Sunday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P1036 - Weight Regain After Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG): Can Redo ESG (R-ESG) Help? What is the Role of Pharmacotherapy? Analysis of 80 Patients
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio

Abdul-Rahman F. Diab, MD
University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine and University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME
Ocala, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Abdul-Rahman F. Diab, MD1, Joseph A. Sujka, MD2, Kathleen Mattingly, DO3, Angelica McCaskey, DO3, Abdullah Elnaji, DO3, Salvatore Docimo, DO2, Christopher G. DuCoin, MD2
1University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine and University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME, Ocala, FL; 2University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine, Tampa, FL; 3University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME, Ocala, FL
Introduction: Although endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) is effective, some patients may experience weight regain. This weight regain can be managed through conversion to bariatric surgery, pharmacotherapy, or redo ESG (R-ESG). Anecdotally, bariatric surgery leads to superior weight loss outcomes, but the question remains whether R-ESG or pharmacotherapy can help, and how do both compare to each other? This study aimed to assess the efficacy of R-ESG and pharmacotherapy in mitigating weight regain after primary ESG (P-ESG).
Methods: We conducted a systematic literature review following PRISMA guidelines to identify articles assessing the efficacy of R-ESG and pharmacotherapy in mitigating weight regain after P-ESG. Mean total weight loss percentages (TWL%) at 1, 3, and 6 months were collected. TWL% reflected the weight lost after the R-ESG or the initiation of pharmacotherapy (not overall TWL% after P-ESG). Analysis was conducted using a continuous random-effects model, specifically the DerSimonian-Laird method.
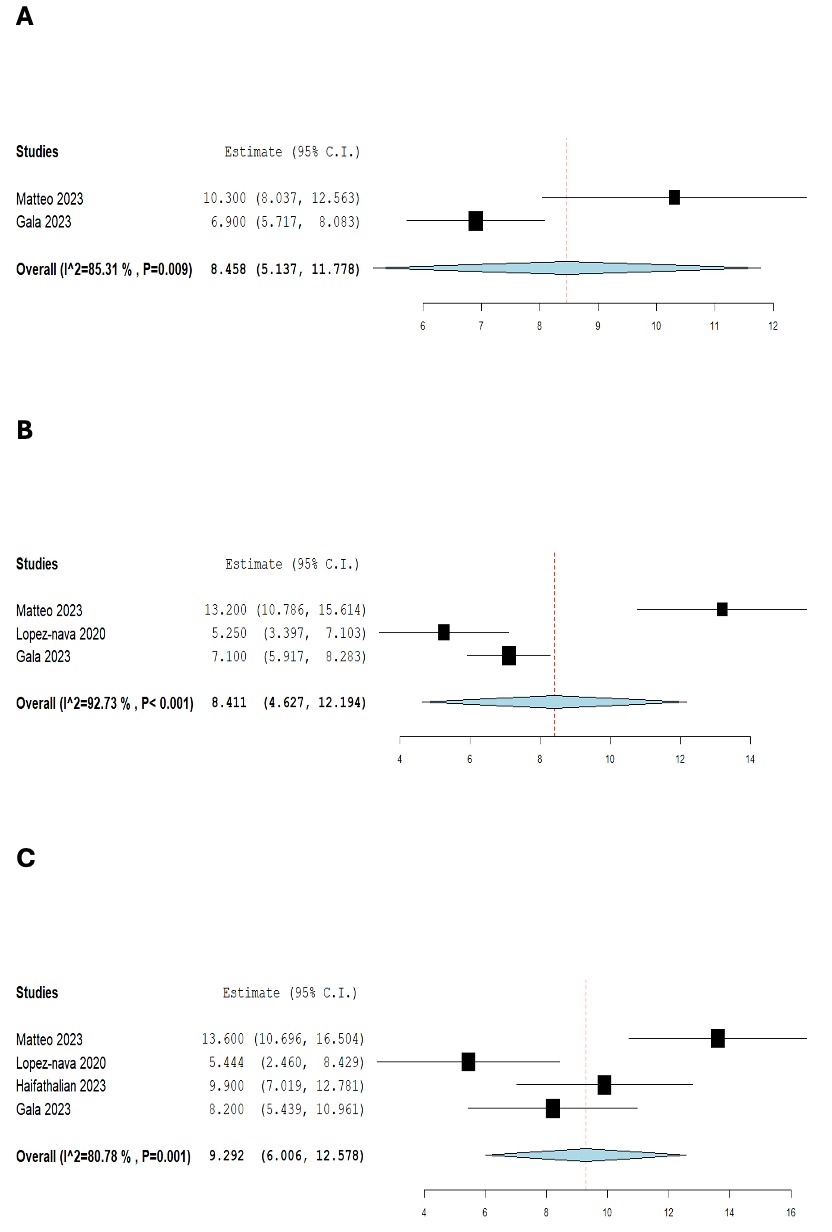
Results: Four studies on R-ESG and one study on pharmacotherapy were identified. Out of 47 patients, the pooled mean TWL% at 1 month after R-ESG (Figure 1A) was 8.458% (95% CI 5.137 – 11.778). There was significant heterogeneity (I² = 85.31%, p = 0.009). Out of 77 patients, the pooled mean TWL% at 3 months (Figure 1B) after R-ESG was 8.411% (95% CI 4.627 – 12.194). Significant heterogeneity was observed (I² = 92.73%, p < 0.001). Out of 80 patients, the pooled mean TWL% at 6 months (Figure 3B) after redo-ESG was 9.292% (95% CI 6.006 – 12.578), with significant heterogeneity (I² = 80.78%, p = 0.001). Haifathalian et al. (2023) is the single study in the literature comparing R-ESG and pharmacotherapy for managing weight regain after P-ESG, showing an additional TWL% after 6 months of 9.9% ± 7.2% with R-ESG versus 2.1% ± 8.6% with pharmacotherapy (p = 0.001).
