Sunday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P1039 - Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Alginate as an Injection Solution in Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E

Has Audio
- OA
Omar Abdelhalim, MD
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Queens, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Hazem Abosheaishaa, MD1, Abdallfatah Abdallfatah, 2, Omar Abdelhalim, MD1, Abdelmalek Abdelghany, MBBCh3, Imad Samman Tahhan, MBBCh4, Azizullah Beran, MD5, Mohamed A. M.. Amer, MD6, Iyiad AlabdulRazzak, MD7, Islam Mohamed, MD8, Ahmed E. Salem, MBBCh9, Mahmoud Nassar, MD, PhD, MSc, MPA10, Mohammed Abusuliman, MD11, Ahmed Abomhya, MD12, Ammar Ayman. Bahbah, MD13, Sherif Andrawes, MD14
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Queens, NY; 2October 6 University, Cairo, Al Jizah, Egypt; 3October 6 University, Giza, Al Jizah, Egypt; 4Ain Shams University, Cairo, Al Qahirah, Egypt; 5Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 6Menoufia University, Waterford, VA; 7St. Elizabeth's Medical Center, Boston, MA; 8University of Missouri, Kansas City, MO; 9Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 10Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY; 11Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI; 12University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY; 13Menoufia University, Shebein Al-Kom, Al Minufiyah, Egypt; 14Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY
Introduction: The increasing incidence of gastrointestinal (GI) tumors, such as colorectal and esophageal cancers, highlights the need for effective treatment methods. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) has emerged as a preferred technique due to its low local recurrence rates. This study evaluates the safety and efficacy of sodium alginate as a submucosal injection solution in ESD.
Methods: A systematic search of Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, Medline, and Cochrane databases up to April 17, 2034, identified randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies on sodium alginate for ESD in GI adenomas and early-stage neoplastic lesions. Data extraction and analysis were independently conducted by two reviewers, with consensus resolving discrepancies. Statistical analyses were performed with Comprehensive Meta-analysis software.
Results: Five studies involving 255 patients were included in this analysis. Overall en-bloc resection rates for sodium alginate were 97% [95% CI (93%-99%); I2:0%]. En-bloc resection subgroup analysis revealed 97% [95% CI (93%-99%); I2:0%] for 0.6% sodium alginate and 95% [95% CI (70%-99%); I2: 0%] for 0.4% sodium alginate. Delayed bleeding rates for sodium alginate were 5% [95% CI (1%-20%); I2: 65.2%]; however, after subgroup analysis delayed bleeding was 2% [95% CI (1%-6%); I2: 0%] for 0.6% sodium alginate and 22% [95% CI (8%-49%); I2:0%] for 0.4% sodium alginate. Perforation rates for 0.6% sodium alginate were 1% [95% CI (0%-5%); I2: 0%]. Procedure times were 60.86 minutes [95% CI (45.06-76.67); I2: 85.31%] for sodium alginate, 45.77 minutes [95% CI (32.94-58.59); I2:80.71% ] for 0.6% sodium alginate, 85.38 minutes [95% CI (61.29-109.47); I2:24.90%] for 0.4% sodium alginate.
Discussion: This study demonstrates that sodium alginate is an effective and safe submucosal injection solution for ESD, offering several advantages over traditional solutions. Sodium alginate provides higher en-bloc resection rates and lower adverse event rates, along with a reliable submucosal cushion that enhances mucosal elevation and stability during ESD. Its properties, including excellent water retention and viscoelasticity, contribute to better mucosal elevation. Injectable sodium alginate hydrogels (ISAHs) also exhibit self-healing abilities and antioxidant activity. Additionally, sodium alginate is cost-effective and has a proven safety profile. These findings suggest sodium alginate, especially at a 0.6% concentration, is a viable and effective alternative for ESD procedures.
