Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0485 - Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection vs Endoscopic Mucosal Resection in Early Barrett’s Neoplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio
- FK
Faisal Kamal, MD
Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University
Philadelphia, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Aamir Saeed, MD1, Saira Yousuf, MD1, Muhammad Hayat, MD1, Marjan Haider, MD2, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD3, Muhammad Aziz, MD4, Umar Hayat, MD5, Christian Salcedo, MD6, Umer Farooq, MD7, Nasir Saleem, MD8, Muhammad Khan, MD9, Faisal Kamal, MD10
1Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN; 2Trinity Health Ann Arbor Hospital, Ann Arbor, MI; 3University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 4Bon Secours Mercy, Toledo, OH; 5Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 6University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN; 7SSM Health Saint Louis University Hospital, St. Louis, MO; 8Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 9MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 10Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA
Introduction: Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) are often used for the endoscopic resection of Barrett's related early neoplastic lesions. Studies have compared the efficacy and safety of these two techniques. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to compare the efficacy and safety of these two interventions in the treatment of Barrett's related early neoplastic lesions.
Methods: Several databases were reviewed from inception to February 16, 2024 to identify studies comparing the outcomes between EMR and ESD for Barrett’s associated early neoplasia. The databases searched including PubMed, Web of Science Core Collection, Embase, and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Our outcomes of interest were en bloc resection, R0 resection, curative resection, adverse events including perforation, bleeding, esophageal stricture formation, recurrence of the tumor and procedure time. We calculated pooled risk ratios (RRs) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for all dichotomous variables and mean difference (MD) with 95% CI for continuous variables. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I² statistic
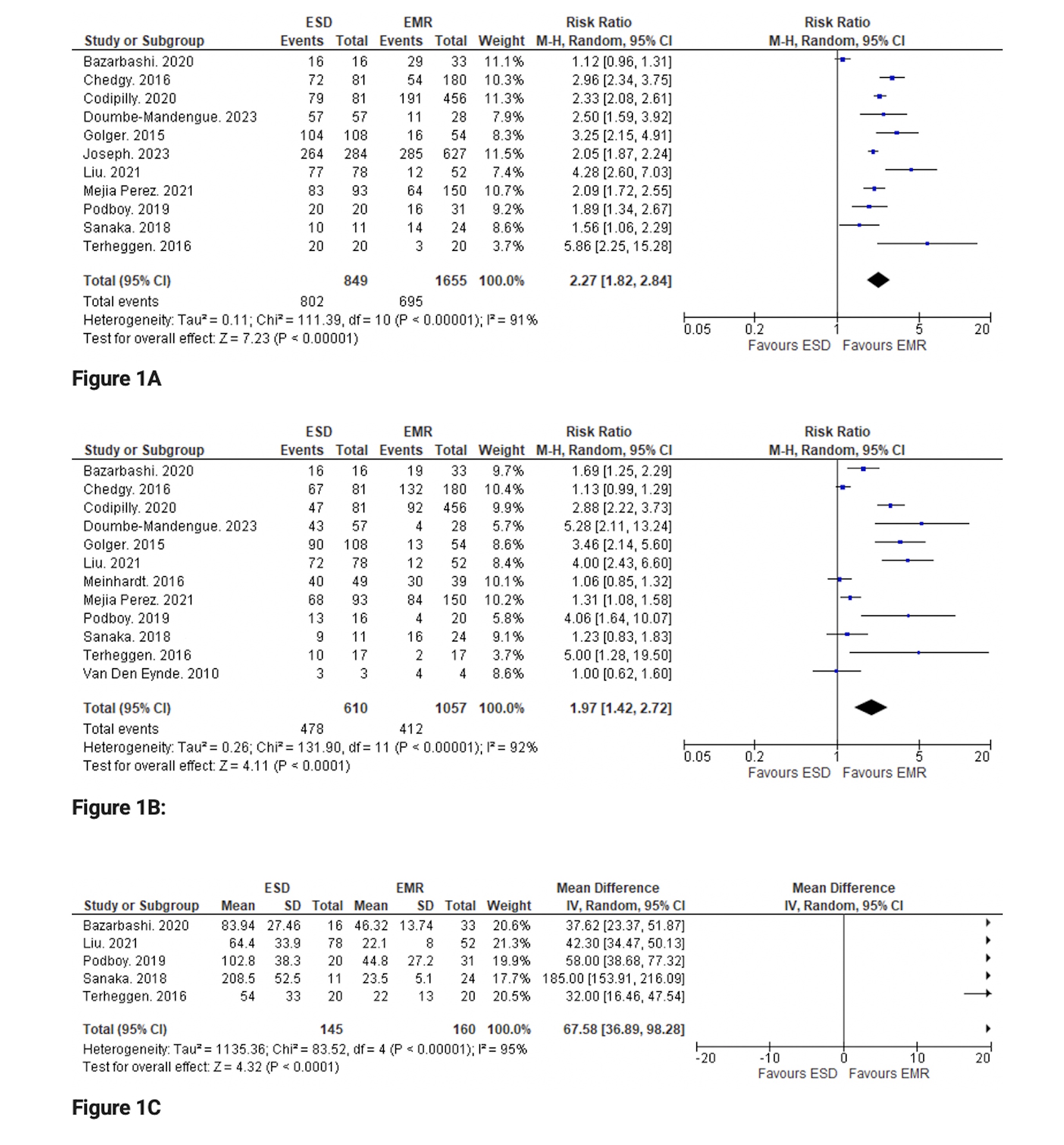
Results: Thirteen studies comprising 2746 patients (ESD 969, EMR 1777) met the inclusion criteria. We found that, the rate of en bloc resection was significantly higher in ESD group compared to EMR, RR (95% CI): 2.27 (1.82,2.84), p< 0.00001 (Figure 1A). The rates of R0 resection; RR (95% CI): 1.97 (1.42,2.72), p< 0.0001 (Figure 1B) and curative resection; RR (95% CI): 2.22 (1.08,4.54), p=0.03 were also significantly higher in ESD group. ESD was associated with significantly longer procedure time, MD (95% CI): 67.58 (36.89,98.28), p=0.0001 (Figure 1C). Rate of recurrence was significantly lower in ESD group compared to EMR group, RR (95% CI): 0.32 (0.12,0.84), p=0.02. There was no significant difference in rate of adverse events between the groups including esophageal perforation; RR (95% CI): 2.96 (0.65,13.58), p=0.16, bleeding; RR (95% CI): 0.87 (0.43,1.73), p=0.68, and esophageal stricture; RR (95% CI): 1.26 (0.88,1.79), p=0.20.
