Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0288 - Endoscopic and Surgical Strategies for Rectal Foreign Body Removal: Case Insights
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
- RR
Rajmohan Rammohan, MD
Nassau University Medical Center
East Meadow, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: Rectal foreign bodies present a complex and delicate medical challenge. The insertion of objects into the rectum can lead to a variety of serious complications, including trauma to the surrounding tissue, which may result in infections, tears, or bleeding. Statistically, individuals most commonly affected range in age from their 30s to their 90s, with the average age of presentation between 44 and 48 years. There is a noted predominance of cases among males. Due to the intricate nature of such cases, managing a rectal foreign body requires a meticulous and stepwise approach. This includes precise diagnosis, careful removal of the object, and thorough post-extraction evaluation to ensure the patient's safety and recovery. Such a methodical approach is critical in preventing further complications and ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
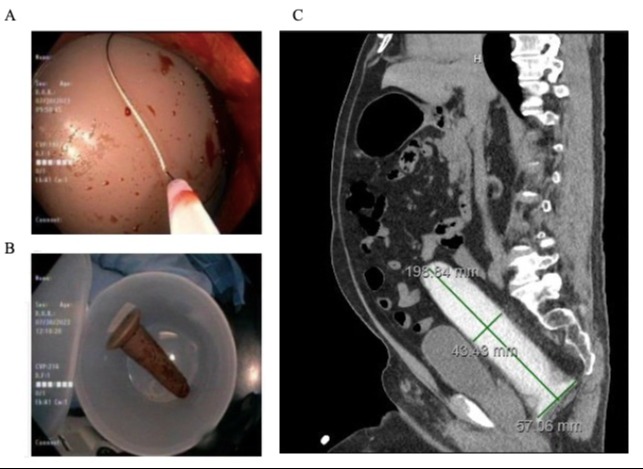
Case Description/Methods: This case report describes the surgical removal of a 20 cm x 4.5 cm cylindrical rectal foreign object with a 7cm x 7cm base, following failed endoscopic attempts through colonoscopy. GI specialists decided on surgical intervention when multiple endoscopic removals were unsuccessful. The surgery involved making an infra-umbilical vertical midline incision to open the abdominal cavity. The foreign body, located in the sigmoid colon, was manually compressed and pushed inferiorly toward the rectum, allowing for successful extraction from the anus.
Discussion: Rectal foreign bodies pose a complex medical challenge, often exacerbated by the patient's embarrassment or reluctance to seek help. Addressing these emotional barriers is crucial in meeting the unique needs of these patients. Clinicians must exercise sensitivity during history taking and physical examinations to maintain respect and empathy. Prompt evaluation of a rectal foreign body is essential, utilizing appropriate imaging techniques to assess the object's size and shape. Medical professionals should remain vigilant for potential complications such as perforation and peritonitis. Post-removal, regular follow-up examinations are vital to check for signs of perforation. With careful consideration of these factors, rectal foreign bodies can be efficiently removed and effectively managed through a comprehensive, phased approach.
Disclosures:
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA. P0288 - Endoscopic and Surgical Strategies for Rectal Foreign Body Removal: Case Insights, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: Rectal foreign bodies present a complex and delicate medical challenge. The insertion of objects into the rectum can lead to a variety of serious complications, including trauma to the surrounding tissue, which may result in infections, tears, or bleeding. Statistically, individuals most commonly affected range in age from their 30s to their 90s, with the average age of presentation between 44 and 48 years. There is a noted predominance of cases among males. Due to the intricate nature of such cases, managing a rectal foreign body requires a meticulous and stepwise approach. This includes precise diagnosis, careful removal of the object, and thorough post-extraction evaluation to ensure the patient's safety and recovery. Such a methodical approach is critical in preventing further complications and ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
Case Description/Methods: This case report describes the surgical removal of a 20 cm x 4.5 cm cylindrical rectal foreign object with a 7cm x 7cm base, following failed endoscopic attempts through colonoscopy. GI specialists decided on surgical intervention when multiple endoscopic removals were unsuccessful. The surgery involved making an infra-umbilical vertical midline incision to open the abdominal cavity. The foreign body, located in the sigmoid colon, was manually compressed and pushed inferiorly toward the rectum, allowing for successful extraction from the anus.
Discussion: Rectal foreign bodies pose a complex medical challenge, often exacerbated by the patient's embarrassment or reluctance to seek help. Addressing these emotional barriers is crucial in meeting the unique needs of these patients. Clinicians must exercise sensitivity during history taking and physical examinations to maintain respect and empathy. Prompt evaluation of a rectal foreign body is essential, utilizing appropriate imaging techniques to assess the object's size and shape. Medical professionals should remain vigilant for potential complications such as perforation and peritonitis. Post-removal, regular follow-up examinations are vital to check for signs of perforation. With careful consideration of these factors, rectal foreign bodies can be efficiently removed and effectively managed through a comprehensive, phased approach.

Figure: A. Foreign body in rectum
B. After removal of foreign body
C. Foreign Body on CT Imaging
B. After removal of foreign body
C. Foreign Body on CT Imaging
Disclosures:
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Reshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Greeshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Melvin Joy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dilman Natt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leeza Pannikodu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhishek Tadikonda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Winghang Lau indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jiten Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Mustacchia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA. P0288 - Endoscopic and Surgical Strategies for Rectal Foreign Body Removal: Case Insights, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
