Sunday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P0631 - Next-Gen Solutions: How ChatGPT and Google Bard Are Innovating IBS Treatments
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
- RR
Rajmohan Rammohan, MD
Nassau University Medical Center
East Meadow, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Rucha Jiyani, MD, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly revolutionized healthcare, particularly in diagnosing and treating Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and various digestive ailments. Vital AI resources, like ChatGPT and Google Bard, can decode endoscopic images, scrutinize various samples, ease administrative tasks, and aid in evaluating medical images and automating devices. These AI solutions have remarkably improved the handling of digestive diseases by personalizing treatments and predicting unfavorable responses.
Methods: This study aimed to assess the accuracy of two prevalently utilized chatbots, ChatGPT and Google BARD, in addressing inquiries associated with medical management. Both bots were assigned a set of questions to respond to, and their answers were rated on a 1-10 Likert scale, where 1 represented low and 10 represented high accuracy. To maintain an unbiased evaluation, the responses from each bot were reviewed by two independent assessors. The intention behind this investigation was to shed light on the capabilities of these chatbots by methodically evaluating their effectiveness and reliability in terms of accuracy. The deployment of two reviewers and the application of the Likert scale methodology served to reduce potential biases, validating the results.
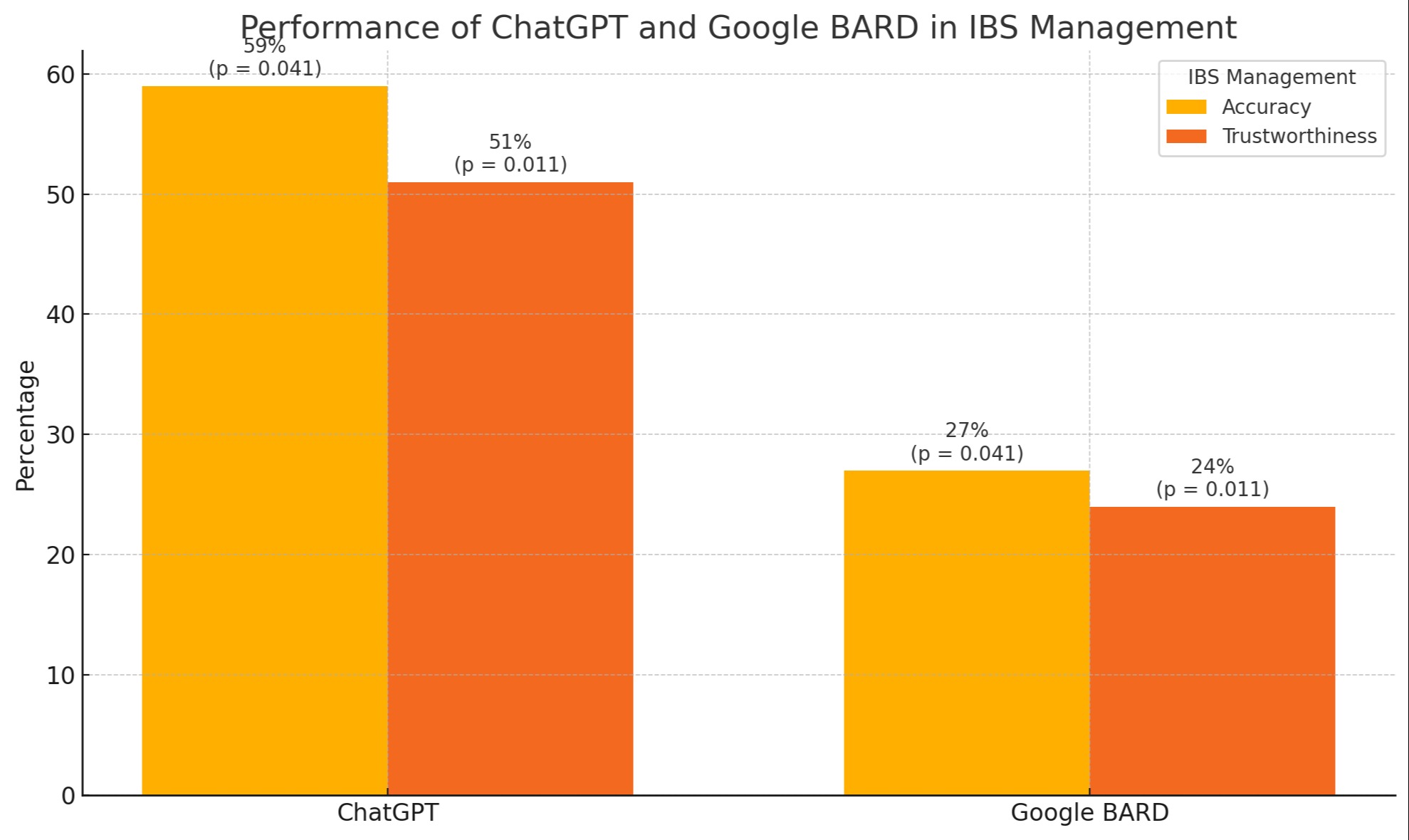
Results: Our research contrasted the effectiveness of ChatGPT and Google BARD in the realm of medical management. ChatGPT exhibited predominant proficiency, securing 59% accuracy compared to 27% by Google BARD (p = 0.041), and 51% against 24% in the trustworthiness of medical information (p = 0.011). This study emphasizes the crucial significance of precision and dependability in developing IBS chatbots. Although ChatGPT displayed notable outcomes, indicating its potential as a reliable source, it also accentuated the urgent requirement for continual exploration and progress in this field.
