Tuesday Poster Session
Category: General Endoscopy
P4129 - Endoscopic Ultrasound Drainage of a Mediastinal Abscess - A Case Report
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Joelle Sleiman, MD
Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health
Staten Island, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Joelle Sleiman, MD, Hassan Al Moussawi, MD, Youssef El Douaihy, MD
Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY
Introduction: Mediastinal collections are conventionally treated by surgical or interventional radiology procedures. However, the use of endoscopic ultrasound(EUS) offers a safe and effective alternative. We describe a successful mediastinal abscess drainage case using EUS with the insertion of a double pigtail stent.
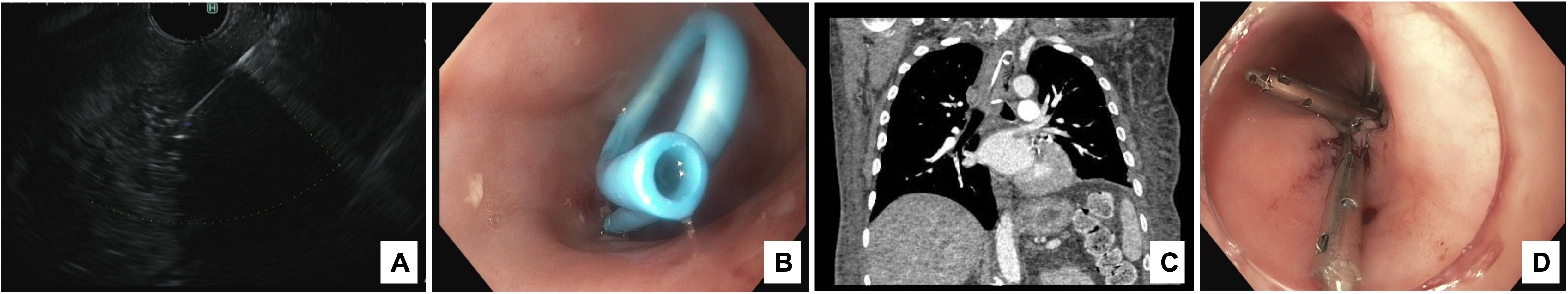
Case Description/Methods: A 50-year-old male presented to the Emergency Room for severe mid-upper back pain. A CT thoracic spine showed discitis and osteomyelitis affecting T3 and T4, with cortical destruction and lytic changes. A rim-enhancing collection in the posterior mediastinal space, anterior to T3-T4 vertebral bodies was observed, causing anterior displacement of the trachea and esophagus. Treatment with antibiotics was initiated and the patient underwent EUS for possible abscess drainage. The linear echoendoscope was used for focused exam of the proximal para-esophageal area. At 25cm from incisors, a 30x31mm heterogenous collection was identified. Finding was consistent with the peri-vertebral abscess described on the previous CT scan. Fine needle aspiration was performed with a 19-gauge needle, using color doppler to avoid vasculature. Five cc of pus was aspirated and sent for microbiology. A guide wire was advanced into the collection using ultrasound guidance. A cystotome was advanced thereafter over the guidewire, with adequate position confirmed by EUS. The scope was exchanged for upper endoscope(EGD), and a 7Fx4cm double pigtail was placed with the distal end in the cavity and proximal end in esophagus. Stent position was confirmed by endoscopy, fluoroscopy, and CT chest(Fig1A,B,C). Blood and fluid cultures were positive for methicillin sensitive staphylococcus aureus. A repeat CT scan showed resolution of the collection. Another EGD was performed where the double-pigtail stent was removed using a rat-tooth and the site of entry was closed using combination of endoclips and suturing(Fig1D). The patient tolerated the intervention well with resolution of all clinical symptoms and signs of infection. Patient was discharged on IV antibiotics for 6 weeks.
Discussion: We report a case of a mediastinal abscess managed solely by EUS with the insertion of a double pigtail stent. Although various treatment methods for mediastinal abscesses have been reported, this case report demonstrated that EUS is a safe and effective option. This procedure necessitates specialized equipment and endoscopic expertise; therefore, additional studies are needed before it can be recommended for standard use.
Disclosures:
Joelle Sleiman, MD, Hassan Al Moussawi, MD, Youssef El Douaihy, MD. P4129 - Endoscopic Ultrasound Drainage of a Mediastinal Abscess - A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
Staten Island University Hospital, Northwell Health, Staten Island, NY
Introduction: Mediastinal collections are conventionally treated by surgical or interventional radiology procedures. However, the use of endoscopic ultrasound(EUS) offers a safe and effective alternative. We describe a successful mediastinal abscess drainage case using EUS with the insertion of a double pigtail stent.
Case Description/Methods: A 50-year-old male presented to the Emergency Room for severe mid-upper back pain. A CT thoracic spine showed discitis and osteomyelitis affecting T3 and T4, with cortical destruction and lytic changes. A rim-enhancing collection in the posterior mediastinal space, anterior to T3-T4 vertebral bodies was observed, causing anterior displacement of the trachea and esophagus. Treatment with antibiotics was initiated and the patient underwent EUS for possible abscess drainage. The linear echoendoscope was used for focused exam of the proximal para-esophageal area. At 25cm from incisors, a 30x31mm heterogenous collection was identified. Finding was consistent with the peri-vertebral abscess described on the previous CT scan. Fine needle aspiration was performed with a 19-gauge needle, using color doppler to avoid vasculature. Five cc of pus was aspirated and sent for microbiology. A guide wire was advanced into the collection using ultrasound guidance. A cystotome was advanced thereafter over the guidewire, with adequate position confirmed by EUS. The scope was exchanged for upper endoscope(EGD), and a 7Fx4cm double pigtail was placed with the distal end in the cavity and proximal end in esophagus. Stent position was confirmed by endoscopy, fluoroscopy, and CT chest(Fig1A,B,C). Blood and fluid cultures were positive for methicillin sensitive staphylococcus aureus. A repeat CT scan showed resolution of the collection. Another EGD was performed where the double-pigtail stent was removed using a rat-tooth and the site of entry was closed using combination of endoclips and suturing(Fig1D). The patient tolerated the intervention well with resolution of all clinical symptoms and signs of infection. Patient was discharged on IV antibiotics for 6 weeks.
Discussion: We report a case of a mediastinal abscess managed solely by EUS with the insertion of a double pigtail stent. Although various treatment methods for mediastinal abscesses have been reported, this case report demonstrated that EUS is a safe and effective option. This procedure necessitates specialized equipment and endoscopic expertise; therefore, additional studies are needed before it can be recommended for standard use.

Figure: Figure 1: The endoscopic examination and treatment. A- EUS image of the double-pigtail stent in the abscess. B- Endoscopic view of the stent in the esophagus. C- CT chest image of the double pigtail stent extending from the proximal esophagus into the abscess. D- Endoscopic image of the entry site closure with clips.
Disclosures:
Joelle Sleiman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hassan Al Moussawi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Youssef El Douaihy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joelle Sleiman, MD, Hassan Al Moussawi, MD, Youssef El Douaihy, MD. P4129 - Endoscopic Ultrasound Drainage of a Mediastinal Abscess - A Case Report, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
