Sunday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P0534 - Middle Term Outcome of POEM on Patients With Ineffective Esophageal Motility: A Case Series
Sunday, October 27, 2024
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Britanny Pass, BS
LSU Health
Shreveport, LA
Presenting Author(s)
Britanny Pass, BS1, Victoria Andrus, MD2, Omar Khan, MD1, Michelle Neice, MD1, David Okuampa, MD2, Natalie Roppolo, MS1, Michael Tran, MD1, Qiang Cai, MD1
1LSU Health, Shreveport, LA; 2Ochsner LSU Health, Shreveport, LA
Introduction: Ineffective esophageal motility (IEM) is a condition of failed and disrupted peristalsis in the
distal esophagus; using conventional manometry, a distal esophageal contraction amplitude of
< 30 mmHg with ≥ 50% ineffective liquid swallows is diagnostic. 1–3 IEM has an estimated
prevalence of 20-30%. 1 Clinically, the most common symptoms are heartburn, reflux, and
dysphagia. 1,2 Management of patients is focused on medical GERD treatment and lifestyle
modification due to limited pharmacological intervention for esophageal motility. 4 There is
currently no established treatment for dysphagia in IEM. However, per oral endoscopic myotomy
(POEM) has emerged as a novel and effective treatment for dysphagia in achalasia, diffuse
esophageal spasm, jackhammer esophagus, and non-malignant esophagogastric junction outlet
obstruction. 5–7 Therefore, it is theorized that it may be a beneficial treatment for IEM-associated
dysphagia.
Case Description/Methods: We retrieved all patients with the diagnosis of IEM who underwent POEM in our endoscopic
center. All of them had extensive work up for their dysphagia, mainly including upper
gastrointestinal endoscopy and HRM before being referred to us. IEM was diagnosed by their
HRM. All of them had dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux symptoms (GERD) and were taking
proton pump inhibitors. All of them tried some other medications, such as buspirone, without
significant effect. Per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) was performed for all of them.
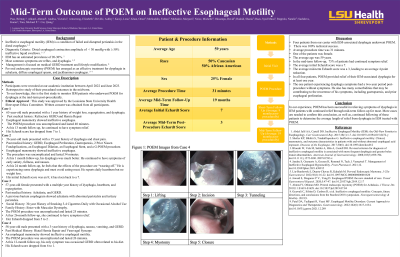
Discussion: Four patients, three male and one female, ages 65, 56, 57, and 58, were retrieved. POEM was successfully performed on all patients. The average procedure time was 31 minutes. The follow up times after POEM were 13 months, 24 months, 26 months, and 12 months, respectively. Dysphagia was resolved in all of them. The Echardt score for the first, third, and fourth patients decreased from 7 and 8 to less than 3. The first, second, and third patients gained 20 pounds, 3 pounds, and 10 pounds in their recent clinic follow ups. The second patient’s Echardt score has increased to 7 at their most recent follow-up. Their GERD is well controlled, except for in the second patient.
To our knowledge, this is the first report of middle-term outcome of POEM on patients with ineffective esophageal motility. For patients with IEM and refractory dysphagia, POEM is effective, though more cases are needed to further confirm the conclusion.
Disclosures:
Britanny Pass, BS1, Victoria Andrus, MD2, Omar Khan, MD1, Michelle Neice, MD1, David Okuampa, MD2, Natalie Roppolo, MS1, Michael Tran, MD1, Qiang Cai, MD1. P0534 - Middle Term Outcome of POEM on Patients With Ineffective Esophageal Motility: A Case Series, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1LSU Health, Shreveport, LA; 2Ochsner LSU Health, Shreveport, LA
Introduction: Ineffective esophageal motility (IEM) is a condition of failed and disrupted peristalsis in the
distal esophagus; using conventional manometry, a distal esophageal contraction amplitude of
< 30 mmHg with ≥ 50% ineffective liquid swallows is diagnostic. 1–3 IEM has an estimated
prevalence of 20-30%. 1 Clinically, the most common symptoms are heartburn, reflux, and
dysphagia. 1,2 Management of patients is focused on medical GERD treatment and lifestyle
modification due to limited pharmacological intervention for esophageal motility. 4 There is
currently no established treatment for dysphagia in IEM. However, per oral endoscopic myotomy
(POEM) has emerged as a novel and effective treatment for dysphagia in achalasia, diffuse
esophageal spasm, jackhammer esophagus, and non-malignant esophagogastric junction outlet
obstruction. 5–7 Therefore, it is theorized that it may be a beneficial treatment for IEM-associated
dysphagia.
Case Description/Methods: We retrieved all patients with the diagnosis of IEM who underwent POEM in our endoscopic
center. All of them had extensive work up for their dysphagia, mainly including upper
gastrointestinal endoscopy and HRM before being referred to us. IEM was diagnosed by their
HRM. All of them had dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux symptoms (GERD) and were taking
proton pump inhibitors. All of them tried some other medications, such as buspirone, without
significant effect. Per oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) was performed for all of them.
Discussion: Four patients, three male and one female, ages 65, 56, 57, and 58, were retrieved. POEM was successfully performed on all patients. The average procedure time was 31 minutes. The follow up times after POEM were 13 months, 24 months, 26 months, and 12 months, respectively. Dysphagia was resolved in all of them. The Echardt score for the first, third, and fourth patients decreased from 7 and 8 to less than 3. The first, second, and third patients gained 20 pounds, 3 pounds, and 10 pounds in their recent clinic follow ups. The second patient’s Echardt score has increased to 7 at their most recent follow-up. Their GERD is well controlled, except for in the second patient.
To our knowledge, this is the first report of middle-term outcome of POEM on patients with ineffective esophageal motility. For patients with IEM and refractory dysphagia, POEM is effective, though more cases are needed to further confirm the conclusion.
Disclosures:
Britanny Pass indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Victoria Andrus indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Omar Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michelle Neice indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Okuampa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Natalie Roppolo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Tran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Qiang Cai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Britanny Pass, BS1, Victoria Andrus, MD2, Omar Khan, MD1, Michelle Neice, MD1, David Okuampa, MD2, Natalie Roppolo, MS1, Michael Tran, MD1, Qiang Cai, MD1. P0534 - Middle Term Outcome of POEM on Patients With Ineffective Esophageal Motility: A Case Series, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.