Discussion: AI has markedly restructured healthcare, especially in diagnosing and handling IBD. ChatGPT and Google Bard are essential AI instruments capable of interpreting medical imagery, examining samples, and refining tasks. Our study scrutinized these chatbots' accuracy and reliability within the medical management domain. ChatGPT outperformed Google Bard, achieving 59% in accuracy and 51% in the reliability of information. Although ChatGPT demonstrates considerable promise as a dependable AI tool in IBS management, the findings also highlight the ongoing need for research and development in this sector.
Disclosures:
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Rucha Jiyani, MD, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA. P0631 - Next-Gen Solutions: How ChatGPT and Google Bard Are Innovating IBS Treatments, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly revolutionized healthcare, particularly in diagnosing and treating Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and various digestive ailments. Vital AI resources, like ChatGPT and Google Bard, can decode endoscopic images, scrutinize various samples, ease administrative tasks, and aid in evaluating medical images and automating devices. These AI solutions have remarkably improved the handling of digestive diseases by personalizing treatments and predicting unfavorable responses.
Methods: This study aimed to assess the accuracy of two prevalently utilized chatbots, ChatGPT and Google BARD, in addressing inquiries associated with medical management. Both bots were assigned a set of questions to respond to, and their answers were rated on a 1-10 Likert scale, where 1 represented low and 10 represented high accuracy. To maintain an unbiased evaluation, the responses from each bot were reviewed by two independent assessors. The intention behind this investigation was to shed light on the capabilities of these chatbots by methodically evaluating their effectiveness and reliability in terms of accuracy. The deployment of two reviewers and the application of the Likert scale methodology served to reduce potential biases, validating the results.
Results: Our research contrasted the effectiveness of ChatGPT and Google BARD in the realm of medical management. ChatGPT exhibited predominant proficiency, securing 59% accuracy compared to 27% by Google BARD (p = 0.041), and 51% against 24% in the trustworthiness of medical information (p = 0.011). This study emphasizes the crucial significance of precision and dependability in developing IBS chatbots. Although ChatGPT displayed notable outcomes, indicating its potential as a reliable source, it also accentuated the urgent requirement for continual exploration and progress in this field.
Discussion: AI has markedly restructured healthcare, especially in diagnosing and handling IBD. ChatGPT and Google Bard are essential AI instruments capable of interpreting medical imagery, examining samples, and refining tasks. Our study scrutinized these chatbots' accuracy and reliability within the medical management domain. ChatGPT outperformed Google Bard, achieving 59% in accuracy and 51% in the reliability of information. Although ChatGPT demonstrates considerable promise as a dependable AI tool in IBS management, the findings also highlight the ongoing need for research and development in this sector.

Figure: Performance of ChatBot's in IBS management
Disclosures:
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Reshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Greeshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Melvin Joy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dilman Natt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Winghang Lau indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhishek Tadikonda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leeza Pannikodu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jiten Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rucha Jiyani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishnaiyer Subramani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Mustacchia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Rucha Jiyani, MD, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA. P0631 - Next-Gen Solutions: How ChatGPT and Google Bard Are Innovating IBS Treatments, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
