Sunday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P0986 - Unexpected Complications of Infliximab: A Rare Case of Drug-Induced AIH-PBC Overlap in Crohn's Disease
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio
- KO
Kashif Osmani, MD
University of Illinois College of Medicine
Chicago, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Kashif Osmani, MD1, Omar T. Ahmed, MD2, Salimah Mohamed, DO1, Grace Guzman, MD3, Itishree Trivedi, MD, MS3
1University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, IL; 2University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL; 3University of Illinois, Chicago, IL
Introduction: The coexistence of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) and autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), known as AIH-PBC overlap syndrome, occurs in only 3-7% of patients with PBC. While drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is known to mimic or trigger AIH, the specific overlap of drug-induced AIH with PBC is scarcely documented. Here, we report a patient with Crohn's disease (CD) on infliximab (IFX) who developed drug-induced AIH with PBC overlap after chronic IFX exposure.
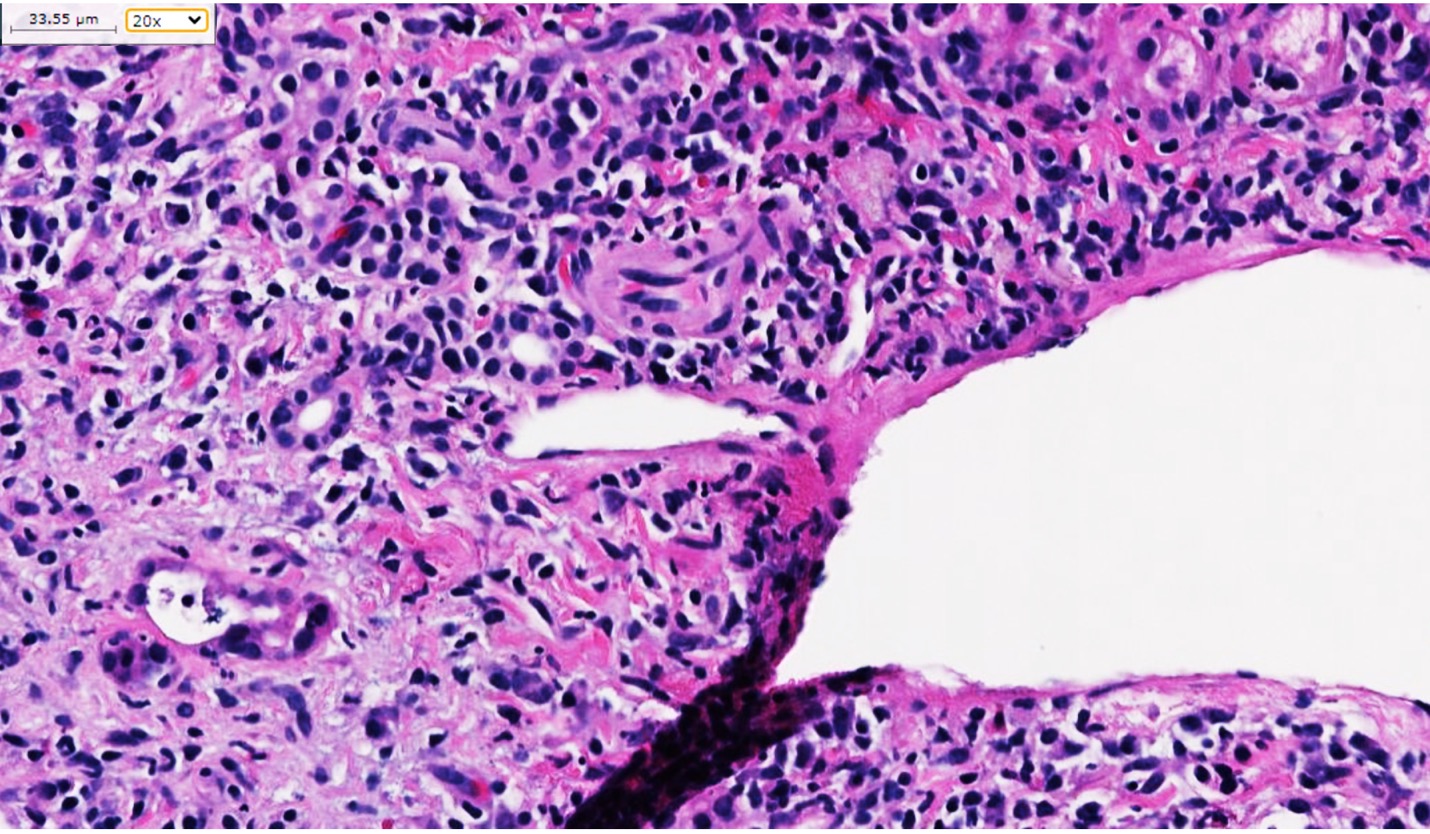
Case Description/Methods: A 28-year-old male with a two-year history of stricturing and internally fistulizing ileocolonic Crohn's disease, on maintenance IFX therapy, was initiated on methotrexate (MTX). After 12 months, he developed mild elevation in transaminase levels, new hepatic steatosis, and mild hepatomegaly on imaging; he was advised to stop MTX. He self-discontinued IFX, in addition to MTX. Transaminase levels normalized. After two months, patient was re-initiated on IFX monotherapy. On routine monitoring, elevated transaminases were noted again within 3 months. Imaging with ultrasound and CT revealed mild hepatomegaly with patent portal vein. Over the next month, transaminase levels rose (AST rose from 29 U/L to 500 U/L, ALT rose from 39 U/L to 812 U/L). Further workup revealed positive antinuclear and anti-mitochondrial antibodies. A liver biopsy with trichrome staining highlighted nodular necro-inflammatory activity, confirming a diagnosis of AIH-PBC overlap (figure). Treatment for drug-induced AIH/PBC involved IFX cessation, corticosteroid therapy, with azathioprine initiation. Despite initial complications involving steroid-induced hyperglycemia, patient responded well to treatment, with normalization of transaminase levels without further exacerbation of CD symptoms.
