Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P0442 - Diagnostic Accuracy of Cell-Free DNA Blood-Based Tests in Screening for Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Prabhat Kumar, MD
Cleveland Clinic Foundation
Richmond, VA
Presenting Author(s)
Prabhat Kumar, MD1, Archana Kharel, MD1, Umesh Bhagat, MD1, Navkiran Randhawa, DO2, Asfand Yar Cheema, MD1, Bobak Moazzami, MD3, Amit Hudgi, MD4, Babu Mohan, MD5, Subbaramiah Sridhar, MBBS, MPH6, Humberto Sifuentes, MD6
1Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 2Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, Augusta, GA; 3Northside Hospital Gwinnett, Atlanta, GA; 4Augusta University Medical Center, Augusta, GA; 5Orlando Gastroenterology PA, Orlando, FL; 6Augusta University, Augusta, GA
Introduction: Population-based colorectal cancer (CRC) screenings have demonstrated significant improvement in mortality. Recently, cell-free DNA (cfDNA) blood-based tests have emerged as a non-invasive alternative, offering the potential for higher compliance and earlier detection. Recent trials, including the ECLIPSE trial, have demonstrated promising results in this field. This meta-analysis aims to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of cfDNA blood-based tests in detecting colorectal cancer.
Methods: A recursive literature search was conducted across multiple databases, including MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane, from inception to May 2024. Studies included in the meta-analysis were those that assessed the diagnostic performance of cfDNA blood-based tests for CRC screening [Table]. Data on sensitivity, specificity, true positive (TP), and true negative (TN) were extracted and pooled using random effects model. Heterogeneity between study-specific estimates was assessed using the I2 statistics.
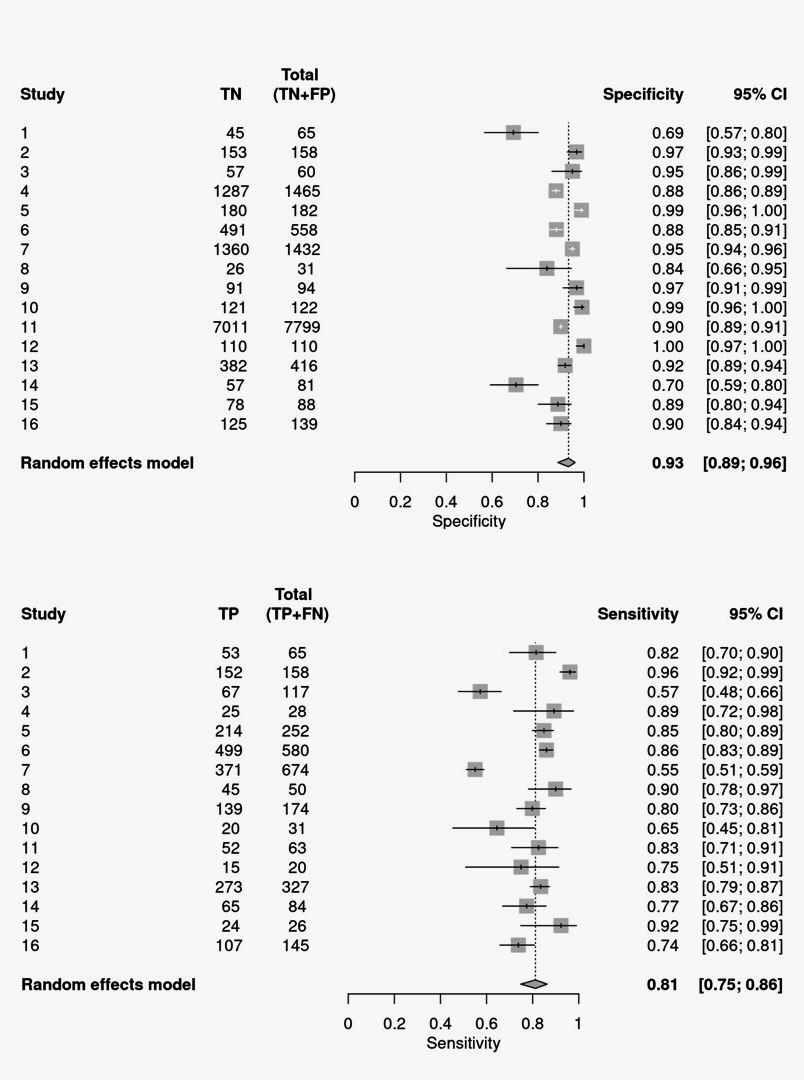
Results: This exploratory meta-analysis included 16 studies involving 15,591 participants. The pooled sensitivity and specificity of cfDNA blood-based tests for CRC screening were 0.81 (95% CI: 0.75-0.86) and 0.93 (95% CI: 0.89-0.96), respectively [Image]. The area under the curve (AUC) for the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) indicated high overall diagnostic accuracy. Our study demonstrates the pooled positive likelihood ratio (PLR) and negative likelihood ratio (NLR) of the circulating cfDNA assay was 12.104 (95% CI, 7.044– 20.798) and 0.201 (95% CI, 0.148–0.274), respectively. The pooled Diagnostic Odds ratio (DOR) in our study was 60.173 (95% CI, 30.268–119.622), indicating a relatively high level of overall accuracy.
