Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P0976 - Newly Diagnosed Ulcerative Colitis While on Nivolumab: A Case Report
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- JB
Jason Barbaretta, MD
University of Nebraska Medical Center
Omaha, NE
Presenting Author(s)
Jason Barbaretta, MD, Kathryn Hutchins, MD
University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have revolutionized cancer treatment, but immune-related adverse effects (irAEs) are common. The most frequently reported gastrointestinal irAE is ICI colitis. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) were frequently excluded from initial ICI clinical trials. In the existing studies, ICIs were associated with a twofold increase in the annual risk of disease relapse compared to the general IBD population. However, most relapses were manageable with steroids or biologic therapy and were associated with low rates of serious complications. To our knowledge, there are no studies examining reinitiation of an ICI following a new diagnosis of IBD during treatment. We present a patient with metastatic gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma on nivolumab who was newly diagnosed with ulcerative colitis.
Case Description/Methods: A 46-year-old male with metastatic gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma presented to the emergency department with hematochezia, fecal urgency, and rectal pain. He had started palliative chemo/immunotherapy with capecitabine, irinotecan, and nivolumab four months prior. He did not have a known history of IBD, but colonoscopy at the time of his cancer diagnosis one year ago showed moderately active proctocolitis.
During his hospitalization, infectious workup was negative. Colonoscopy showed pancolitis with ulcerated mucosa. Colonic biopsies revealed cryptitis, crypt abscesses, and regenerative glands. Few apoptotic bodies and prominent basal plasmacytosis on histology favored the diagnosis of UC over ICI colitis. Due to minimal clinical improvement with intravenous steroids, infliximab was initiated. He was discharged in stable condition on an oral steroid taper with a plan to receive his next infliximab dose in two weeks.
Discussion: Immune checkpoint inhibitor use is expanding, and they are currently used to treat many gastrointestinal malignancies. Overlap between ICI use and underlying IBD will likely increase. No study has examined reinitiation of an ICI following a new diagnosis of IBD during treatment. Our patient has excellent functional status and strongly desires continued chemoimmunotherapy, emphasizing the importance of clarifying all treatment options. He did not require a colectomy for his IBD flare, but it is unclear how a colectomy would impact the decision of future ICI use in this population. This case identifies multiple paths of future research within the overlapping realm of ICIs and IBD.
Disclosures:
Jason Barbaretta, MD, Kathryn Hutchins, MD. P0976 - Newly Diagnosed Ulcerative Colitis While on Nivolumab: A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have revolutionized cancer treatment, but immune-related adverse effects (irAEs) are common. The most frequently reported gastrointestinal irAE is ICI colitis. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) were frequently excluded from initial ICI clinical trials. In the existing studies, ICIs were associated with a twofold increase in the annual risk of disease relapse compared to the general IBD population. However, most relapses were manageable with steroids or biologic therapy and were associated with low rates of serious complications. To our knowledge, there are no studies examining reinitiation of an ICI following a new diagnosis of IBD during treatment. We present a patient with metastatic gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma on nivolumab who was newly diagnosed with ulcerative colitis.
Case Description/Methods: A 46-year-old male with metastatic gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma presented to the emergency department with hematochezia, fecal urgency, and rectal pain. He had started palliative chemo/immunotherapy with capecitabine, irinotecan, and nivolumab four months prior. He did not have a known history of IBD, but colonoscopy at the time of his cancer diagnosis one year ago showed moderately active proctocolitis.
During his hospitalization, infectious workup was negative. Colonoscopy showed pancolitis with ulcerated mucosa. Colonic biopsies revealed cryptitis, crypt abscesses, and regenerative glands. Few apoptotic bodies and prominent basal plasmacytosis on histology favored the diagnosis of UC over ICI colitis. Due to minimal clinical improvement with intravenous steroids, infliximab was initiated. He was discharged in stable condition on an oral steroid taper with a plan to receive his next infliximab dose in two weeks.
Discussion: Immune checkpoint inhibitor use is expanding, and they are currently used to treat many gastrointestinal malignancies. Overlap between ICI use and underlying IBD will likely increase. No study has examined reinitiation of an ICI following a new diagnosis of IBD during treatment. Our patient has excellent functional status and strongly desires continued chemoimmunotherapy, emphasizing the importance of clarifying all treatment options. He did not require a colectomy for his IBD flare, but it is unclear how a colectomy would impact the decision of future ICI use in this population. This case identifies multiple paths of future research within the overlapping realm of ICIs and IBD.

