Sunday Poster Session
Category: Pediatrics
P1479 - Not Just a Pirate's Tale: Uncovering Scurvy in Modern Kids
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Palack Agrawal, MD
Memorial Healthcare System
Hollywood, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Palack Agrawal, MD1, Ramiro Cardenas, MD1, Keshav Bhattar, MD1, Aniruddh Setya, MD2
1Memorial Healthcare System, Hollywood, FL; 2SSM Health Saint Louis University Hospital, St. Louis, MO
Introduction: Limping is a common complaint seen in Pediatric Emergency Room visits. Transient synovitis is the most common diagnosis; however, limping may signify a more ominous pathology. Given the broad differentials, causes such as fracture, child abuse, autoimmune disease, and malignant etiologies must be excluded. Vitamin C deficiency (scurvy) is a differential not typically explored in acute settings. Children most at risk include those with neurodevelopmental conditions such as autism which is associated with a restrictive diet.
Case Description/Methods: A
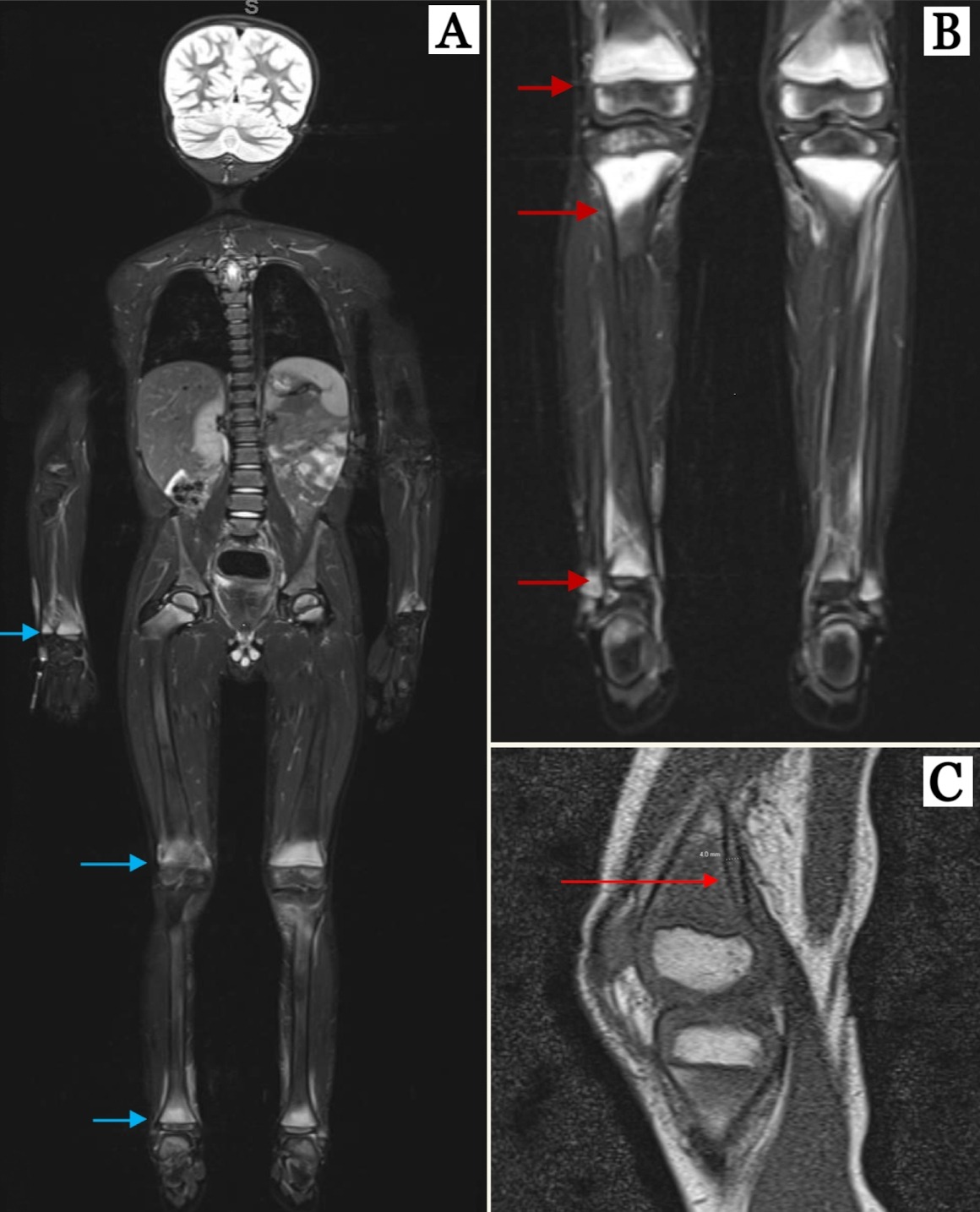
4yo male with Autism presented for a second ED evaluation due to 2 weeks of limping. The exam noted an antalgic gait with limited ROM at the hips. However, X-ray and hip US were normal. Investigations revealed microcytic anemia and elevated inflammatory markers. On further questioning, the diet consisted strictly of macaroni & cheese and water. Scout MRI revealed metaphyseal abnormalities suggestive of Scurvy (Figure A). Diagnosis confirmed by Vit C level of < 0.1 mg/dL. GI consulted and initiated Vit C supplementation. Upon discharge patient had normal gait.
