Tuesday Poster Session
Category: GI Bleeding
P4162 - Ischemic Stroke Patients Bleed More: A Nationwide Inpatient Database Analysis
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM ET
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Has Audio

Umar Hayat, MD
Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center
Wilkes-Barre, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Umar Hayat, MD1, Muhammad Kamal, MD2, Waqas Rasheed, MD3, Hassam Ali, MD4, M Danial Ali Shah, MD5, Kamran Zahoor, MD6, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD7, Aamir Saeed, MD8, Amna Iqbal, MD9, Azhar Hussain, MBBS10, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD11, Faisal Kamal, MD12, Kishore Kumar, MD13
1Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 2Hackensack Meridian Health, Roselle Park, NJ; 3University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY; 4ECU Health Medical Center, Greenville, NC; 5King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 7University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 8Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN; 9University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 10SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY; 11The University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS; 12Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA; 13Geisinger Community Medical Center, Scranton, PA
Introduction: Ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke, accounting for approximately 80% of all strokes, and is caused by blockage in the cerebrovascular system. Recent studies have shown that patients with ischemic stroke are at an increased risk of Upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB), which is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Our study aims to explore the relationship between UGIB and stroke and prognostic factors leading to worse outcomes if stroke patients have UGIB.
Methods: National Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2016-2020 was queried using ICD-10-CM Codes to identify a cohort of inpatient admissions with a primary discharge diagnosis of ischemic stroke and a secondary diagnosis of UGIB. A weighted sample was used to get baseline characteristics, length of hospital stays (LOS), and resource utilization during the inpatient admissions. Multivariate logistic regression analysis followed by predictive margins was used to obtain adjusted estimates of the length of hospital stay, mechanical ventilation, shock development, resource utilization, and mortality.
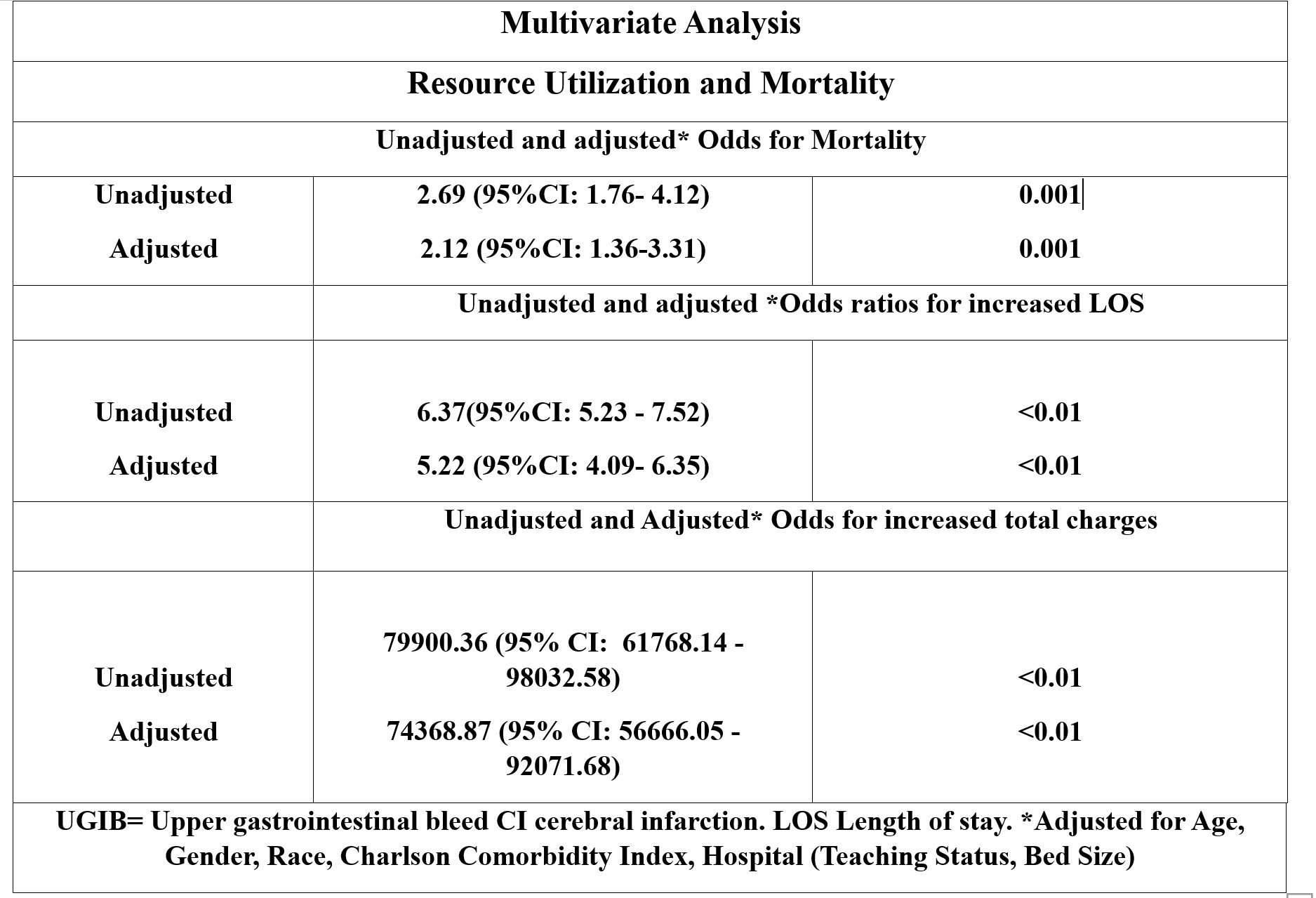