Discussion: This rare presentation highlights the complex interplay between autoimmune diseases and DILI related to biologic therapies. IFX liver injury can present with autoantibody induction, focal liver cell necrosis, and intense mononuclear cell infiltrates. However, drug-induced AIH/PBC overlap has not been extensively documented in the literature, particularly in the context of inflammatory bowel disease. Patients with true overlap syndrome, meeting the Paris Criteria, often have more severe liver inflammation and poorer outcomes. Recognizing and managing drug-induced AIH/PBC overlap in IBD patients on biologic therapy is essential for improving patient outcomes and highlights the need for vigilant monitoring and a coordinated multi-disciplinary approach.
Disclosures:
Kashif Osmani, MD1, Omar T. Ahmed, MD2, Salimah Mohamed, DO1, Grace Guzman, MD3, Itishree Trivedi, MD, MS3. P0986 - Unexpected Complications of Infliximab: A Rare Case of Drug-Induced AIH-PBC Overlap in Crohn's Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, IL; 2University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL; 3University of Illinois, Chicago, IL
Introduction: The coexistence of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) and autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), known as AIH-PBC overlap syndrome, occurs in only 3-7% of patients with PBC. While drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is known to mimic or trigger AIH, the specific overlap of drug-induced AIH with PBC is scarcely documented. Here, we report a patient with Crohn's disease (CD) on infliximab (IFX) who developed drug-induced AIH with PBC overlap after chronic IFX exposure.
Case Description/Methods: A 28-year-old male with a two-year history of stricturing and internally fistulizing ileocolonic Crohn's disease, on maintenance IFX therapy, was initiated on methotrexate (MTX). After 12 months, he developed mild elevation in transaminase levels, new hepatic steatosis, and mild hepatomegaly on imaging; he was advised to stop MTX. He self-discontinued IFX, in addition to MTX. Transaminase levels normalized. After two months, patient was re-initiated on IFX monotherapy. On routine monitoring, elevated transaminases were noted again within 3 months. Imaging with ultrasound and CT revealed mild hepatomegaly with patent portal vein. Over the next month, transaminase levels rose (AST rose from 29 U/L to 500 U/L, ALT rose from 39 U/L to 812 U/L). Further workup revealed positive antinuclear and anti-mitochondrial antibodies. A liver biopsy with trichrome staining highlighted nodular necro-inflammatory activity, confirming a diagnosis of AIH-PBC overlap (figure). Treatment for drug-induced AIH/PBC involved IFX cessation, corticosteroid therapy, with azathioprine initiation. Despite initial complications involving steroid-induced hyperglycemia, patient responded well to treatment, with normalization of transaminase levels without further exacerbation of CD symptoms.
Discussion: This rare presentation highlights the complex interplay between autoimmune diseases and DILI related to biologic therapies. IFX liver injury can present with autoantibody induction, focal liver cell necrosis, and intense mononuclear cell infiltrates. However, drug-induced AIH/PBC overlap has not been extensively documented in the literature, particularly in the context of inflammatory bowel disease. Patients with true overlap syndrome, meeting the Paris Criteria, often have more severe liver inflammation and poorer outcomes. Recognizing and managing drug-induced AIH/PBC overlap in IBD patients on biologic therapy is essential for improving patient outcomes and highlights the need for vigilant monitoring and a coordinated multi-disciplinary approach.

Figure: Liver biopsy showing marked autoimmune hepatitis overlap primary biliary cholangitis with bridging to nodular necro-inflammatory activity compatible with grade 3 to 4 AIH
Disclosures:
Kashif Osmani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Ahmed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Salimah Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Grace Guzman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Itishree Trivedi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kashif Osmani, MD1, Omar T. Ahmed, MD2, Salimah Mohamed, DO1, Grace Guzman, MD3, Itishree Trivedi, MD, MS3. P0986 - Unexpected Complications of Infliximab: A Rare Case of Drug-Induced AIH-PBC Overlap in Crohn's Disease, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
