Sunday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P1530 - Statewide Burden of Peptic Ulcer Disease in the United States and its Trend From 1990-2021: A Benchmarking Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Janmay Vala, MBBS
Terna Medical College
Boisar, Maharashtra, India
Presenting Author(s)
Janmay Vala, MBBS1, Sravani Bhavanam, MBBS, MD2, Nanki Singh, MBBS3, Mandeepsinh Vashi, MBBS4, Aishwar Dixit, MBBS5, George Mathew Mukalil, MD6, Muhammad Waqas, MBBS7, Ashwinikumar Shandilya, MBBS8, Bhargav Koyani, MD9, Awan Muhammad Raheel, MBBS, MD10, Mohit Lakkimsetti, MBBS11, Vishrant P. Amin, MBBS12, Juhi R. Patel, MBBS13, Hardik Dineshbhai. Desai, MBBS14
1Terna Medical College, Boisar, Maharashtra, India; 2One Brooklyn Health-Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 3School of Medical Sciences and Research, Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India; 4Surat Municipal Institute of Medical Education and Research (SMIMER), Surat, Gujarat, India; 5Baba Raghav Das Medical College, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India; 6Central Michigan University, Saginaw, MI; 7Jinnah Sindh Medical University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 8Rural Medical College, Pravara Institute of Medical Sciences, Ahmednagar, Maharashtra, India; 9Saint Francis Hospital, Evanston, Evanston, IL; 10Carle Health, Urbana, IL; 11Mamata Medical College, Khammam, Telangana, India; 12GMERS Medical College Valsad, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 13GMERS Medical College and Hospital Valsad, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 14Gujarat Adani Institute of Medical Sciences, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India
Introduction: Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) is increasingly becoming a public health concern in the United States. There remains a lack of consistent and comparative data on PUD in the USA. This study represents the first comprehensive estimation of the PUD burden across the last three decades in the USA, including the initial two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, which posed significant challenges in managing non-COVID-19 cases.
