Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1245 - Improving Hepatitis B Screening Using EMR Hard-Stop Across Health System Enterprise
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Beatriz Torre, MD
Thomas Jefferson University Hospital
Philadelphia, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Beatriz Torre, MD, Jonathan M. Fenkel, MD, Benjamin Young, MD, Bracken Babula, MD
Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA
Introduction: In March 2023, the CDC recommended Hepatitis B virus (HBV) universal triple screening for all adults, testing surface antigen (sAg), surface antibody (sAb), and total core antibody (cAb), regardless of perceived risk. Electronic medical record (EMR) systems have proven to be a powerful tool to improve quality metrics like universal screening. We designed a quality improvement (QI) project to explore whether utilizing an EMR-based tool called a Care Gap, a "hard-stop" mechanism of QI, within our academic health system’s EPIC-based EMR could increase HBV screening throughout the enterprise.
Methods: The HBV screening Care Gap was instituted from 2/13/24–5/2/24 for all adult patients at a large metropolitan health enterprise encompassing 10 EPIC-based hospitals surrounding an academic tertiary care center. HBV test rates were collected at an enterprise level pre (6 weeks leading up to intervention) and post-intervention (14 weeks after the intervention). The pre- and post-intervention groups were compared using descriptive statistics.
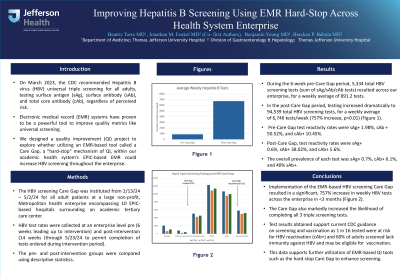
Results: During the 6 week pre-Care Gap period, 5,334 total HBV screening tests (sum of sAg/sAb/cAb tests) resulted across our enterprise, for a weekly average of 891.2 tests. Notable among the pre-Care Gap phase was an sAg:cAb test ratio of 3.14 and an sAg:sAb test ratio of 1.87, suggesting triple screening was not routinely performed. In the post-Care Gap period, testing increased dramatically to 94,539 total HBV screening tests, for a weekly average of 6,746 tests/week (757% increase, p< 0.01). The ratio of sAg:cAb tests decreased to 1.14 and sAg:sAb ratio decreased to 1.09, both suggestive that more triple screening occurred. Pre-Care Gap test reactivity rates were sAg+ 1.98%, sAb + 50.52%, and cAb+ 10.45%. Post-Care Gap, test reactivity rates were sAg+ 0.6%, sAb+ 38.02%, and cAb+ 5.6%. The overall prevalence of each test was sAg+ 0.7%, cAb+ 6.1%, and 40% sAb+.
Discussion: Implementation of the EMR-based HBV screening Care Gap resulted in a significant, 757% increase in weekly HBV tests across the enterprise in < 3 months. The Care Gap also markedly increased the likelihood of completing all 3 triple screening tests. Test results obtained support current CDC guidance on screening and vaccination as 1 in 16 tested were at risk for HBV reactivation (cAb+) and 60% of adults screened lack immunity against HBV and would benefit from vaccination. This data supports further utilization of EMR-based QI tools such as the hard-stop Care Gap to enhance screening.
Disclosures:
Beatriz Torre, MD, Jonathan M. Fenkel, MD, Benjamin Young, MD, Bracken Babula, MD. P1245 - Improving Hepatitis B Screening Using EMR Hard-Stop Across Health System Enterprise, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Beatriz Torre, MD, Jonathan M. Fenkel, MD, Benjamin Young, MD, Bracken Babula, MD
Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA
Introduction: In March 2023, the CDC recommended Hepatitis B virus (HBV) universal triple screening for all adults, testing surface antigen (sAg), surface antibody (sAb), and total core antibody (cAb), regardless of perceived risk. Electronic medical record (EMR) systems have proven to be a powerful tool to improve quality metrics like universal screening. We designed a quality improvement (QI) project to explore whether utilizing an EMR-based tool called a Care Gap, a "hard-stop" mechanism of QI, within our academic health system’s EPIC-based EMR could increase HBV screening throughout the enterprise.
Methods: The HBV screening Care Gap was instituted from 2/13/24–5/2/24 for all adult patients at a large metropolitan health enterprise encompassing 10 EPIC-based hospitals surrounding an academic tertiary care center. HBV test rates were collected at an enterprise level pre (6 weeks leading up to intervention) and post-intervention (14 weeks after the intervention). The pre- and post-intervention groups were compared using descriptive statistics.
Results: During the 6 week pre-Care Gap period, 5,334 total HBV screening tests (sum of sAg/sAb/cAb tests) resulted across our enterprise, for a weekly average of 891.2 tests. Notable among the pre-Care Gap phase was an sAg:cAb test ratio of 3.14 and an sAg:sAb test ratio of 1.87, suggesting triple screening was not routinely performed. In the post-Care Gap period, testing increased dramatically to 94,539 total HBV screening tests, for a weekly average of 6,746 tests/week (757% increase, p< 0.01). The ratio of sAg:cAb tests decreased to 1.14 and sAg:sAb ratio decreased to 1.09, both suggestive that more triple screening occurred. Pre-Care Gap test reactivity rates were sAg+ 1.98%, sAb + 50.52%, and cAb+ 10.45%. Post-Care Gap, test reactivity rates were sAg+ 0.6%, sAb+ 38.02%, and cAb+ 5.6%. The overall prevalence of each test was sAg+ 0.7%, cAb+ 6.1%, and 40% sAb+.
Discussion: Implementation of the EMR-based HBV screening Care Gap resulted in a significant, 757% increase in weekly HBV tests across the enterprise in < 3 months. The Care Gap also markedly increased the likelihood of completing all 3 triple screening tests. Test results obtained support current CDC guidance on screening and vaccination as 1 in 16 tested were at risk for HBV reactivation (cAb+) and 60% of adults screened lack immunity against HBV and would benefit from vaccination. This data supports further utilization of EMR-based QI tools such as the hard-stop Care Gap to enhance screening.
Disclosures:
Beatriz Torre indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jonathan Fenkel: Abbvie – Grant/Research Support. Alexion – Grant/Research Support. Gilead – Grant/Research Support. Ipsen – Grant/Research Support.
Benjamin Young indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Bracken Babula indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Beatriz Torre, MD, Jonathan M. Fenkel, MD, Benjamin Young, MD, Bracken Babula, MD. P1245 - Improving Hepatitis B Screening Using EMR Hard-Stop Across Health System Enterprise, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