Results: Among 503345 patients hospitalized with ischemic stroke, 1215 (0.24%) patients had a concurrent diagnosis of UGIB; compared to males, females with ischemic stroke were less likely to have UGIB (58.7% vs. 41.3%). The mean age was similar in both groups (69.7 years vs. 72.5 years). The patients admitted with ischemic stroke, and UGIB has medicare insurance as their primary payer. Patients with ischemic stroke with UGIB were more likely to go into shock (9.1% vs. 0.13%) and have mechanical ventilation (3.3% vs. 1.2%), resulting in a more extended LOS than those without UGIB (10.85d vs. 4.52d)—table 1. On multivariate analysis, patients with ischemic stroke were more likely to have extended hospitalization aOR: 5.22 days (95% CI: 4.09- 6.35) and higher hospital charges (74368.87 (95% CI: 56666.05 - 92071.68), which were statistically significant. Moreover, these patients have a higher mortality aOR: 2.12 (95% CI: 1.36- 3.31) than those without UGIB Figure 1.
Discussion: This study demonstrated that patients with ischemic stroke who had UGIB were more likely to be admitted to the ICU and had an increased LOS and a higher mortality. Furthermore, these patients had higher total hospitalization charges than those without UGIB. It underscores the importance of early recognition of high-risk individuals at an increased risk of UGIB to optimize their health care for better health outcomes.
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Umar Hayat, MD1, Muhammad Kamal, MD2, Waqas Rasheed, MD3, Hassam Ali, MD4, M Danial Ali Shah, MD5, Kamran Zahoor, MD6, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD7, Aamir Saeed, MD8, Amna Iqbal, MD9, Azhar Hussain, MBBS10, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD11, Faisal Kamal, MD12, Kishore Kumar, MD13. P4162 - Ischemic Stroke Patients Bleed More: A Nationwide Inpatient Database Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center, Wilkes-Barre, PA; 2Hackensack Meridian Health, Roselle Park, NJ; 3University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY; 4ECU Health Medical Center, Greenville, NC; 5King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 6Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; 7University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 8Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN; 9University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 10SUNY Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY; 11The University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS; 12Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA; 13Geisinger Community Medical Center, Scranton, PA
Introduction: Ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke, accounting for approximately 80% of all strokes, and is caused by blockage in the cerebrovascular system. Recent studies have shown that patients with ischemic stroke are at an increased risk of Upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB), which is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Our study aims to explore the relationship between UGIB and stroke and prognostic factors leading to worse outcomes if stroke patients have UGIB.
