Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P0982 - A Rare Case of Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonitis (NSIP) Secondary to Infliximab in a Patient With Ulcerative Pancolitis and PANCA Positivity
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- PM
Padmavathi Mali, MD
Gundersen Health Systems
Lacrosse, WI
Presenting Author(s)
Padmavathi Mali, MD
Gundersen Health Systems, Onalaska, WI
Introduction: Infliximab is a monoclonal antibody that targets TNF alpha and common side effects include infections and infusion reactions. Although rare, there have also been few case reports describing non-specific interstitial pneumonitis (NSIP) which is a class of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. We present a unique case of a young female patient with UC (Ulcerative Colitis) and PSC (Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis) diagnosed with NSIP on Infliximab with a complete resolution of symptoms after stopping Infliximab and treatment with steroids.
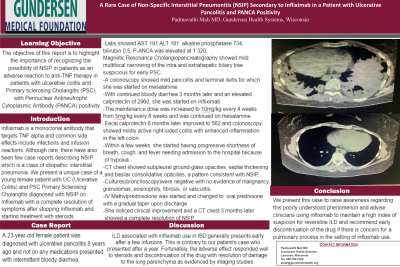
Case Description/Methods: A 23-year-old female patient was diagnosed with ulcerative pan colitis 8 years ago and not on any medications, presented with intermittent bloody diarrhea. AST 191 ALT 181, alkaline phosphatase 734, bilirubin 0.5, P-ANCA was elevated at 1:320 and MRCP showed mild multifocal narrowing of the intra and extrahepatic biliary tree suspicious for early PSC. A colonoscopy showed mild pancolitis and terminal ileitis for which she was started on mesalamine. With continued bloody diarrhea 3 months later and an elevated calprotectin of 2960, she was started on Infliximab the levels of which were undetectable with no detectable antibodies after the loading dose. The maintenance dose was increased to 10mg/kg every 4 weeks from 5mg/kg every 8 weeks and was continued on mesalamine. Fecal calprotectin 6 months later improved to 562, and colonoscopy showed mildly active colitis right colitis with improved inflammation in the left colon. Within a few weeks, she started having progressive shortness of breath, cough, and fever needing admission to the hospital because of hypoxia. CT chest showed subpleural ground-glass opacities, septal thickening, and basilar consolidative opacities, a pattern consistent with NSIP. Cultures via bronchoscopy were negative with no evidence of malignancy, granulomas, eosinophils, fibrosis, or vasculitis. IV Methylprednisone was changed to oral prednisone with a gradual taper upon discharge. She noticed clinical improvement and a CT chest 3 months later showed a complete resolution of NSIP findings.
Discussion: This is a unique case of a young female patient with ulcerative pan colitis, PSC, and PANCA positivity presenting with NSIP on high-dose Infliximab. This case highlights the importance of recognizing the possibility of NSIP in patients as an adverse reaction to anti-TNF therapy in patients with PSC and PANCA positivity initiating prompt treatment with steroids and stopping Infliximab
Disclosures:
Padmavathi Mali, MD. P0982 - A Rare Case of Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonitis (NSIP) Secondary to Infliximab in a Patient With Ulcerative Pancolitis and PANCA Positivity, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Gundersen Health Systems, Onalaska, WI
Introduction: Infliximab is a monoclonal antibody that targets TNF alpha and common side effects include infections and infusion reactions. Although rare, there have also been few case reports describing non-specific interstitial pneumonitis (NSIP) which is a class of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. We present a unique case of a young female patient with UC (Ulcerative Colitis) and PSC (Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis) diagnosed with NSIP on Infliximab with a complete resolution of symptoms after stopping Infliximab and treatment with steroids.
Case Description/Methods: A 23-year-old female patient was diagnosed with ulcerative pan colitis 8 years ago and not on any medications, presented with intermittent bloody diarrhea. AST 191 ALT 181, alkaline phosphatase 734, bilirubin 0.5, P-ANCA was elevated at 1:320 and MRCP showed mild multifocal narrowing of the intra and extrahepatic biliary tree suspicious for early PSC. A colonoscopy showed mild pancolitis and terminal ileitis for which she was started on mesalamine. With continued bloody diarrhea 3 months later and an elevated calprotectin of 2960, she was started on Infliximab the levels of which were undetectable with no detectable antibodies after the loading dose. The maintenance dose was increased to 10mg/kg every 4 weeks from 5mg/kg every 8 weeks and was continued on mesalamine. Fecal calprotectin 6 months later improved to 562, and colonoscopy showed mildly active colitis right colitis with improved inflammation in the left colon. Within a few weeks, she started having progressive shortness of breath, cough, and fever needing admission to the hospital because of hypoxia. CT chest showed subpleural ground-glass opacities, septal thickening, and basilar consolidative opacities, a pattern consistent with NSIP. Cultures via bronchoscopy were negative with no evidence of malignancy, granulomas, eosinophils, fibrosis, or vasculitis. IV Methylprednisone was changed to oral prednisone with a gradual taper upon discharge. She noticed clinical improvement and a CT chest 3 months later showed a complete resolution of NSIP findings.
Discussion: This is a unique case of a young female patient with ulcerative pan colitis, PSC, and PANCA positivity presenting with NSIP on high-dose Infliximab. This case highlights the importance of recognizing the possibility of NSIP in patients as an adverse reaction to anti-TNF therapy in patients with PSC and PANCA positivity initiating prompt treatment with steroids and stopping Infliximab
Disclosures:
Padmavathi Mali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Padmavathi Mali, MD. P0982 - A Rare Case of Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonitis (NSIP) Secondary to Infliximab in a Patient With Ulcerative Pancolitis and PANCA Positivity, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