A 6yo male with Autism presented to ED for intermittent and worsening right sided limp for past 1 year. Labs wit microcytic anemia and elevated sedimentation rate. Imaging was normal. Exam with significant limitation in ROM to bilateral knees. MRI of bilateral lower extremities with lumbar spine was done which showed significant metaphyseal bone marrow signal changes (Figure B) with subperiosteal hematoma (Figure C) favored to reflect Scurvy confirmed with a Vit C level of < 0.1 mg/dL. Also found to have Celiac disease and Vit D deficiency, started on a gluten-free diet with Vitamins C & D supplementation. After starting oral Vit C, he was discharged home with normal ROM and gait.
Discussion: < !
Vitamin C is a water-soluble micronutrient, classified as essential, with a half-life of 10-20 days. Body stores are depleted within 3 months if not supplemented in the diet. Early non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss appear in 2-3 months, while visible features like gingival hemorrhage, ecchymosis, petechiae, and hyperkeratosis emerge in 5-6 months of chronic deficiency. Musculoskeletal manifestations are present in about 80% of patients with scurvy. Diagnosis confirmed by vitamin C level < 0.2 mg/dL.
Disclosures:
Palack Agrawal, MD1, Ramiro Cardenas, MD1, Keshav Bhattar, MD1, Aniruddh Setya, MD2. P1479 - Not Just a Pirate's Tale: Uncovering Scurvy in Modern Kids, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Memorial Healthcare System, Hollywood, FL; 2SSM Health Saint Louis University Hospital, St. Louis, MO
Introduction: Limping is a common complaint seen in Pediatric Emergency Room visits. Transient synovitis is the most common diagnosis; however, limping may signify a more ominous pathology. Given the broad differentials, causes such as fracture, child abuse, autoimmune disease, and malignant etiologies must be excluded. Vitamin C deficiency (scurvy) is a differential not typically explored in acute settings. Children most at risk include those with neurodevelopmental conditions such as autism which is associated with a restrictive diet.
Case Description/Methods: A
4yo male with Autism presented for a second ED evaluation due to 2 weeks of limping. The exam noted an antalgic gait with limited ROM at the hips. However, X-ray and hip US were normal. Investigations revealed microcytic anemia and elevated inflammatory markers. On further questioning, the diet consisted strictly of macaroni & cheese and water. Scout MRI revealed metaphyseal abnormalities suggestive of Scurvy (Figure A). Diagnosis confirmed by Vit C level of < 0.1 mg/dL. GI consulted and initiated Vit C supplementation. Upon discharge patient had normal gait.
A 6yo male with Autism presented to ED for intermittent and worsening right sided limp for past 1 year. Labs wit microcytic anemia and elevated sedimentation rate. Imaging was normal. Exam with significant limitation in ROM to bilateral knees. MRI of bilateral lower extremities with lumbar spine was done which showed significant metaphyseal bone marrow signal changes (Figure B) with subperiosteal hematoma (Figure C) favored to reflect Scurvy confirmed with a Vit C level of < 0.1 mg/dL. Also found to have Celiac disease and Vit D deficiency, started on a gluten-free diet with Vitamins C & D supplementation. After starting oral Vit C, he was discharged home with normal ROM and gait.
Discussion: < !
Vitamin C is a water-soluble micronutrient, classified as essential, with a half-life of 10-20 days. Body stores are depleted within 3 months if not supplemented in the diet. Early non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss appear in 2-3 months, while visible features like gingival hemorrhage, ecchymosis, petechiae, and hyperkeratosis emerge in 5-6 months of chronic deficiency. Musculoskeletal manifestations are present in about 80% of patients with scurvy. Diagnosis confirmed by vitamin C level < 0.2 mg/dL.

Figure: Figure (A) Mild symmetric regional bone marrow edema bilaterally in distal radial and ulnar metaphysis, proximal and distal femoral, tibia and fibular metaphysis (blue arrow)
Figure (B) Metaphyseal predominant bone marrow signal changes bilaterally distal femoral, proximal and distal tibia and fibular metaphysis (Red arrow)
Figure (C) Subperiosteal hematoma along the posterior medial left distal femoral metaphysis measuring 4 mm
Figure (B) Metaphyseal predominant bone marrow signal changes bilaterally distal femoral, proximal and distal tibia and fibular metaphysis (Red arrow)
Figure (C) Subperiosteal hematoma along the posterior medial left distal femoral metaphysis measuring 4 mm
Disclosures:
Palack Agrawal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ramiro Cardenas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Keshav Bhattar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aniruddh Setya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Palack Agrawal, MD1, Ramiro Cardenas, MD1, Keshav Bhattar, MD1, Aniruddh Setya, MD2. P1479 - Not Just a Pirate's Tale: Uncovering Scurvy in Modern Kids, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