Methods: Utilizing the Global Burden of Disease tool, we estimated the incidence, prevalence, deaths, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) associated with PUD, stratified by age, sex, year, and location across the USA from 1990 to 2021. Non-fatal health outcomes were estimated using the DISMOD MR-2.1 meta-regression tool, while fatal health outcomes were derived from the Cause of Death Ensemble Model (CODEm).
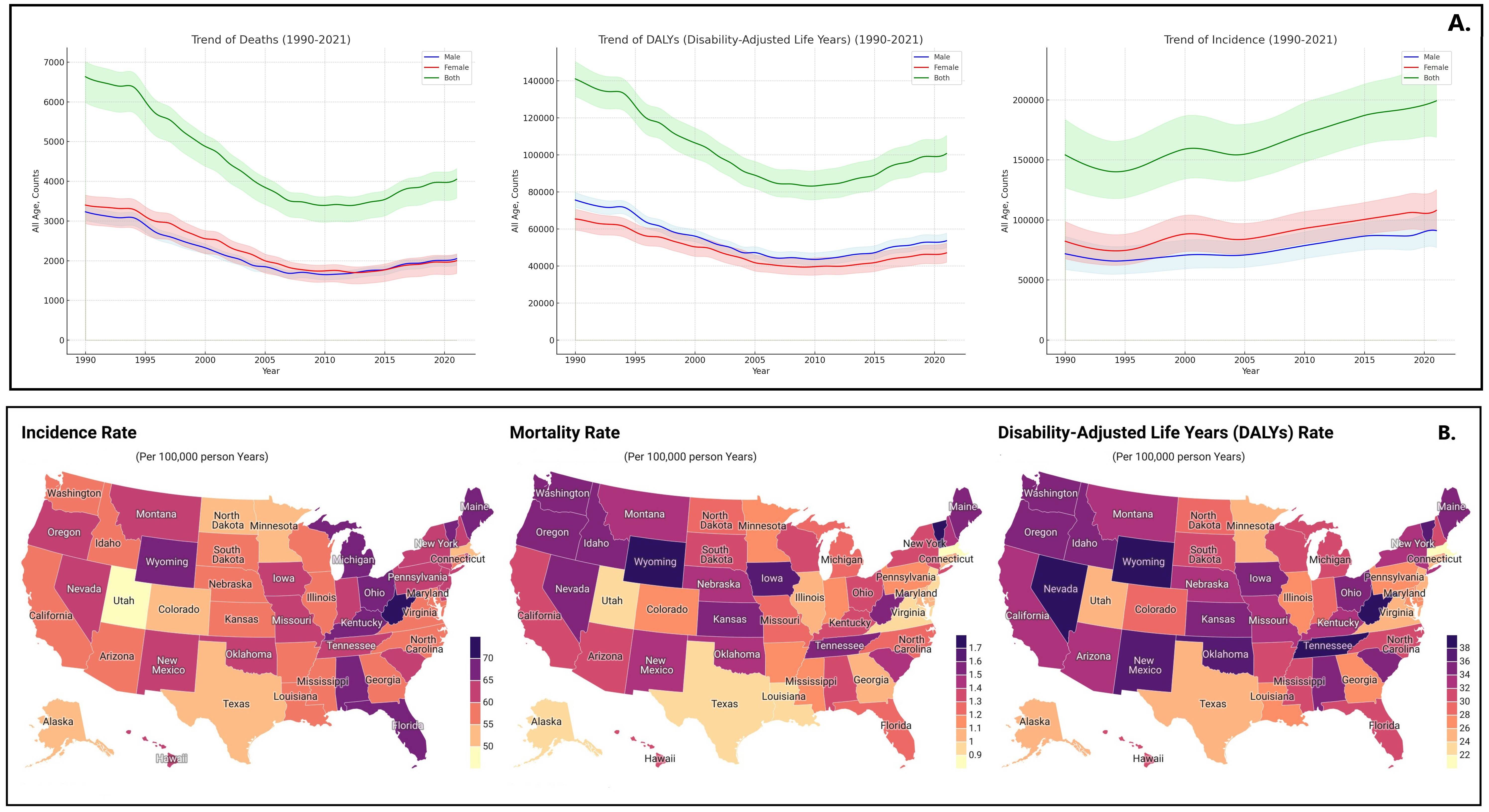
Results: The total prevalence count of Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) in the U.S. rose from 375,151 (95% uncertainty interval: 314,701-451,354) in 1990 to 485,057 (419,149-560,778) in 2021. The total percentage change (TPC) in the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) decreased by 21%, while the age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) and the age-standardized disability-adjusted life years rate (ASDALR) decreased by 66% and 58% respectively from 1990 to 2021. The highest TPC in ASIR was observed in Massachusetts with a 26% decrease, and the smallest was in Alabama at 15%. In terms of ASMR, the greatest reduction was seen in South Dakota at 61%. Age-wise, the highest incidence count in 2021 was in individuals aged 70-74 years, with 29,610 cases (95% UI: 19,345-40,820), while the highest number of deaths occurred in the 85-89 age group with 556 (439-621), and the highest DALYs were in the 70-74 age group with 12,447 (11,237-13,960). Over the past three decades, males consistently exhibited a higher burden of disease compared to females.
Discussion: Despite a decreasing trend, the overall burden of Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) remains high, emphasizing the need for ongoing public health initiatives, effective policy-making, and updated clinical practices. Public health officials must continue prioritizing PUD by focusing on prevention and management strategies, while policymakers need to ensure adequate resource allocation for improved care. Clinicians should keep current with treatment advancements and prevention techniques to effectively manage and educate patients, helping to further alleviate the disease's impact.