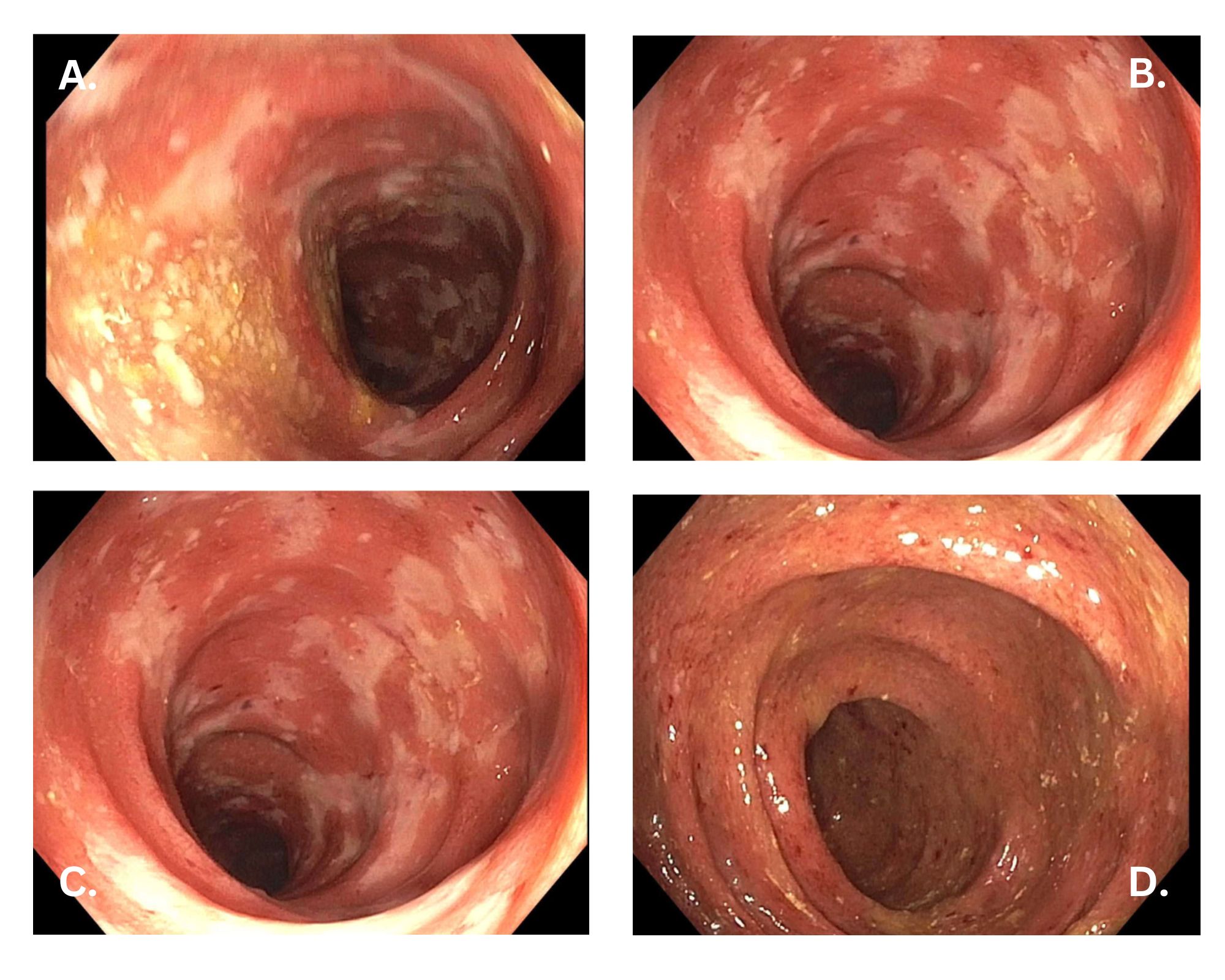
Figure: Endoscopic images during hospitalization depicting pancolitis
A - Rectum
B - Sigmoid colon
C - Transverse colon
D - Ascending colon
A - Rectum
B - Sigmoid colon
C - Transverse colon
D - Ascending colon
Disclosures:
Jason Barbaretta indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kathryn Hutchins indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jason Barbaretta, MD, Kathryn Hutchins, MD. P0976 - Newly Diagnosed Ulcerative Colitis While on Nivolumab: A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