Methods: National Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2016-2020 was queried using ICD-10-CM Codes to identify a cohort of inpatient admissions with a primary discharge diagnosis of ischemic stroke and a secondary diagnosis of UGIB. A weighted sample was used to get baseline characteristics, length of hospital stays (LOS), and resource utilization during the inpatient admissions. Multivariate logistic regression analysis followed by predictive margins was used to obtain adjusted estimates of the length of hospital stay, mechanical ventilation, shock development, resource utilization, and mortality.
Results: Among 503345 patients hospitalized with ischemic stroke, 1215 (0.24%) patients had a concurrent diagnosis of UGIB; compared to males, females with ischemic stroke were less likely to have UGIB (58.7% vs. 41.3%). The mean age was similar in both groups (69.7 years vs. 72.5 years). The patients admitted with ischemic stroke, and UGIB has medicare insurance as their primary payer. Patients with ischemic stroke with UGIB were more likely to go into shock (9.1% vs. 0.13%) and have mechanical ventilation (3.3% vs. 1.2%), resulting in a more extended LOS than those without UGIB (10.85d vs. 4.52d)—table 1. On multivariate analysis, patients with ischemic stroke were more likely to have extended hospitalization aOR: 5.22 days (95% CI: 4.09- 6.35) and higher hospital charges (74368.87 (95% CI: 56666.05 - 92071.68), which were statistically significant. Moreover, these patients have a higher mortality aOR: 2.12 (95% CI: 1.36- 3.31) than those without UGIB Figure 1.
Discussion: This study demonstrated that patients with ischemic stroke who had UGIB were more likely to be admitted to the ICU and had an increased LOS and a higher mortality. Furthermore, these patients had higher total hospitalization charges than those without UGIB. It underscores the importance of early recognition of high-risk individuals at an increased risk of UGIB to optimize their health care for better health outcomes.

Figure: Multivariate analysis showing comparison of resource utilization, LOS, and mortality among stroke patients with and without UGIB
Abbreviations: UGIB: Upper gastrointestinal bleed CI: cerebral infarction. LOS: Length of stay. *Adjusted for Age, Gender, Race, Charlson Comorbidity Index, Hospital (Teaching Status, Bed Size)
Abbreviations: UGIB: Upper gastrointestinal bleed CI: cerebral infarction. LOS: Length of stay. *Adjusted for Age, Gender, Race, Charlson Comorbidity Index, Hospital (Teaching Status, Bed Size)
Note: The table for this abstract can be viewed in the ePoster Gallery section of the ACG 2024 ePoster Site or in The American Journal of Gastroenterology's abstract supplement issue, both of which will be available starting October 27, 2024.
Disclosures:
Umar Hayat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Waqas Rasheed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hassam Ali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
M Danial Ali Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kamran Zahoor indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manesh Kumar Gangwani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aamir Saeed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amna Iqbal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Azhar Hussain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dushyant Dahiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faisal Kamal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kishore Kumar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Umar Hayat, MD1, Muhammad Kamal, MD2, Waqas Rasheed, MD3, Hassam Ali, MD4, M Danial Ali Shah, MD5, Kamran Zahoor, MD6, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD7, Aamir Saeed, MD8, Amna Iqbal, MD9, Azhar Hussain, MBBS10, Dushyant S. Dahiya, MD11, Faisal Kamal, MD12, Kishore Kumar, MD13. P4162 - Ischemic Stroke Patients Bleed More: A Nationwide Inpatient Database Analysis, ACG 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Philadelphia, PA: American College of Gastroenterology.