Disclosures:
Janmay Vala, MBBS1, Sravani Bhavanam, MBBS, MD2, Nanki Singh, MBBS3, Mandeepsinh Vashi, MBBS4, Aishwar Dixit, MBBS5, George Mathew Mukalil, MD6, Muhammad Waqas, MBBS7, Ashwinikumar Shandilya, MBBS8, Bhargav Koyani, MD9, Awan Muhammad Raheel, MBBS, MD10, Mohit Lakkimsetti, MBBS11, Vishrant P. Amin, MBBS12, Juhi R. Patel, MBBS13, Hardik Dineshbhai. Desai, MBBS14. P1530 - Statewide Burden of Peptic Ulcer Disease in the United States and its Trend From 1990-2021: A Benchmarking Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Terna Medical College, Boisar, Maharashtra, India; 2One Brooklyn Health-Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 3School of Medical Sciences and Research, Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India; 4Surat Municipal Institute of Medical Education and Research (SMIMER), Surat, Gujarat, India; 5Baba Raghav Das Medical College, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India; 6Central Michigan University, Saginaw, MI; 7Jinnah Sindh Medical University, Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan; 8Rural Medical College, Pravara Institute of Medical Sciences, Ahmednagar, Maharashtra, India; 9Saint Francis Hospital, Evanston, Evanston, IL; 10Carle Health, Urbana, IL; 11Mamata Medical College, Khammam, Telangana, India; 12GMERS Medical College Valsad, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 13GMERS Medical College and Hospital Valsad, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 14Gujarat Adani Institute of Medical Sciences, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India
Introduction: Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) is increasingly becoming a public health concern in the United States. There remains a lack of consistent and comparative data on PUD in the USA. This study represents the first comprehensive estimation of the PUD burden across the last three decades in the USA, including the initial two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, which posed significant challenges in managing non-COVID-19 cases.
Methods: Utilizing the Global Burden of Disease tool, we estimated the incidence, prevalence, deaths, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) associated with PUD, stratified by age, sex, year, and location across the USA from 1990 to 2021. Non-fatal health outcomes were estimated using the DISMOD MR-2.1 meta-regression tool, while fatal health outcomes were derived from the Cause of Death Ensemble Model (CODEm).
Results: The total prevalence count of Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) in the U.S. rose from 375,151 (95% uncertainty interval: 314,701-451,354) in 1990 to 485,057 (419,149-560,778) in 2021. The total percentage change (TPC) in the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) decreased by 21%, while the age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) and the age-standardized disability-adjusted life years rate (ASDALR) decreased by 66% and 58% respectively from 1990 to 2021. The highest TPC in ASIR was observed in Massachusetts with a 26% decrease, and the smallest was in Alabama at 15%. In terms of ASMR, the greatest reduction was seen in South Dakota at 61%. Age-wise, the highest incidence count in 2021 was in individuals aged 70-74 years, with 29,610 cases (95% UI: 19,345-40,820), while the highest number of deaths occurred in the 85-89 age group with 556 (439-621), and the highest DALYs were in the 70-74 age group with 12,447 (11,237-13,960). Over the past three decades, males consistently exhibited a higher burden of disease compared to females.
Discussion: Despite a decreasing trend, the overall burden of Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) remains high, emphasizing the need for ongoing public health initiatives, effective policy-making, and updated clinical practices. Public health officials must continue prioritizing PUD by focusing on prevention and management strategies, while policymakers need to ensure adequate resource allocation for improved care. Clinicians should keep current with treatment advancements and prevention techniques to effectively manage and educate patients, helping to further alleviate the disease's impact.

Figure: A: Burden and Trend of Peptic Ulcer Disease in the United States from 1990-2021, B: Statewide Burden of Peptic Ulcer Disease in the United States, Unadjusted Rate (per 100,000) in 2021
Disclosures:
Janmay Vala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sravani Bhavanam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nanki Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mandeepsinh Vashi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aishwar Dixit indicated no relevant financial relationships.
George Mathew Mukalil indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Waqas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashwinikumar Shandilya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bhargav Koyani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Awan Muhammad Raheel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohit Lakkimsetti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vishrant Amin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Juhi Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hardik Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Janmay Vala, MBBS1, Sravani Bhavanam, MBBS, MD2, Nanki Singh, MBBS3, Mandeepsinh Vashi, MBBS4, Aishwar Dixit, MBBS5, George Mathew Mukalil, MD6, Muhammad Waqas, MBBS7, Ashwinikumar Shandilya, MBBS8, Bhargav Koyani, MD9, Awan Muhammad Raheel, MBBS, MD10, Mohit Lakkimsetti, MBBS11, Vishrant P. Amin, MBBS12, Juhi R. Patel, MBBS13, Hardik Dineshbhai. Desai, MBBS14. P1530 - Statewide Burden of Peptic Ulcer Disease in the United States and its Trend From 1990-2021: A Benchmarking Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
