Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P0410 - The Role of Chatbot’s in Enhancing Post-Colonoscopy Patient Follow-Up: A Quantitative Analysis
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
- RR
Rajmohan Rammohan, MD
Nassau University Medical Center
East Meadow, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: In this study, we evaluate the effectiveness of chatbot technology, specifically ChatGPT 4.0 and Google GEMINI, in providing post-colonoscopy follow-up information to patients. Utilizing a structured questionnaire rated by independent reviewers on a 1-10 Likert scale, we explored three main metrics: accuracy, reliability, and user interface to compare the performance of each chatbot in handling patient inquiries about polyps and post-procedure care. This research aims to ascertain if these AI tools can reliably supplement traditional patient follow-up methods.
Methods: The study evaluated if patients could trust ChatGPT and Google GEMINI for post-colonoscopy queries using a questionnaire rated by five reviewers on a 1-10 scale. We compared the chatbots on accuracy, reliability, and user interface based on patient questions about polyps and follow-up care. Data analysis involved descriptive statistics and t-tests to check significant differences between the chatbots, with p-values determining statistical significance.
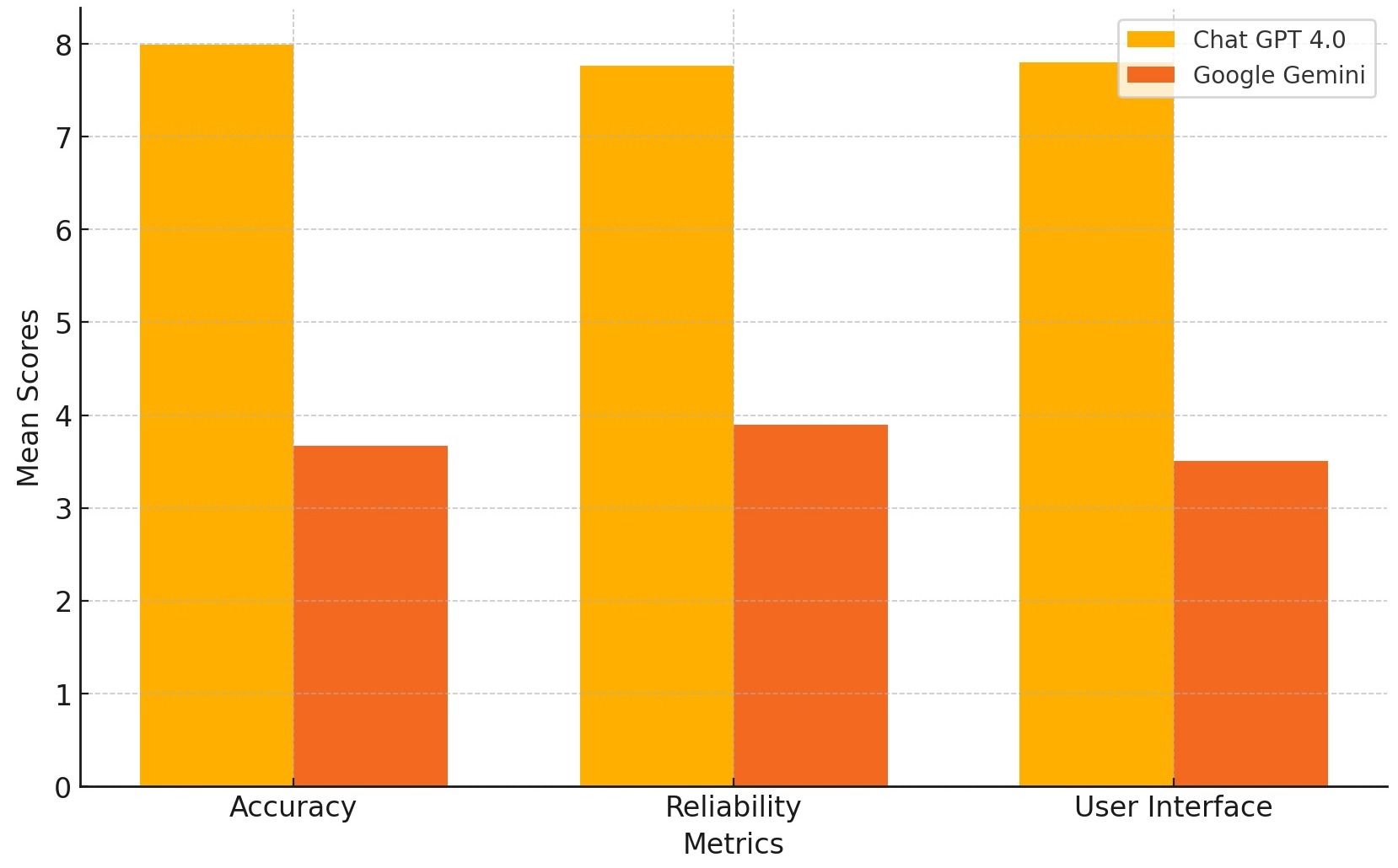
Results: Comparative analysis of ChatGPT 4.0 and Google Gemini across accuracy, reliability, and user interface showed ChatGPT 4.0 with higher scores: accuracy 7.99 ± 0.71, reliability 7.76 ± 0.63, user interface 7.80 ± 0.67. Google Gemini scored lower: accuracy 3.67± 1.42, reliability 3.90 ± 1.17, user interface 3.51 ± 0.69. T-tests confirmed ChatGPT 4.0 significantly outperforms Google Gemini, suggesting its better suitability for patient queries post-colonoscopy
Discussion: The study shows ChatGPT 4.0 outperforms Google GEMINI in accuracy, reliability, and usability for post-colonoscopy care. Notably better at addressing queries about polyps and follow-ups, ChatGPT 4.0 supports integrating AI chatbots to enhance traditional patient care methods, ensuring timely, accurate information. Further research is needed on the long-term effects of chatbot-assisted care on clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA. P0410 - The Role of Chatbot’s in Enhancing Post-Colonoscopy Patient Follow-Up: A Quantitative Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: In this study, we evaluate the effectiveness of chatbot technology, specifically ChatGPT 4.0 and Google GEMINI, in providing post-colonoscopy follow-up information to patients. Utilizing a structured questionnaire rated by independent reviewers on a 1-10 Likert scale, we explored three main metrics: accuracy, reliability, and user interface to compare the performance of each chatbot in handling patient inquiries about polyps and post-procedure care. This research aims to ascertain if these AI tools can reliably supplement traditional patient follow-up methods.
