Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0217 - From Diagnosis to Surgery: Exploring Preoperative Factors and Treatment Delays in Colorectal Cancer Patients at an Urban Medical Center
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Ahmad Alnasarat, MD
DMC Sinai-Grace Hospital
Detroit, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Ahmad Alnasarat, MD1, Talin Darian, MD2, Awni Shahait, MD3, Gamal Mostafa, MD2
1DMC Sinai-Grace Hospital, Farmington Hills, MI; 2Corewell Health, Dearborn, MI; 3Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IL
Introduction: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer in the United States. Delays between diagnosis and treatment initiation may influence patient outcomes negatively. We aimed to examine various preoperative variables Impact on the timing between diagnosis and surgical resection of colorectal cancer.
Methods: Data on patients who underwent surgical resection between 2005 and 2014 were analyzed retrospectively. Patients who did not have surgery or had non-curative surgical resection were excluded. Collected data included demographics (gender, race, and insurance status), comorbidities, and method of diagnosis. We defined treatment delay as more than 30 days between the confirmation of colorectal cancer through biopsy and surgical resection. Unpaired t-test analysis was used for continuous variables and categorical variables with Pearson Chi-squared or Fisher exact test as appropriate and p< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
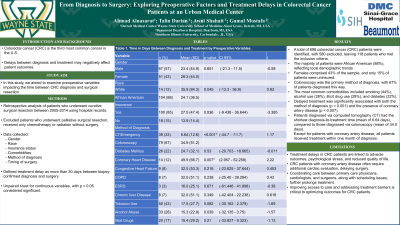
Results: A total of 118 patients in this single medical center database met our inclusion criteria. Majority of the patients were African American (88%) and males (57%). Only 15% did not have insurance. Colonoscopy was the commonest method of diagnosis (67%). Smoking (44%), Alcohol (28%), illicit drug use (28%) and DM (22%) were the most prevalent comorbidities. Delayed treatment was strongly associated with method of diagnosis (p< 0.001) and coronary artery disease (p< 0.007), as summarized in Table 1. Patients who were diagnosed by Computed Tomography had the shortest diagnosis-treatment time (mean 6.64 days) as compared to colonoscopy (mean 34.0 days). Except for coronary artery disease patients, all patients received treatment approximately within a month of diagnosis.
Discussion: Delays in initiation of treatment in CRC patients are associated with increased risk of adverse outcomes, psychological stress, and poor quality of life. CRC patients with coronary artery disease often need further cardiac testing and evaluation prior to surgery. Coordinating these tests among primary care physicians, cardiologists, and surgeons, along with fitting into clinic and operative schedules, further delays treatment. Therefore, improving medical accessibility and addressing treatment barriers are crucial to optimize patient care and enhancing outcomes.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Ahmad Alnasarat, MD1, Talin Darian, MD2, Awni Shahait, MD3, Gamal Mostafa, MD2. P0217 - From Diagnosis to Surgery: Exploring Preoperative Factors and Treatment Delays in Colorectal Cancer Patients at an Urban Medical Center, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1DMC Sinai-Grace Hospital, Farmington Hills, MI; 2Corewell Health, Dearborn, MI; 3Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IL
Introduction: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer in the United States. Delays between diagnosis and treatment initiation may influence patient outcomes negatively. We aimed to examine various preoperative variables Impact on the timing between diagnosis and surgical resection of colorectal cancer.
Methods: Data on patients who underwent surgical resection between 2005 and 2014 were analyzed retrospectively. Patients who did not have surgery or had non-curative surgical resection were excluded. Collected data included demographics (gender, race, and insurance status), comorbidities, and method of diagnosis. We defined treatment delay as more than 30 days between the confirmation of colorectal cancer through biopsy and surgical resection. Unpaired t-test analysis was used for continuous variables and categorical variables with Pearson Chi-squared or Fisher exact test as appropriate and p< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: A total of 118 patients in this single medical center database met our inclusion criteria. Majority of the patients were African American (88%) and males (57%). Only 15% did not have insurance. Colonoscopy was the commonest method of diagnosis (67%). Smoking (44%), Alcohol (28%), illicit drug use (28%) and DM (22%) were the most prevalent comorbidities. Delayed treatment was strongly associated with method of diagnosis (p< 0.001) and coronary artery disease (p< 0.007), as summarized in Table 1. Patients who were diagnosed by Computed Tomography had the shortest diagnosis-treatment time (mean 6.64 days) as compared to colonoscopy (mean 34.0 days). Except for coronary artery disease patients, all patients received treatment approximately within a month of diagnosis.
Discussion: Delays in initiation of treatment in CRC patients are associated with increased risk of adverse outcomes, psychological stress, and poor quality of life. CRC patients with coronary artery disease often need further cardiac testing and evaluation prior to surgery. Coordinating these tests among primary care physicians, cardiologists, and surgeons, along with fitting into clinic and operative schedules, further delays treatment. Therefore, improving medical accessibility and addressing treatment barriers are crucial to optimize patient care and enhancing outcomes.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Ahmad Alnasarat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Talin Darian indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Awni Shahait indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gamal Mostafa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmad Alnasarat, MD1, Talin Darian, MD2, Awni Shahait, MD3, Gamal Mostafa, MD2. P0217 - From Diagnosis to Surgery: Exploring Preoperative Factors and Treatment Delays in Colorectal Cancer Patients at an Urban Medical Center, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
