Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0509 - Comparison of Discharge Trends in Patients Undergoing POEM for Achalasia: Insights From NRD 2015-2020
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Prabhat Kumar, MD
Cleveland Clinic Foundation
Richmond, VA
Presenting Author(s)
Prabhat Kumar, MD1, Umesh Bhagat, MD1, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD2, Archana Kharel, MD1, Ankit Agrawal, MD1, Mounir Ibrahim, MD1, Sanya Chandna, MD1, Prashanthi N. Thota, MD1, Madhusudhan R. Sanaka, MD1
1Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 2The University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS
Introduction: Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) has emerged as a pivotal treatment for achalasia, demonstrating significant efficacy and favorable recovery outcomes. This study evaluates discharge trends, healthcare utilization, and readmission rates following POEM using data from the National Readmission Database (NRD) from 2015 to 2020.
Methods: We queried the National Readmission Database (NRD) from 2016 to 2020 using the ICD-10-CM coding system to identify patients with a primary diagnosis of achalasia who underwent POEM. The primary outcome was the incidence of 30-day readmission based on discharge day, categorized as same-day discharge (SDD), next-day discharge (NDD), and second-day discharge or beyond (ScDD). Statistical analysis was performed using STATA software, with T-tests for continuous variables and chi-square tests for categorical variables. Survival analysis, including unadjusted and adjusted hazard ratios, was conducted to assess 30-day readmission risk, and cumulative incidence was calculated to compare the discharge timing groups.
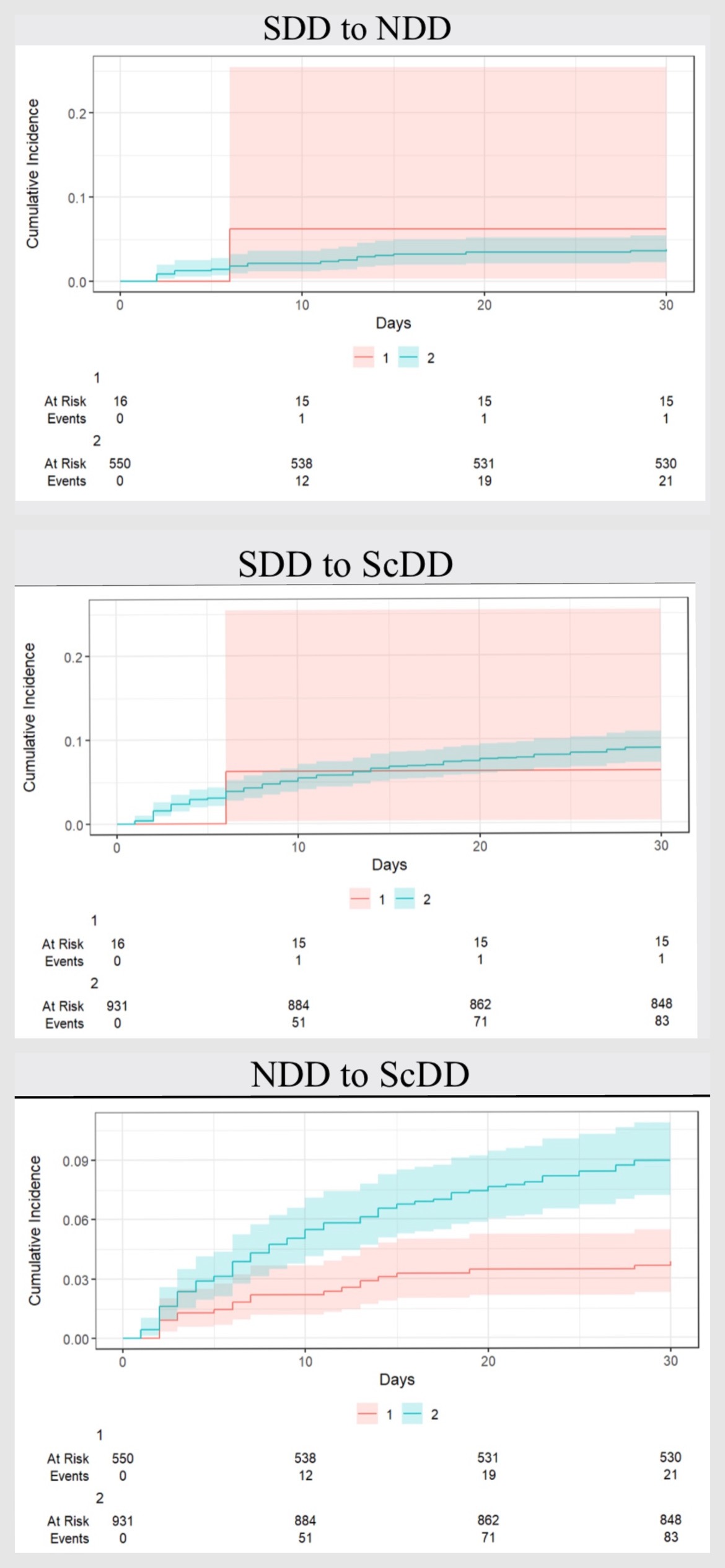
Results: A total of 2,920 patients underwent POEM for achalasia from 2015 to 2020, with 2,552 patients discharged post-procedure. The mean age for SDD was 54.2 years, NDD was 57.38, and ScDD was 59.75 years. An Elxihouser comorbidity burden for SDD was 1.2, NDD 1.7, and 2.5 for ScDD (table 1). The fraction of patients with SDD was 1.2% vs. 37.7% NDD and 61% ScDD. Readmission rates were 1.3% for SDD, 3.6% for NDD, and 14.1% for ScDD. No significant difference in readmission rates was observed between SDD vs. NDD and SDD vs. ScDD. However, a statistically significant difference was noted between NDD and ScDD, which decreased cumulative readmission in NDD patients compared to ScDD. Over the years, there has been a gradual increase in the number of POEM procedures.