Disclosures:
Hazem Abosheaishaa, MD1, Abdallfatah Abdallfatah, 2, Omar Abdelhalim, MD1, Abdelmalek Abdelghany, MBBCh3, Imad Samman Tahhan, MBBCh4, Azizullah Beran, MD5, Mohamed A. M.. Amer, MD6, Iyiad AlabdulRazzak, MD7, Islam Mohamed, MD8, Ahmed E. Salem, MBBCh9, Mahmoud Nassar, MD, PhD, MSc, MPA10, Mohammed Abusuliman, MD11, Ahmed Abomhya, MD12, Ammar Ayman. Bahbah, MD13, Sherif Andrawes, MD14. P1039 - Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Alginate as an Injection Solution in Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, Queens, NY; 2October 6 University, Cairo, Al Jizah, Egypt; 3October 6 University, Giza, Al Jizah, Egypt; 4Ain Shams University, Cairo, Al Qahirah, Egypt; 5Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN; 6Menoufia University, Waterford, VA; 7St. Elizabeth's Medical Center, Boston, MA; 8University of Missouri, Kansas City, MO; 9Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 10Jacobs School of Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY; 11Henry Ford Health, Detroit, MI; 12University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY; 13Menoufia University, Shebein Al-Kom, Al Minufiyah, Egypt; 14Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY
Introduction: The increasing incidence of gastrointestinal (GI) tumors, such as colorectal and esophageal cancers, highlights the need for effective treatment methods. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) has emerged as a preferred technique due to its low local recurrence rates. This study evaluates the safety and efficacy of sodium alginate as a submucosal injection solution in ESD.
Methods: A systematic search of Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, Medline, and Cochrane databases up to April 17, 2034, identified randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies on sodium alginate for ESD in GI adenomas and early-stage neoplastic lesions. Data extraction and analysis were independently conducted by two reviewers, with consensus resolving discrepancies. Statistical analyses were performed with Comprehensive Meta-analysis software.
Results: Five studies involving 255 patients were included in this analysis. Overall en-bloc resection rates for sodium alginate were 97% [95% CI (93%-99%); I2:0%]. En-bloc resection subgroup analysis revealed 97% [95% CI (93%-99%); I2:0%] for 0.6% sodium alginate and 95% [95% CI (70%-99%); I2: 0%] for 0.4% sodium alginate. Delayed bleeding rates for sodium alginate were 5% [95% CI (1%-20%); I2: 65.2%]; however, after subgroup analysis delayed bleeding was 2% [95% CI (1%-6%); I2: 0%] for 0.6% sodium alginate and 22% [95% CI (8%-49%); I2:0%] for 0.4% sodium alginate. Perforation rates for 0.6% sodium alginate were 1% [95% CI (0%-5%); I2: 0%]. Procedure times were 60.86 minutes [95% CI (45.06-76.67); I2: 85.31%] for sodium alginate, 45.77 minutes [95% CI (32.94-58.59); I2:80.71% ] for 0.6% sodium alginate, 85.38 minutes [95% CI (61.29-109.47); I2:24.90%] for 0.4% sodium alginate.
Discussion: This study demonstrates that sodium alginate is an effective and safe submucosal injection solution for ESD, offering several advantages over traditional solutions. Sodium alginate provides higher en-bloc resection rates and lower adverse event rates, along with a reliable submucosal cushion that enhances mucosal elevation and stability during ESD. Its properties, including excellent water retention and viscoelasticity, contribute to better mucosal elevation. Injectable sodium alginate hydrogels (ISAHs) also exhibit self-healing abilities and antioxidant activity. Additionally, sodium alginate is cost-effective and has a proven safety profile. These findings suggest sodium alginate, especially at a 0.6% concentration, is a viable and effective alternative for ESD procedures.