Discussion: Overall, a high level of diagnostic accuracy was demonstrated in this study evaluating the cfDNA assay in CRC screening. Future studies are warranted to compare its performance with colonoscopy with regards to overall reduction in CRC-related mortality. Furthermore, cost-effectiveness data is needed to help establish its role in CRC screening.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Prabhat Kumar, MD1, Archana Kharel, MD1, Umesh Bhagat, MD1, Navkiran Randhawa, DO2, Asfand Yar Cheema, MD1, Bobak Moazzami, MD3, Amit Hudgi, MD4, Babu Mohan, MD5, Subbaramiah Sridhar, MBBS, MPH6, Humberto Sifuentes, MD6. P0442 - Diagnostic Accuracy of Cell-Free DNA Blood-Based Tests in Screening for Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 2Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University, Augusta, GA; 3Northside Hospital Gwinnett, Atlanta, GA; 4Augusta University Medical Center, Augusta, GA; 5Orlando Gastroenterology PA, Orlando, FL; 6Augusta University, Augusta, GA
Introduction: Population-based colorectal cancer (CRC) screenings have demonstrated significant improvement in mortality. Recently, cell-free DNA (cfDNA) blood-based tests have emerged as a non-invasive alternative, offering the potential for higher compliance and earlier detection. Recent trials, including the ECLIPSE trial, have demonstrated promising results in this field. This meta-analysis aims to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of cfDNA blood-based tests in detecting colorectal cancer.
Methods: A recursive literature search was conducted across multiple databases, including MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane, from inception to May 2024. Studies included in the meta-analysis were those that assessed the diagnostic performance of cfDNA blood-based tests for CRC screening [Table]. Data on sensitivity, specificity, true positive (TP), and true negative (TN) were extracted and pooled using random effects model. Heterogeneity between study-specific estimates was assessed using the I2 statistics.
Results: This exploratory meta-analysis included 16 studies involving 15,591 participants. The pooled sensitivity and specificity of cfDNA blood-based tests for CRC screening were 0.81 (95% CI: 0.75-0.86) and 0.93 (95% CI: 0.89-0.96), respectively [Image]. The area under the curve (AUC) for the summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) indicated high overall diagnostic accuracy. Our study demonstrates the pooled positive likelihood ratio (PLR) and negative likelihood ratio (NLR) of the circulating cfDNA assay was 12.104 (95% CI, 7.044– 20.798) and 0.201 (95% CI, 0.148–0.274), respectively. The pooled Diagnostic Odds ratio (DOR) in our study was 60.173 (95% CI, 30.268–119.622), indicating a relatively high level of overall accuracy.
Discussion: Overall, a high level of diagnostic accuracy was demonstrated in this study evaluating the cfDNA assay in CRC screening. Future studies are warranted to compare its performance with colonoscopy with regards to overall reduction in CRC-related mortality. Furthermore, cost-effectiveness data is needed to help establish its role in CRC screening.

Figure: Image: Forest Plot Showing Pooled Sensitivity and Specificity of the 16 Studies.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Prabhat Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Archana Kharel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umesh Bhagat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Navkiran Randhawa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asfand Yar Cheema indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bobak Moazzami indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amit Hudgi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Babu Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Subbaramiah Sridhar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Humberto Sifuentes indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prabhat Kumar, MD1, Archana Kharel, MD1, Umesh Bhagat, MD1, Navkiran Randhawa, DO2, Asfand Yar Cheema, MD1, Bobak Moazzami, MD3, Amit Hudgi, MD4, Babu Mohan, MD5, Subbaramiah Sridhar, MBBS, MPH6, Humberto Sifuentes, MD6. P0442 - Diagnostic Accuracy of Cell-Free DNA Blood-Based Tests in Screening for Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
