Sunday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P1047 - Use of Intranasal Nitroglycerin During POEM : A Pilot Study
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Neel Kanth Issar, MBBS, MD
Army Hospital Research and Referral
New Delhi, Delhi, India
Presenting Author(s)
Neel Kanth Issar, MBBS, MD1, Priyank Dhiman, MBBS, MD1, Ritu Grewal, MBBS, MD2, Ajay Shankar Prasad, MBBS, MD1, Rahul Jain, MBBS, MD1
1Army Hospital Research and Referral, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 2Army Hospital Research and Referral, Delhi, Delhi, India
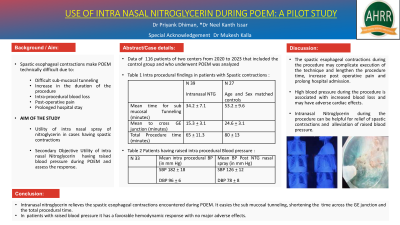
Introduction: Esophageal motility disorders like achalasia are characterized by various degrees of ineffective peristalsis and failure of the Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to relax. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) has recently emerged as a minimally invasive technique for Achlasia. However spastic esophageal contractions make POEM technically difficult due to difficult sub-mucosal tunneling increasing the duration of the procedure, intra-procedural blood loss, hemodynamic instability and post-operative pain causing prolonged hospital admission. We studied the use of intra nasal spray of nitroglycerin in select cases having spastic contractions and or having raised blood pressure during POEM and assessed the response.
Methods: Data from 2020 to 2023 of two centers for 127 patients who successfully underwent POEM was analyzed. Nitroglycerin spray was used in 33 patients with raised intra-procedure blood pressure. Intra nasal Nitroglycerin was used in 39 patients with spastic contractions that were hampering the tunneling procedure. The response was assessed by hemodynamic parameters, relief of spastic esophageal contraction, sub mucosal tunneling time, time to cross GE junction and total procedure time.
Results: Intra nasal Nitroglycerin was used in 33 patients with raised intra-operative blood pressure (Mean SBP 182 + 18 and DBP 96 + 6 mm of Hg ). 15/33 patients required a two intra-nasal puffs and 18/33 required three puffs to maintain the target blood pressure. Post administration the BP remained in the range of SBP 126-138 mmHg DBP 78 -86 mm Hg during the procedure. We observed that the spastic esophageal contractions where in no intervention was done increased the difficulty and time of sub mucosal tunneling , the time across the GE junction and prolonged the total procedural time to 53.2+9.6 min, 24.6+3.1 minutes, 80+13 min respectively vs standard time of 36± 8 min, 17+2.5 mins, 67+13 min respectively1. Intra nasal administration of nitroglycerin spray diminished the spastic contractions, shortened the sub mucosal tunneling, time across the GE junction and total procedure time to 34.2 + 7.1, 15.3 + 3.1 and 65 + 11.3 minutes respectively. The difference of these procedural times in the interventional group was statistically significant (p < 0.05)
Discussion: Administration of intranasal nitroglycerin is useful in relieving the spastic esophageal contractions encountered during POEM. It easies the sub mucosal tunneling, shortening the time across the GE junction and the total procedural time.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Neel Kanth Issar, MBBS, MD1, Priyank Dhiman, MBBS, MD1, Ritu Grewal, MBBS, MD2, Ajay Shankar Prasad, MBBS, MD1, Rahul Jain, MBBS, MD1. P1047 - Use of Intranasal Nitroglycerin During POEM : A Pilot Study, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Army Hospital Research and Referral, New Delhi, Delhi, India; 2Army Hospital Research and Referral, Delhi, Delhi, India
Introduction: Esophageal motility disorders like achalasia are characterized by various degrees of ineffective peristalsis and failure of the Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) to relax. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) has recently emerged as a minimally invasive technique for Achlasia. However spastic esophageal contractions make POEM technically difficult due to difficult sub-mucosal tunneling increasing the duration of the procedure, intra-procedural blood loss, hemodynamic instability and post-operative pain causing prolonged hospital admission. We studied the use of intra nasal spray of nitroglycerin in select cases having spastic contractions and or having raised blood pressure during POEM and assessed the response.
Methods: Data from 2020 to 2023 of two centers for 127 patients who successfully underwent POEM was analyzed. Nitroglycerin spray was used in 33 patients with raised intra-procedure blood pressure. Intra nasal Nitroglycerin was used in 39 patients with spastic contractions that were hampering the tunneling procedure. The response was assessed by hemodynamic parameters, relief of spastic esophageal contraction, sub mucosal tunneling time, time to cross GE junction and total procedure time.
Results: Intra nasal Nitroglycerin was used in 33 patients with raised intra-operative blood pressure (Mean SBP 182 + 18 and DBP 96 + 6 mm of Hg ). 15/33 patients required a two intra-nasal puffs and 18/33 required three puffs to maintain the target blood pressure. Post administration the BP remained in the range of SBP 126-138 mmHg DBP 78 -86 mm Hg during the procedure. We observed that the spastic esophageal contractions where in no intervention was done increased the difficulty and time of sub mucosal tunneling , the time across the GE junction and prolonged the total procedural time to 53.2+9.6 min, 24.6+3.1 minutes, 80+13 min respectively vs standard time of 36± 8 min, 17+2.5 mins, 67+13 min respectively1. Intra nasal administration of nitroglycerin spray diminished the spastic contractions, shortened the sub mucosal tunneling, time across the GE junction and total procedure time to 34.2 + 7.1, 15.3 + 3.1 and 65 + 11.3 minutes respectively. The difference of these procedural times in the interventional group was statistically significant (p < 0.05)
Discussion: Administration of intranasal nitroglycerin is useful in relieving the spastic esophageal contractions encountered during POEM. It easies the sub mucosal tunneling, shortening the time across the GE junction and the total procedural time.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Neel Kanth Issar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Priyank Dhiman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ritu Grewal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ajay Shankar Prasad indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rahul Jain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neel Kanth Issar, MBBS, MD1, Priyank Dhiman, MBBS, MD1, Ritu Grewal, MBBS, MD2, Ajay Shankar Prasad, MBBS, MD1, Rahul Jain, MBBS, MD1. P1047 - Use of Intranasal Nitroglycerin During POEM : A Pilot Study, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
