Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0590 - The Unexpected Pagetoid Spread of Paget Cells from Non-Invasive Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Vanessa F. Eller, MD
University of Arizona College of Medicine
Phoenix, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Vanessa F. Eller, MD1, Jennifer Martinez, MS2, Kevin Liu, MD1, Prathab Devaraj, MD3
1University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ; 2Banner MD Anderson Cancer Center, Mesa, AZ; 3Banner MD Anderson Cancer Center, Gilbert, AZ
Introduction: Paget’s disease, which was initially described in breast tissue, is defined as a malignant invasion of intraepithelial cells. Extramammary Paget’s disease (EMPD), while rare, has been reported mostly in the vulva and the perianal region. There have been rare case reports of Paget’s squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCCIS) involving the esophagus. We report on a case of esophageal Paget’s SCCIS treated with curative resection by endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
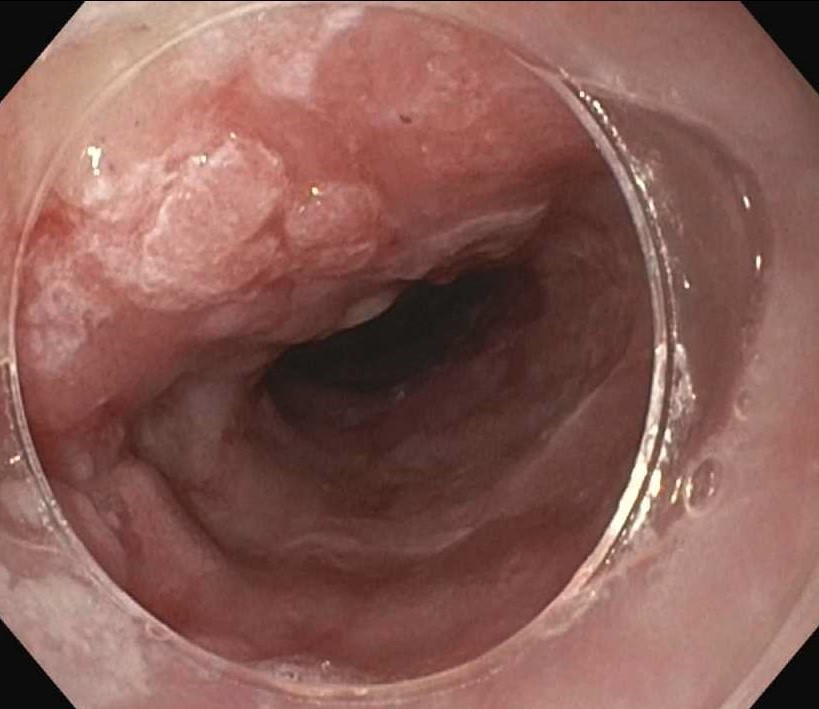
Case Description/Methods: The patient is an 83-year-old male who presented with 6 months of progressive dysphagia to solid foods. On esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), the patient was found to have nodular, abnormal mucosa in the distal esophagus (Figure) with esophageal biopsy demonstrating squamous mucosa with carcinoma in situ/high-grade dysplasia. A repeat EGD and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) provided further evidence of the lesion being superficial without any deep wall invasion and with all margins negative for tumor. The patient underwent positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) scan with no evidence of metastatic disease and without focal esophageal radiotracer activity. ESD was performed to remove the lesion en bloc and pathology results were consistent with intramucosal squamous cell carcinoma with Paget’s disease and clear margins. The patient recovered well after the ESD.
Discussion: EMPD of the esophagus is exceedingly rare with most cases originating from underlying invasive carcinoma, specifically adenocarcinoma. Esophageal Paget’s SCCIS is an extremely rare phenomenon which has only limited reports in the literature, with only three previously reported cases identified. Previous case reports describe diffuse esophageal involvement of Paget’s SCCIS. This is the first case report to our knowledge on localized esophageal Paget’s SCCIS successfully treated with ESD.
Chen IY, Bartell N, Ettel MG. Diffuse Pagetoid Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Situ of the Esophagus: A Rare Case Report and Review of Literature. 2022, 326-330.
Chu P, Stagias J, West AB, Traube M. Diffuse pagetoid squamous cell carcinoma in situ of the esophagus: a case report. 1997, 1865-1870.
Ishihara A, Mori T, Koono M. Diffuse pagetoid squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus combined with choriocarcinoma and mucoepidermoid carcinoma: an autopsy case report. 2002, 147-152.
Disclosures:
Vanessa F. Eller, MD1, Jennifer Martinez, MS2, Kevin Liu, MD1, Prathab Devaraj, MD3. P0590 - The Unexpected Pagetoid Spread of Paget Cells from Non-Invasive Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ; 2Banner MD Anderson Cancer Center, Mesa, AZ; 3Banner MD Anderson Cancer Center, Gilbert, AZ
Introduction: Paget’s disease, which was initially described in breast tissue, is defined as a malignant invasion of intraepithelial cells. Extramammary Paget’s disease (EMPD), while rare, has been reported mostly in the vulva and the perianal region. There have been rare case reports of Paget’s squamous cell carcinoma in situ (SCCIS) involving the esophagus. We report on a case of esophageal Paget’s SCCIS treated with curative resection by endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
Case Description/Methods: The patient is an 83-year-old male who presented with 6 months of progressive dysphagia to solid foods. On esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), the patient was found to have nodular, abnormal mucosa in the distal esophagus (Figure) with esophageal biopsy demonstrating squamous mucosa with carcinoma in situ/high-grade dysplasia. A repeat EGD and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) provided further evidence of the lesion being superficial without any deep wall invasion and with all margins negative for tumor. The patient underwent positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) scan with no evidence of metastatic disease and without focal esophageal radiotracer activity. ESD was performed to remove the lesion en bloc and pathology results were consistent with intramucosal squamous cell carcinoma with Paget’s disease and clear margins. The patient recovered well after the ESD.
Discussion: EMPD of the esophagus is exceedingly rare with most cases originating from underlying invasive carcinoma, specifically adenocarcinoma. Esophageal Paget’s SCCIS is an extremely rare phenomenon which has only limited reports in the literature, with only three previously reported cases identified. Previous case reports describe diffuse esophageal involvement of Paget’s SCCIS. This is the first case report to our knowledge on localized esophageal Paget’s SCCIS successfully treated with ESD.
Chen IY, Bartell N, Ettel MG. Diffuse Pagetoid Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Situ of the Esophagus: A Rare Case Report and Review of Literature. 2022, 326-330.
Chu P, Stagias J, West AB, Traube M. Diffuse pagetoid squamous cell carcinoma in situ of the esophagus: a case report. 1997, 1865-1870.
Ishihara A, Mori T, Koono M. Diffuse pagetoid squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus combined with choriocarcinoma and mucoepidermoid carcinoma: an autopsy case report. 2002, 147-152.

Figure: FIGURE: Endoscopic image of the esophagus with mucosal changes and nodularity concerning for squamous cell dysplasia.
Disclosures:
Vanessa Eller indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jennifer Martinez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kevin Liu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prathab Devaraj indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vanessa F. Eller, MD1, Jennifer Martinez, MS2, Kevin Liu, MD1, Prathab Devaraj, MD3. P0590 - The Unexpected Pagetoid Spread of Paget Cells from Non-Invasive Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
