mediated multisystemic inflammatory condition, characterized by IgG4-predominant lymphoplasmacytic infiltration. It manifests as obstructive jaundice due to biliary tract stenosis. It can affect the gallbladder wall and cystic duct, mimicking cholecystitis or gallbladder mass. Diagnosis is challenging due to clinical and imaging heterogeneity, similarities to other autoimmune conditions and malignancy. Diagnosis is made multimodally, via cholangiogram findings, histology and serology. Treatment entails corticosteroid therapy or Rituximab, with or without immunomodulator supplementation, requiring long-term follow-up. This case highlights need for heightened clinical suspicion for IgG4-SC, especially in atypical presentation, when there is concern for malignancy, thus avoiding potentially unnecessary surgical procedures.
Disclosures:
Daksh Ahluwalia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Victor Udechukwu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhanu Siva Mohan Pinnam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daksh Ahluwalia, MD, Victor Udechukwu, MD, Bhanu Siva Mohan Pinnam, MD. P0176 - IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis Mimicking a Gallbladder Mass With Biliary Infiltration, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