Discussion: R-ESG appears to be an effective approach to mitigate weight regain after P-ESG. However, questions remain about how R-ESG compares to pharmacotherapy and how each approach compares to a combined strategy (pharmacotherapy plus R-ESG). Further research is needed to optimize the management of weight regain after P-ESG.
Disclosures:
Abdul-Rahman F. Diab, MD1, Joseph A. Sujka, MD2, Kathleen Mattingly, DO3, Angelica McCaskey, DO3, Abdullah Elnaji, DO3, Salvatore Docimo, DO2, Christopher G. DuCoin, MD2. P1036 - Weight Regain After Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG): Can Redo ESG (R-ESG) Help? What is the Role of Pharmacotherapy? Analysis of 80 Patients, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine and University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME, Ocala, FL; 2University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine, Tampa, FL; 3University of Central Florida, HCA Healthcare GME, Ocala, FL
Introduction: Although endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty (ESG) is effective, some patients may experience weight regain. This weight regain can be managed through conversion to bariatric surgery, pharmacotherapy, or redo ESG (R-ESG). Anecdotally, bariatric surgery leads to superior weight loss outcomes, but the question remains whether R-ESG or pharmacotherapy can help, and how do both compare to each other? This study aimed to assess the efficacy of R-ESG and pharmacotherapy in mitigating weight regain after primary ESG (P-ESG).
Methods: We conducted a systematic literature review following PRISMA guidelines to identify articles assessing the efficacy of R-ESG and pharmacotherapy in mitigating weight regain after P-ESG. Mean total weight loss percentages (TWL%) at 1, 3, and 6 months were collected. TWL% reflected the weight lost after the R-ESG or the initiation of pharmacotherapy (not overall TWL% after P-ESG). Analysis was conducted using a continuous random-effects model, specifically the DerSimonian-Laird method.
Results: Four studies on R-ESG and one study on pharmacotherapy were identified. Out of 47 patients, the pooled mean TWL% at 1 month after R-ESG (Figure 1A) was 8.458% (95% CI 5.137 – 11.778). There was significant heterogeneity (I² = 85.31%, p = 0.009). Out of 77 patients, the pooled mean TWL% at 3 months (Figure 1B) after R-ESG was 8.411% (95% CI 4.627 – 12.194). Significant heterogeneity was observed (I² = 92.73%, p < 0.001). Out of 80 patients, the pooled mean TWL% at 6 months (Figure 3B) after redo-ESG was 9.292% (95% CI 6.006 – 12.578), with significant heterogeneity (I² = 80.78%, p = 0.001). Haifathalian et al. (2023) is the single study in the literature comparing R-ESG and pharmacotherapy for managing weight regain after P-ESG, showing an additional TWL% after 6 months of 9.9% ± 7.2% with R-ESG versus 2.1% ± 8.6% with pharmacotherapy (p = 0.001).
Discussion: R-ESG appears to be an effective approach to mitigate weight regain after P-ESG. However, questions remain about how R-ESG compares to pharmacotherapy and how each approach compares to a combined strategy (pharmacotherapy plus R-ESG). Further research is needed to optimize the management of weight regain after P-ESG.

Figure: Total weight loss percentage at 1 month (A), 3 months (B), and 6 months (C).
Disclosures:
Abdul-Rahman Diab indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Sujka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kathleen Mattingly indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Angelica McCaskey indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdullah Elnaji indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Salvatore Docimo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Christopher DuCoin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdul-Rahman F. Diab, MD1, Joseph A. Sujka, MD2, Kathleen Mattingly, DO3, Angelica McCaskey, DO3, Abdullah Elnaji, DO3, Salvatore Docimo, DO2, Christopher G. DuCoin, MD2. P1036 - Weight Regain After Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG): Can Redo ESG (R-ESG) Help? What is the Role of Pharmacotherapy? Analysis of 80 Patients, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