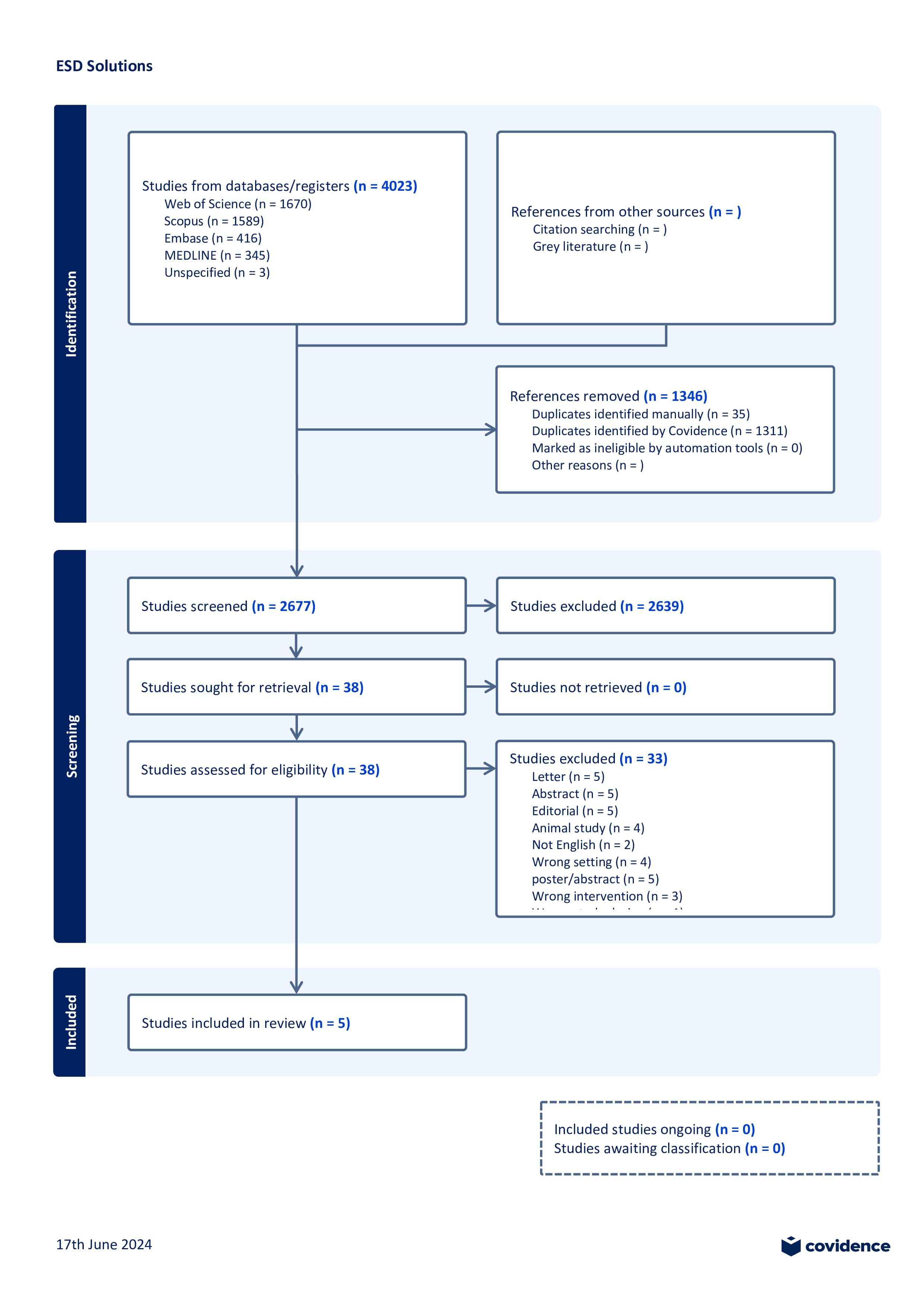
Figure: PRISMA Flowchart
Disclosures:
Hazem Abosheaishaa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdallfatah Abdallfatah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Abdelhalim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Abdelmalek Abdelghany indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Imad Samman Tahhan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Azizullah Beran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohamed Amer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iyiad AlabdulRazzak indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Islam Mohamed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Salem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahmoud Nassar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Abusuliman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Abomhya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ammar Bahbah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sherif Andrawes indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hazem Abosheaishaa, MD1, Abdallfatah Abdallfatah, 2, Omar Abdelhalim, MD1, Abdelmalek Abdelghany, MBBCh3, Imad Samman Tahhan, MBBCh4, Azizullah Beran, MD5, Mohamed A. M.. Amer, MD6, Iyiad AlabdulRazzak, MD7, Islam Mohamed, MD8, Ahmed E. Salem, MBBCh9, Mahmoud Nassar, MD, PhD, MSc, MPA10, Mohammed Abusuliman, MD11, Ahmed Abomhya, MD12, Ammar Ayman. Bahbah, MD13, Sherif Andrawes, MD14. P1039 - Efficacy and Safety of Sodium Alginate as an Injection Solution in Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