Methods: The study evaluated if patients could trust ChatGPT and Google GEMINI for post-colonoscopy queries using a questionnaire rated by five reviewers on a 1-10 scale. We compared the chatbots on accuracy, reliability, and user interface based on patient questions about polyps and follow-up care. Data analysis involved descriptive statistics and t-tests to check significant differences between the chatbots, with p-values determining statistical significance.
Results: Comparative analysis of ChatGPT 4.0 and Google Gemini across accuracy, reliability, and user interface showed ChatGPT 4.0 with higher scores: accuracy 7.99 ± 0.71, reliability 7.76 ± 0.63, user interface 7.80 ± 0.67. Google Gemini scored lower: accuracy 3.67± 1.42, reliability 3.90 ± 1.17, user interface 3.51 ± 0.69. T-tests confirmed ChatGPT 4.0 significantly outperforms Google Gemini, suggesting its better suitability for patient queries post-colonoscopy
Discussion: The study shows ChatGPT 4.0 outperforms Google GEMINI in accuracy, reliability, and usability for post-colonoscopy care. Notably better at addressing queries about polyps and follow-ups, ChatGPT 4.0 supports integrating AI chatbots to enhance traditional patient care methods, ensuring timely, accurate information. Further research is needed on the long-term effects of chatbot-assisted care on clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction

Figure: ChatBots outcome with relation to colon polyp
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Reshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Greeshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Melvin Joy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dilman Natt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leeza Pannikodu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhishek Tadikonda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Winghang Lau indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jiten Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishnaiyer Subramani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Mustacchia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA. P0410 - The Role of Chatbot’s in Enhancing Post-Colonoscopy Patient Follow-Up: A Quantitative Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
