Sunday Poster Session
Category: General Endoscopy
P0701 - Treatment of a Challenging Duodeno-Cutaneous Fistula With an Amplatzer Vascular Plug
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- MO
Matthew Orosa, DO
Riverside University Health System
Moreno Valley, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Matthew Orosa, DO1, Emily Lin, MD2, Wichit Srikureja, MD1
1Riverside University Health System, Moreno Valley, CA; 2Loma Linda University Medical Center, Loma Linda, CA
Introduction: Closure of duodenal fistulae is challenging but critical to avoid potential complications of infection, malnutrition, and electrolyte derangements. Closure techniques have included surgical resection, endoscopic over-the-scope clips (OTSC), endoscopic suturing, and endoscopic vacuum therapy. We present a case employing a novel closure therapy for a duodeno-cutaneous fistula with a vascular plug.
Case Description/Methods: A 43-year-old female presented with an abdominal gunshot wound with duodenal injury. She underwent multiple surgeries and developed a duodeno-cutaneous fistula with persistent leak. Several endoscopic closures with OTSC were attempted without success. She then underwent fistulous tract resection and debridement but continued to have persistent percutaneous output. She was then managed with nil-per-os and parenteral nutrition. After discussion with surgical and interventional radiology teams, a decision was made to attempt endoscopic closure of the fistula with vascular plug.
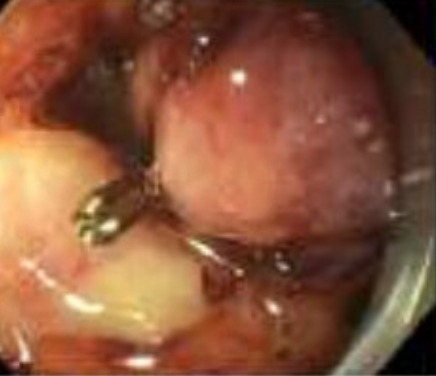
EGD was done with findings of partially detached OTSC at the site of the duodenal fistula. After removing the clip, the fistula tract was cannulated with 0.025in guidewire. Contrast injection revealed a tract 4mm in width draining into a 3cm cavity. A pre-trimmed rigid 3mm dilator was placed over the guidewire and passed into the fistula opening. An 8mm x 13.5mm AmplatzerTM Vascular Plug 4 (Abbot, Plymouth, MN) was selected. The selected plug was 50% greater than the fistula luminal diameter. It also had a maximal deployment catheter length of 120cm allowing it to be loaded into the dilator through the scope working channel. The deployment of the plug into fistulous tract was successful. To assist in epithelization of the plug a total of 4 mL of n-butyl-cyanoacrylate glue was sprayed across the plug. Contrast study showed no evidence of leak. The patient improved significantly over the next several days with resolution of drain output leading to drain removal. She tolerated regular diet and was discharged.
Discussion: Enteric fistulae and leaks are complex and often require a multidisciplinary approach for management. Endoscopically placed vascular plug for gastro-bronchial and aorto-enteric fistulae and post gastric sleeve staple line leak have been reported. To our knowledge, this is the first case describing the novel use of AmplatzerTM Vascular Plug 4 in successfully closing a duodeno-cutaneous fistula.
Disclosures:
Matthew Orosa, DO1, Emily Lin, MD2, Wichit Srikureja, MD1. P0701 - Treatment of a Challenging Duodeno-Cutaneous Fistula With an Amplatzer Vascular Plug, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Riverside University Health System, Moreno Valley, CA; 2Loma Linda University Medical Center, Loma Linda, CA
Introduction: Closure of duodenal fistulae is challenging but critical to avoid potential complications of infection, malnutrition, and electrolyte derangements. Closure techniques have included surgical resection, endoscopic over-the-scope clips (OTSC), endoscopic suturing, and endoscopic vacuum therapy. We present a case employing a novel closure therapy for a duodeno-cutaneous fistula with a vascular plug.
Case Description/Methods: A 43-year-old female presented with an abdominal gunshot wound with duodenal injury. She underwent multiple surgeries and developed a duodeno-cutaneous fistula with persistent leak. Several endoscopic closures with OTSC were attempted without success. She then underwent fistulous tract resection and debridement but continued to have persistent percutaneous output. She was then managed with nil-per-os and parenteral nutrition. After discussion with surgical and interventional radiology teams, a decision was made to attempt endoscopic closure of the fistula with vascular plug.
EGD was done with findings of partially detached OTSC at the site of the duodenal fistula. After removing the clip, the fistula tract was cannulated with 0.025in guidewire. Contrast injection revealed a tract 4mm in width draining into a 3cm cavity. A pre-trimmed rigid 3mm dilator was placed over the guidewire and passed into the fistula opening. An 8mm x 13.5mm AmplatzerTM Vascular Plug 4 (Abbot, Plymouth, MN) was selected. The selected plug was 50% greater than the fistula luminal diameter. It also had a maximal deployment catheter length of 120cm allowing it to be loaded into the dilator through the scope working channel. The deployment of the plug into fistulous tract was successful. To assist in epithelization of the plug a total of 4 mL of n-butyl-cyanoacrylate glue was sprayed across the plug. Contrast study showed no evidence of leak. The patient improved significantly over the next several days with resolution of drain output leading to drain removal. She tolerated regular diet and was discharged.
Discussion: Enteric fistulae and leaks are complex and often require a multidisciplinary approach for management. Endoscopically placed vascular plug for gastro-bronchial and aorto-enteric fistulae and post gastric sleeve staple line leak have been reported. To our knowledge, this is the first case describing the novel use of AmplatzerTM Vascular Plug 4 in successfully closing a duodeno-cutaneous fistula.

Figure: Vascular Plug Placed in Fistula
Disclosures:
Matthew Orosa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Emily Lin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Wichit Srikureja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Matthew Orosa, DO1, Emily Lin, MD2, Wichit Srikureja, MD1. P0701 - Treatment of a Challenging Duodeno-Cutaneous Fistula With an Amplatzer Vascular Plug, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