Discussion: Our meta-analysis demonstrates superiority of ESD over EMR in achieving higher rates of en bloc resection, R0 resection, and curative resection and lower rates of recurrence in patients with Barrett’s associated early neoplasia. However, ESD was also associated with longer procedure time.
Disclosures:
Aamir Saeed, MD1, Saira Yousuf, MD1, Muhammad Hayat, MD1, Marjan Haider, MD2, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD3, Muhammad Aziz, MD4, Umar Hayat, MD5, Christian Salcedo, MD6, Umer Farooq, MD7, Nasir Saleem, MD8, Muhammad Khan, MD9, Faisal Kamal, MD10. P0485 - Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection vs Endoscopic Mucosal Resection in Early Barrett’s Neoplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN; 2Trinity Health Ann Arbor Hospital, Ann Arbor, MI; 3University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 4Bon Secours Mercy, Toledo, OH; 5Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 6University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN; 7SSM Health Saint Louis University Hospital, St. Louis, MO; 8Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 9MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 10Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA
Introduction: Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) are often used for the endoscopic resection of Barrett's related early neoplastic lesions. Studies have compared the efficacy and safety of these two techniques. We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to compare the efficacy and safety of these two interventions in the treatment of Barrett's related early neoplastic lesions.
Methods: Several databases were reviewed from inception to February 16, 2024 to identify studies comparing the outcomes between EMR and ESD for Barrett’s associated early neoplasia. The databases searched including PubMed, Web of Science Core Collection, Embase, and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Our outcomes of interest were en bloc resection, R0 resection, curative resection, adverse events including perforation, bleeding, esophageal stricture formation, recurrence of the tumor and procedure time. We calculated pooled risk ratios (RRs) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for all dichotomous variables and mean difference (MD) with 95% CI for continuous variables. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I² statistic
Results: Thirteen studies comprising 2746 patients (ESD 969, EMR 1777) met the inclusion criteria. We found that, the rate of en bloc resection was significantly higher in ESD group compared to EMR, RR (95% CI): 2.27 (1.82,2.84), p< 0.00001 (Figure 1A). The rates of R0 resection; RR (95% CI): 1.97 (1.42,2.72), p< 0.0001 (Figure 1B) and curative resection; RR (95% CI): 2.22 (1.08,4.54), p=0.03 were also significantly higher in ESD group. ESD was associated with significantly longer procedure time, MD (95% CI): 67.58 (36.89,98.28), p=0.0001 (Figure 1C). Rate of recurrence was significantly lower in ESD group compared to EMR group, RR (95% CI): 0.32 (0.12,0.84), p=0.02. There was no significant difference in rate of adverse events between the groups including esophageal perforation; RR (95% CI): 2.96 (0.65,13.58), p=0.16, bleeding; RR (95% CI): 0.87 (0.43,1.73), p=0.68, and esophageal stricture; RR (95% CI): 1.26 (0.88,1.79), p=0.20.
Discussion: Our meta-analysis demonstrates superiority of ESD over EMR in achieving higher rates of en bloc resection, R0 resection, and curative resection and lower rates of recurrence in patients with Barrett’s associated early neoplasia. However, ESD was also associated with longer procedure time.

Figure: Comparison of en bloc resection (Figure 1A), R0 resection (Figure 1B) and procedure time (Figure 1C) between groups.
Disclosures:
Aamir Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saira Yousuf indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marjan Haider indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manesh Kumar Gangwani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Aziz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umar Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christian Salcedo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umer Farooq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nasir Saleem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faisal Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aamir Saeed, MD1, Saira Yousuf, MD1, Muhammad Hayat, MD1, Marjan Haider, MD2, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD3, Muhammad Aziz, MD4, Umar Hayat, MD5, Christian Salcedo, MD6, Umer Farooq, MD7, Nasir Saleem, MD8, Muhammad Khan, MD9, Faisal Kamal, MD10. P0485 - Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection vs Endoscopic Mucosal Resection in Early Barrett’s Neoplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
