Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P0868 - Social Media and AI in Healthcare: Understanding Patient Perspectives on Chatbots for Managing IBD
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
- RR
Rajmohan Rammohan, MD
Nassau University Medical Center
East Meadow, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: Social media platforms, online tools that facilitate user engagement and the sharing of content, are being increasingly adopted to manage chronic illnesses. Sentiment Analysis, a developing technology, aids in understanding public sentiments regarding specific health conditions or their treatments. Our study focuses on investigating how patients use Artificial Intelligence to manage Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Methods: We utilized the Twitter API, PHP, and RAI to gather data from platforms like Twitter, YouTube, Reddit, and Facebook. We analyzed the sentiment of tweets using the VADER tool. We compiled descriptive statistics and conducted t-tests to compare positive and negative sentiments. A correlation analysis was used to examine changes in sentiment. All data analysis was carried out using SPSS
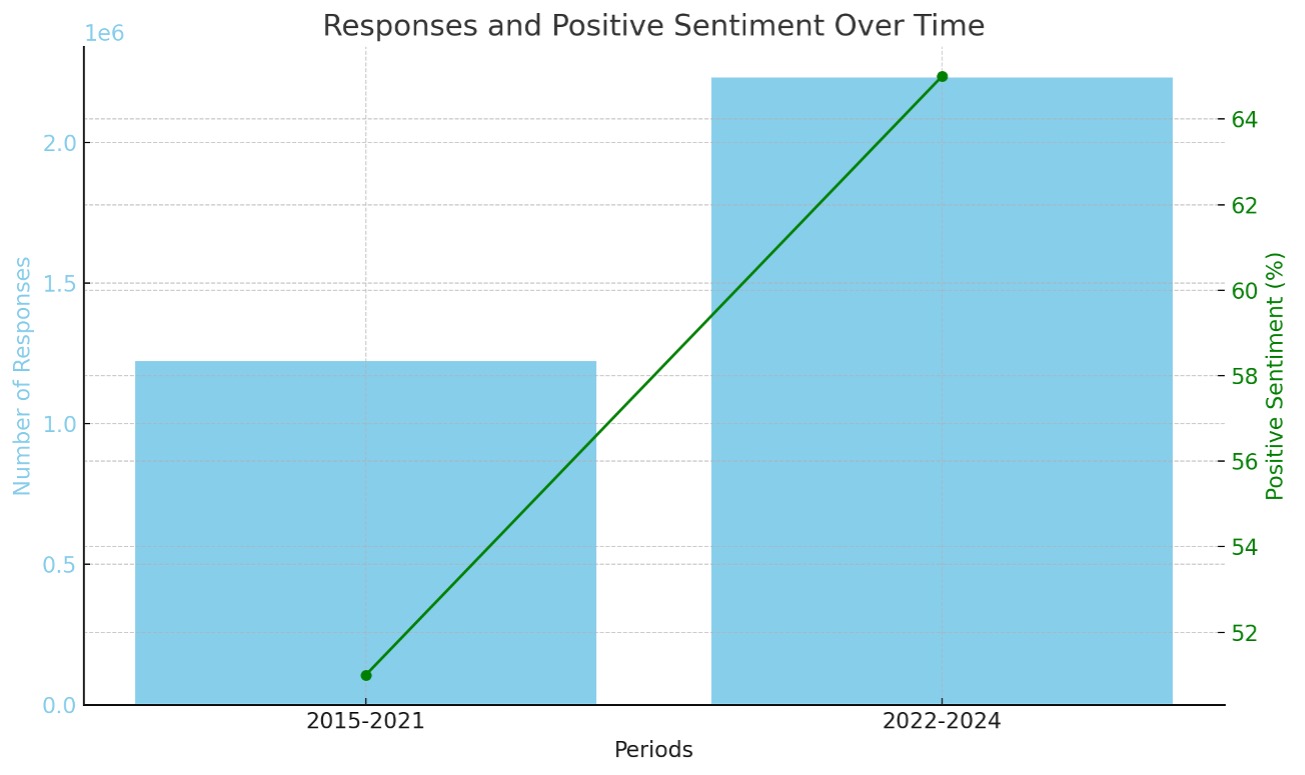
Results: From December 2015 to March 2024, we collected a total of 3,451,110 responses. Of these, 1,221,663 responses were gathered from December 2015 to November 2021, and 2,229,447 responses were collected from January 2022 to March 2024. We observed a significant increase in positive sentiment regarding the use of Chatbots for obtaining information about Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), rising from 51% in the period 2015-2021 to 65% between 2022-2024 (P=0.012, 95% CI)
Discussion: Our research underscores the growing role of AI-driven platforms in healthcare, particularly in managing chronic diseases like IBD. The significant rise in positive sentiment towards the use of chatbots, as evidenced by our data from social media analysis, suggests that patients increasingly appreciate the convenience and accessibility of AI tools. This shift may reflect greater trust in AI's capability to provide reliable health information and support. Further, our findings highlight the potential for chatbots to enhance patient engagement and education, indicating a promising avenue for future innovations in healthcare technology
Disclosures:
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA. P0868 - Social Media and AI in Healthcare: Understanding Patient Perspectives on Chatbots for Managing IBD, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Nassau University Medical Center, East Meadow, NY
Introduction: Social media platforms, online tools that facilitate user engagement and the sharing of content, are being increasingly adopted to manage chronic illnesses. Sentiment Analysis, a developing technology, aids in understanding public sentiments regarding specific health conditions or their treatments. Our study focuses on investigating how patients use Artificial Intelligence to manage Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Methods: We utilized the Twitter API, PHP, and RAI to gather data from platforms like Twitter, YouTube, Reddit, and Facebook. We analyzed the sentiment of tweets using the VADER tool. We compiled descriptive statistics and conducted t-tests to compare positive and negative sentiments. A correlation analysis was used to examine changes in sentiment. All data analysis was carried out using SPSS
Results: From December 2015 to March 2024, we collected a total of 3,451,110 responses. Of these, 1,221,663 responses were gathered from December 2015 to November 2021, and 2,229,447 responses were collected from January 2022 to March 2024. We observed a significant increase in positive sentiment regarding the use of Chatbots for obtaining information about Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), rising from 51% in the period 2015-2021 to 65% between 2022-2024 (P=0.012, 95% CI)
Discussion: Our research underscores the growing role of AI-driven platforms in healthcare, particularly in managing chronic diseases like IBD. The significant rise in positive sentiment towards the use of chatbots, as evidenced by our data from social media analysis, suggests that patients increasingly appreciate the convenience and accessibility of AI tools. This shift may reflect greater trust in AI's capability to provide reliable health information and support. Further, our findings highlight the potential for chatbots to enhance patient engagement and education, indicating a promising avenue for future innovations in healthcare technology

Figure: Sentiment analysis for patients' perspective towards IBD management
Disclosures:
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Reshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sai Greeshma Magam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Melvin Joy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Leeza Pannikodu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dilman Natt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abhishek Tadikonda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Winghang Lau indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jiten Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Krishnaiyer Subramani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul Mustacchia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Raj Mohan Ram Mohan, MD, Sai Reshma Magam, MD, Sai Greeshma Magam, MD, Melvin Joy, MD, Leeza Pannikodu, MD, Dilman Natt, MD, Abhishek Tadikonda, MD, Winghang Lau, MD, Jiten Desai, MD, Krishnaiyer Subramani, MD, Paul Mustacchia, MD, MBA. P0868 - Social Media and AI in Healthcare: Understanding Patient Perspectives on Chatbots for Managing IBD, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
