Sunday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P1174 - Incidence of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients Treated With Terlipressin for Hepatorenal Syndrome
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Shefali Amin, DO, MSEd
Geisinger Health System
Wilkes-Barre, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Shefali Amin, DO, MSEd1, Manish Shrestha, MD2, Iman Waheed. Khan, MD2, Devi Nair, MD2, Marisa Caminos, DO2, Sandesh Parajuli, MD2, Christopher Reggio, DO2, Anthony Donato, MD2
1Geisinger Health System, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 2Reading Tower Health, Reading, PA
Introduction: Terlipressin is a synthetic analog of vasopressin recently approved by the FDA for use in hepatorenal syndrome (HRS). In HRS, terlipressin administration results in splanchnic vasoconstriction which shunts the blood to the systemic circulation. Additionally, randomized controlled studies have shown that terlipressin increases cerebral perfusion pressure with a resultant increase in intracranial pressure. Cerebral hyperemia has also been postulated to be one of the key modulators in hepatic encephalopathy (HE), causing increased brain ammonia delivery and neuronal dysfunction. Given that HE potentially has a significant impact on quality of life, we performed a meta-analysis to clarify the incidence of HE in patients with HRS treated with terlipressin.
Methods: Medline, EMBASE, and Cochrane central registry of controlled trials were queried since inception through January 1, 2024. Relevant terms and their synonyms, including but not limited to “Hepatic Encephalopathy” AND “Terlipressin,” were used. PRISMA guidelines were used for abstracting data and assessing data quality and validity. Two studies were included in the final analysis.
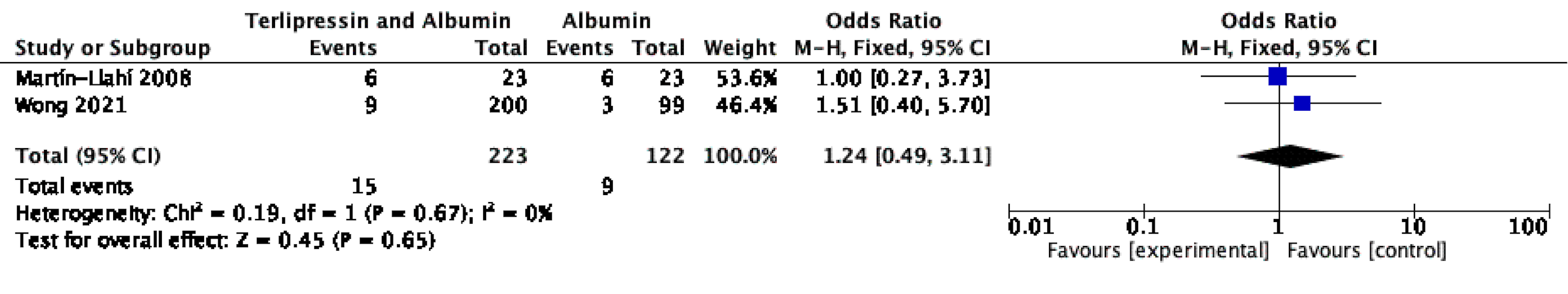
Results: We identified two RCTs with 346 patients for the study, comparing teripressin to albumin infusion in a 2:1 ratio. Fifteen (4.3%) patients developed HE in the terlipressin plus albumin group while 9 (4%) patients developed HE in the albumin group. There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of HE in the terlipressin plus albumin group compared to only albumin group. The odds ratio for HE was calculated to be 1.24; 95% CI 0.49 to 3.11; p=0.67.
Discussion: Our study concluded that there is no increased incidence of HE in patients with HRS treated with terlipressin plus albumin compared to albumin, but wide confidence intervals suggest that this analysis was too underpowered for a definitive answer of harm or benefit with respect to HE. More high-quality RCTs are needed to compare the two groups to better answer this question.
Disclosures:
Shefali Amin, DO, MSEd1, Manish Shrestha, MD2, Iman Waheed. Khan, MD2, Devi Nair, MD2, Marisa Caminos, DO2, Sandesh Parajuli, MD2, Christopher Reggio, DO2, Anthony Donato, MD2. P1174 - Incidence of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients Treated With Terlipressin for Hepatorenal Syndrome, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Geisinger Health System, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 2Reading Tower Health, Reading, PA
Introduction: Terlipressin is a synthetic analog of vasopressin recently approved by the FDA for use in hepatorenal syndrome (HRS). In HRS, terlipressin administration results in splanchnic vasoconstriction which shunts the blood to the systemic circulation. Additionally, randomized controlled studies have shown that terlipressin increases cerebral perfusion pressure with a resultant increase in intracranial pressure. Cerebral hyperemia has also been postulated to be one of the key modulators in hepatic encephalopathy (HE), causing increased brain ammonia delivery and neuronal dysfunction. Given that HE potentially has a significant impact on quality of life, we performed a meta-analysis to clarify the incidence of HE in patients with HRS treated with terlipressin.
Methods: Medline, EMBASE, and Cochrane central registry of controlled trials were queried since inception through January 1, 2024. Relevant terms and their synonyms, including but not limited to “Hepatic Encephalopathy” AND “Terlipressin,” were used. PRISMA guidelines were used for abstracting data and assessing data quality and validity. Two studies were included in the final analysis.
Results: We identified two RCTs with 346 patients for the study, comparing teripressin to albumin infusion in a 2:1 ratio. Fifteen (4.3%) patients developed HE in the terlipressin plus albumin group while 9 (4%) patients developed HE in the albumin group. There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of HE in the terlipressin plus albumin group compared to only albumin group. The odds ratio for HE was calculated to be 1.24; 95% CI 0.49 to 3.11; p=0.67.
Discussion: Our study concluded that there is no increased incidence of HE in patients with HRS treated with terlipressin plus albumin compared to albumin, but wide confidence intervals suggest that this analysis was too underpowered for a definitive answer of harm or benefit with respect to HE. More high-quality RCTs are needed to compare the two groups to better answer this question.

Figure: Figure 1: Forest Plot
Caption: Forest Plot of comparison: Terlipression plus Albumin vs Albumin, outcome: Incidence of HE
Caption: Forest Plot of comparison: Terlipression plus Albumin vs Albumin, outcome: Incidence of HE
Disclosures:
Shefali Amin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manish Shrestha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iman Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Devi Nair indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marisa Caminos indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sandesh Parajuli indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christopher Reggio indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anthony Donato indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shefali Amin, DO, MSEd1, Manish Shrestha, MD2, Iman Waheed. Khan, MD2, Devi Nair, MD2, Marisa Caminos, DO2, Sandesh Parajuli, MD2, Christopher Reggio, DO2, Anthony Donato, MD2. P1174 - Incidence of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients Treated With Terlipressin for Hepatorenal Syndrome, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