Discussion: From 2015 to 2020, there has been a marked trend toward earlier discharge post-POEM, with reductions in LOS and hospital charges, alongside stable and low readmission rates. The data support the safety and efficiency of early discharge protocols for POEM patients, highlighting the procedure's growing acceptance and improved healthcare resource utilization. Enhanced patient management and procedural techniques contribute to these positive outcomes, suggesting that next-day discharge is a feasible and safe practice for the majority of POEM patients.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Prabhat Kumar, MD1, Umesh Bhagat, MD1, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD2, Archana Kharel, MD1, Ankit Agrawal, MD1, Mounir Ibrahim, MD1, Sanya Chandna, MD1, Prashanthi N. Thota, MD1, Madhusudhan R. Sanaka, MD1. P0509 - Comparison of Discharge Trends in Patients Undergoing POEM for Achalasia: Insights From NRD 2015-2020, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 2The University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS
Introduction: Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) has emerged as a pivotal treatment for achalasia, demonstrating significant efficacy and favorable recovery outcomes. This study evaluates discharge trends, healthcare utilization, and readmission rates following POEM using data from the National Readmission Database (NRD) from 2015 to 2020.
Methods: We queried the National Readmission Database (NRD) from 2016 to 2020 using the ICD-10-CM coding system to identify patients with a primary diagnosis of achalasia who underwent POEM. The primary outcome was the incidence of 30-day readmission based on discharge day, categorized as same-day discharge (SDD), next-day discharge (NDD), and second-day discharge or beyond (ScDD). Statistical analysis was performed using STATA software, with T-tests for continuous variables and chi-square tests for categorical variables. Survival analysis, including unadjusted and adjusted hazard ratios, was conducted to assess 30-day readmission risk, and cumulative incidence was calculated to compare the discharge timing groups.
Results: A total of 2,920 patients underwent POEM for achalasia from 2015 to 2020, with 2,552 patients discharged post-procedure. The mean age for SDD was 54.2 years, NDD was 57.38, and ScDD was 59.75 years. An Elxihouser comorbidity burden for SDD was 1.2, NDD 1.7, and 2.5 for ScDD (table 1). The fraction of patients with SDD was 1.2% vs. 37.7% NDD and 61% ScDD. Readmission rates were 1.3% for SDD, 3.6% for NDD, and 14.1% for ScDD. No significant difference in readmission rates was observed between SDD vs. NDD and SDD vs. ScDD. However, a statistically significant difference was noted between NDD and ScDD, which decreased cumulative readmission in NDD patients compared to ScDD. Over the years, there has been a gradual increase in the number of POEM procedures.
Discussion: From 2015 to 2020, there has been a marked trend toward earlier discharge post-POEM, with reductions in LOS and hospital charges, alongside stable and low readmission rates. The data support the safety and efficiency of early discharge protocols for POEM patients, highlighting the procedure's growing acceptance and improved healthcare resource utilization. Enhanced patient management and procedural techniques contribute to these positive outcomes, suggesting that next-day discharge is a feasible and safe practice for the majority of POEM patients.

Figure: Cumulative readmission rates in Achalasia patients.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Prabhat Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umesh Bhagat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dushyant Dahiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Archana Kharel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ankit Agrawal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mounir Ibrahim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sanya Chandna indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prashanthi Thota indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhusudhan R. Sanaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prabhat Kumar, MD1, Umesh Bhagat, MD1, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD2, Archana Kharel, MD1, Ankit Agrawal, MD1, Mounir Ibrahim, MD1, Sanya Chandna, MD1, Prashanthi N. Thota, MD1, Madhusudhan R. Sanaka, MD1. P0509 - Comparison of Discharge Trends in Patients Undergoing POEM for Achalasia: Insights From NRD 2015-2020, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
